Agility in cultural heritage management—Advancing competence within uncertainty as a sustainable and resilient adaptation to processes of dynamic change
2024-01-10
(Press-News.org)
The intense changes in our modern society and the associated challenges are constantly increasing, not least due to the meta-crisis of climate change. Yet our approach to cultural heritage is still strongly influenced by the narrative of preservation. The article aims to find solutions within the interplay of preservation and change. Based on the psychological impact on society resulting from the current challenges, it is argued that cultural heritage experts need competencies in dealing with uncertainty and tolerance of ambiguity in order to provide security of action. The article applies insights from multiple disciplines to urban environment studies and advocates for a systemic understanding of cultural heritage as a prerequisite for sustainable and resilient adaptation to current challenges. It also contributes to a body of knowledge on what skills cultural heritage professionals need to be competent and confident in their daily work. The case study provides some valuable examples from Regensburg of Germany by taking an integrated and holistic approach that views the city as a multi-layered system in cultural heritage management.
The work entitled “Agility in Cultural Heritage Management—Advancing Competence Within Uncertainty as a Sustainable and Resilient Adaptation to Processes of Dynamic Change” was published on the journal of Landscape Architecture Frontiers.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-10
Tore Olsson put his students in touch with American history through his popular and award-winning class “Red Dead America: Exploring America’s Violent Past Through the Hit Video Games.” Now this engagement has reached beyond the classroom—the historical profession’s most prestigious journal, the American Historical Review, just published a major feature on the class as an example of creative and innovative history teaching.
Olsson is an associate professor and director of graduate studies in UT’s Department of History. His focus as a historian is the United States since the Civil War, with a particular interest in the US South, ...
2024-01-10
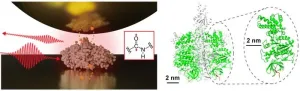
Infrared vibrational spectrum of a single protein is observed using advanced measurement techniques based on near-field optical microscopy. This method utilizes light confined at the nanometer scale, allowing for the detailed analysis of extremely small samples, which was previously challenging with conventional infrared spectroscopy. The achievement represents a major advancement towards technological innovations such as ultra-sensitive and super-resolution infrared imaging, as well as single-molecule vibrational spectroscopy.
Infrared ...
2024-01-10
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience has found an association between a reduction in grey matter in the brain and Early Onset Psychosis (EOP).
The study, published in Molecular Psychiatry, is the largest ever brain imaging study in EOP and has provided unprecedented levels of detail about the illness. It shows that, in contrast to other mental health disorders, people with EOP have a reduced volume of grey matter across nearly all regions of their brain. Researchers hope that this detailed mapping ...
2024-01-10
Novel findings from a preclinical head-to-head comparison show that administering a COVID-19 vaccine as a nasal spray rather than a subcutaneous injection enhances the body’s long-term immune memory, thereby increasing the vaccine’s overall effectiveness.
This research could pave the way for a COVID-19 vaccination strategy that depends on fewer boosters to achieve the same level of protection against SARS-CoV-2 viruses.
SINGAPORE, 10 January 2024 – A team of scientists, led by Duke-NUS Medical School, has discovered a potential intranasal vaccine candidate that provides improved, ...
2024-01-10
DURHAM, N.C. – Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums, according to new research from a Duke-led brain imaging study.
The cerebellum, a part of the brain well known for helping to coordinate movement and balance, can influence emotion and memory, which are impacted by PTSD. What isn’t known yet is whether a smaller cerebellum predisposes a person to PTSD or PTSD shrinks the brain region.
“The differences were largely within the posterior lobe, where a lot of the more cognitive functions attributed to the cerebellum seem to localize, as well as the vermis, which is linked to a lot of emotional processing ...
2024-01-10
Psilocybe fungi, known colloquially as “magic mushrooms,” have held deep significance in Indigenous cultures of Mesoamerica for centuries. They captured the wider world’s attention as a psychedelic staple in the 60s and 70s. Now, these infamous organisms are at the forefront of a mental health revolution. Psilocybin and psilocin, the psychoactive compounds found in nearly all species of Psilocybe, have shown promise as a treatment for conditions including PTSD, depression, and for easing end-of-life care.
To ...
2024-01-10
A sex-specific panel of 10 proteins can pick up 18 different early stage cancers, representing all the major organs of the human body, finds a proof of concept study published in the open access journal BMJ Oncology.
The findings could kick-start a new generation of screening tests for early detection of the disease, say the researchers, particularly as there are many sex specific differences in cancer—including age at occurrence, cancer types, and genetic alterations—points out a linked editorial.
Cancer accounts for 1 in every 6 deaths around the globe, with nearly 60% of these deaths ...
2024-01-10
A predominantly plant-based or vegetarian diet is linked to 39% lower odds of COVID-19 infection, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
The findings prompt the researchers to suggest that a diet high in vegetables, legumes, and nuts, and low in dairy products and meat may help to ward off the infection.
Several studies have suggested that diet may have an important role in the evolution of COVID-19 infection, as well as in the factors that heighten the risk of its associated ...
2024-01-10
Early menopause—before the age of 45—taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and having 4 or more children are among several hormonal and reproductive factors linked to a heightened risk of rheumatoid arthritis in women, finds a large long term study published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Women are more susceptible to this autoimmune disease than men, note the researchers. They are 4–5 times as likely as men to develop rheumatoid arthritis under the age of 50, and twice as likely to do so between the ages of 60 and 70. And the disease seems to take a greater physical toll on women than it does on men.
While ...
2024-01-10
LOS ANGELES — Physicians at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, in cooperation with the Children’s Oncology Group (COG), have conducted the largest clinical trial to date seeking to reduce the risk of people who have survived childhood cancer from developing heart failure. The findings published in The Lancet Oncology show that the blood vessel relaxing medication carvedilol is safe for childhood cancer survivors to take and may improve important markers of heart injury sustained as a result of chemotherapy exposure.
One devastating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Agility in cultural heritage management—Advancing competence within uncertainty as a sustainable and resilient adaptation to processes of dynamic change