(Press-News.org) New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience has found an association between a reduction in grey matter in the brain and Early Onset Psychosis (EOP).
The study, published in Molecular Psychiatry, is the largest ever brain imaging study in EOP and has provided unprecedented levels of detail about the illness. It shows that, in contrast to other mental health disorders, people with EOP have a reduced volume of grey matter across nearly all regions of their brain. Researchers hope that this detailed mapping could be used to assist in future diagnosis, as well as to track the effects of treatment in patients with EOP.
EOP occurs before the age of 18 during a critical period of development in the brain. Individuals diagnosed with the illness are likely to experience severe and long-lasting symptoms that respond less well to treatment. Despite this, research into EOP has been limited in sample size and statistical power.
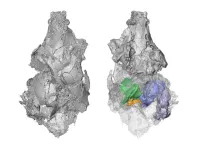
The study represents an international effort, combining brain scans from Norway, Spain, Canada, Italy, Australia & UK, 482 individuals with EOP being compared to 469 healthy controls. An analysis of the data revealed that individuals with EOP had lower volumes of grey matter in almost all regions of the brain compared to the healthy controls, with a marked effect in the left median cingulate – an area of the brain associated with the formation and processing of emotions, learning and memory.
Dr Matthew Kempton, Reader in Neuroimaging Psychiatry at King’s IoPPN and the study’s senior author said, “Early Onset Psychosis can have a devastating impact on a person’s life and wellbeing, but our understanding of the illness is still sadly relatively limited. This study, the largest neuroimaging analysis of EOP to date, used newly developed technologies to combine scans from different sites to examine hundreds of thousands of data points measuring volume in the brain. We found that people with EOP experience a lower volume of grey matter in nearly all regions of their brains compared to people without the illness. This detailed map will hopefully provide the basis for future research, as it could help as a diagnostic tool, and even track the effectiveness of treatments.”
Further analysis of the data revealed that those individuals who developed EOP at a later age had lower volumes of grey matter in a number of small brain regions compared to those with an earlier age of onset.
Shuqing Si, the study’s first author from King’s IoPPN said, “Grey matter’s primary purpose is to process information in the brain and plays a significant role in day to day functions like memory, emotions and movement. This study used specially created software (ENIGMA-VBM) developed at King’s that can accurately map where there have been local increases and decreases in brain volume. It’s allowed our team to process significantly more data and has meant that our sample reflects brain scans from many parts of the world. The effectiveness of this software means we’re now investigating the brains of those with several other disorders.”
This study represents independent research, partly funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London.
Ends
For more information, please contact Patrick O’Brien (Media Manager)
Mapping gray and white matter volume abnormalities in early-onset psychosis - an ENIGMA multicenter voxel-based morphometry study (DOI 10.1038/s41380-023-02343-1 ) (Shuqing Si, Anbreen Bi, Zhaoying Yu, Cheryl See, Sinead Kelly, Sonia Ambrogi, Celso Arango, Inmaculada Baeza, Nerisa Banaj, Michael Berk, Josefina Castro-Fornieles, Benedicto Crespo-Facorro, Jacob J. Crouse, Covadonga M. Díaz-Caneja, Anne-Kathrin Fett, Adriana Fortea, Sophia Frangou, Benjamin I. Goldstein, Ian B. Hickie, Joost Janssen, Kody G. Kennedy, Lydia Krabbendam, Marinos Kyriakopoulos, Bradley J. MacIntosh, Pedro Morgado, Stener Nerland, Saül Pascual-Diaz, Maria Picó-Pérez, Fabrizio Piras, Bjørn Rishovd Rund, Elena de la Serna, Gianfranco Spalletta, Gisela Sugranyes, Chao Suo, Diana Tordesillas-Gutiérrez, Daniela Vecchio, Joaquim Radua, Philip McGuire, Sophia I. Thomopoulos, Neda Jahanshad, Paul M. Thompson, Claudia Barth, Ingrid Agartz, Anthony James, Matthew J Kempton) was published in Molecular Psychiatry.
END
Volume of grey brain matter significantly lower in people with Early Onset Psychosis
2024-01-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Duke-NUS scientists discover potential nasal COVID-19 vaccine candidate that offers better and longer protection
2024-01-10
Novel findings from a preclinical head-to-head comparison show that administering a COVID-19 vaccine as a nasal spray rather than a subcutaneous injection enhances the body’s long-term immune memory, thereby increasing the vaccine’s overall effectiveness.
This research could pave the way for a COVID-19 vaccination strategy that depends on fewer boosters to achieve the same level of protection against SARS-CoV-2 viruses.
SINGAPORE, 10 January 2024 – A team of scientists, led by Duke-NUS Medical School, has discovered a potential intranasal vaccine candidate that provides improved, ...
Traumatic stress associated with smaller brain region
2024-01-10
DURHAM, N.C. – Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums, according to new research from a Duke-led brain imaging study.
The cerebellum, a part of the brain well known for helping to coordinate movement and balance, can influence emotion and memory, which are impacted by PTSD. What isn’t known yet is whether a smaller cerebellum predisposes a person to PTSD or PTSD shrinks the brain region.
“The differences were largely within the posterior lobe, where a lot of the more cognitive functions attributed to the cerebellum seem to localize, as well as the vermis, which is linked to a lot of emotional processing ...
Largest diversity study of ‘magic mushrooms’ investigates the evolution of psychoactive psilocybin production
2024-01-10
Psilocybe fungi, known colloquially as “magic mushrooms,” have held deep significance in Indigenous cultures of Mesoamerica for centuries. They captured the wider world’s attention as a psychedelic staple in the 60s and 70s. Now, these infamous organisms are at the forefront of a mental health revolution. Psilocybin and psilocin, the psychoactive compounds found in nearly all species of Psilocybe, have shown promise as a treatment for conditions including PTSD, depression, and for easing end-of-life care.
To ...
Sex-specific panel of 10 proteins can pick up 18 different early stage cancers
2024-01-10
A sex-specific panel of 10 proteins can pick up 18 different early stage cancers, representing all the major organs of the human body, finds a proof of concept study published in the open access journal BMJ Oncology.
The findings could kick-start a new generation of screening tests for early detection of the disease, say the researchers, particularly as there are many sex specific differences in cancer—including age at occurrence, cancer types, and genetic alterations—points out a linked editorial.
Cancer accounts for 1 in every 6 deaths around the globe, with nearly 60% of these deaths ...
Predominantly plant-based or vegetarian diet linked to 39% lower odds of COVID-19
2024-01-10
A predominantly plant-based or vegetarian diet is linked to 39% lower odds of COVID-19 infection, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
The findings prompt the researchers to suggest that a diet high in vegetables, legumes, and nuts, and low in dairy products and meat may help to ward off the infection.
Several studies have suggested that diet may have an important role in the evolution of COVID-19 infection, as well as in the factors that heighten the risk of its associated ...
Early menopause and HRT among hormonal factors linked to heightened rheumatoid arthritis risk
2024-01-10
Early menopause—before the age of 45—taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and having 4 or more children are among several hormonal and reproductive factors linked to a heightened risk of rheumatoid arthritis in women, finds a large long term study published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Women are more susceptible to this autoimmune disease than men, note the researchers. They are 4–5 times as likely as men to develop rheumatoid arthritis under the age of 50, and twice as likely to do so between the ages of 60 and 70. And the disease seems to take a greater physical toll on women than it does on men.
While ...
City of Hope Children’s Cancer Center, Children’s Oncology Group conduct largest clinical trial seeking to prevent heart failure among childhood cancer survivors
2024-01-10
LOS ANGELES — Physicians at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, in cooperation with the Children’s Oncology Group (COG), have conducted the largest clinical trial to date seeking to reduce the risk of people who have survived childhood cancer from developing heart failure. The findings published in The Lancet Oncology show that the blood vessel relaxing medication carvedilol is safe for childhood cancer survivors to take and may improve important markers of heart injury sustained as a result of chemotherapy exposure.
One devastating ...
New research sheds light on an old fossil solving an evolutionary mystery
2024-01-10
New York, January 9, 2024 — A research paper published in Royal Society’s Biology Letters on January 10 has revealed that picrodontids —an extinct family of placental mammals that lived several million years after the extinction of the dinosaurs—are not primates as previously believed.
The paper—co-authored by Jordan Crowell, an Anthropology Ph.D. candidate at the CUNY Graduate Center; Stephen Chester, an Associate Professor of Anthropology at Brooklyn College and the Graduate Center; ...
No laughing matter: Leadership critical to help address NHS retention crisis
2024-01-10
Frontline healthcare workers in busy hospitals feel that they are “just rearranging the deckchairs on the Titanic” according to new research into the impact of under-resourced and high-pressure emergency hospital departments in the UK.
A study from the Royal College of Emergency Medicine and University of Bath, led by clinical psychologist Dr Jo Daniels in collaboration with colleagues at UWE Bristol and the University of Bristol, argues that hospitals need better leadership to help change cultures and support people’s basic needs.
In addition to reflections ...
Acidity of Antarctic waters could double by century’s end, threatening biodiversity
2024-01-10
The acidity of Antarctica’s coastal waters could double by the end of the century, threatening whales, penguins and hundreds of other species that inhabit the Southern Ocean, according to new research from the Univeristy of Colorado Boulder.
Scientists projected that by 2100, the upper 650 feet (200 meters) of the ocean—where much marine life resides—could see more than a 100% increase in acidity compared with 1990s levels. The paper, appeared Jan. 4 in the journal Nature Communications.
“The findings are critical for our understanding ...