(Press-News.org) The inner workings of the human brain are a gradually unraveling mystery and Dr. Richard Naud of the University of Ottawa’s Faculty of Medicine has led a highly compelling new study that brings us closer to answering these big questions. The study’s results have important implications for theories of learning and working memory and could potentially help lead to future developments in artificial intelligence (AI) since AI developers and programmers watch the work of Dr. Naud and other leading neuroscientists.
Published in Nature Computational Science, the study tackles the many-layered mystery of the “response variability” of neurons, brain cells that use electric signals and chemicals to process information and greenlights all the remarkable aspects of human consciousness.
The findings unveil the nuts and bolts of how neuronal variability is controlled by dendrites, the antenna that reach out from each neuron to receive synaptic inputs in our own personal neural communication networks. The rigorous study establishes properties of dendrites potently control output variability, a property that’s been shown to control synaptic plasticity in the brain.
“The intensity of a neuron’s response is controlled by inputs to its core, but the variability of a neuron’s response is controlled by the inputs to its little antennas – the dendrites,” says Dr. Naud, an Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine’s Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine and the uOttawa Department of Physics . “This study establishes more precisely how single neurons can have this crucial property of controlling response variability with their inputs.”
Dr. Naud suspected that if a mathematical framework he’d used to describe the cell body of neurons was extended to take their dendrites into account, then they might have luck efficiently simulating networks of neurons with active dendrites.
Cue the contribution of Zachary Friedenberger, a PhD student at the Department of Physics and a member of Dr. Naud’s lab, with a background in theoretical physics to solve the theoretical challenges and the math in a record time. Fast forward to the completed study: The predictions of the model were validated by analysis of in vivo recording data and observed over a wide range of model parameters.
“He managed to solve the math in a record time and solved a number of theoretical challenges I had not foreseen,” Dr. Naud says.
Dr. Naud believed that their technique could provide insight on the neuronal response to variable inputs. So they began working on a technique that would be able to compute statistics from a neuronal model with an active dendrite.
One of the work’s reviewers noted that the theoretical analysis “provides key insight into biological computation and will be of interest to a broad audience of computational and experimental neuroscientists.”
END
New study aims to unlock secrets of the human brain
University of Ottawa's Dr. Richard Naud’s work has important implications for theories of learning and memory and could potentially lead to future developments in AI
2024-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pudukotai Dinakarrao studying ways to protect autonomous vehicle supply chains
2024-01-16
Sai Manoj Pudukotai Dinakarrao, Assistant Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering, received funding for the project: "Cyber Sentinel: Safeguarding Autonomous Vehicle Supply Chains against Backdoors in Hardware."
Pudukotai Dinakarrao is working with University of Virginia researchers who aim to deploy a backdoor attack mitigation and avoidance approach for vehicles.
Haiying Shen, Associate Professor, Computer Science; Associate Professor, Electrical and ...
Thermoelectric permanent magnet opens new possibilities in thermal management technologies
2024-01-16
1. A NIMS research team has demonstrated that the transverse thermoelectric conversion (i.e., energy conversion between charge and heat currents that flow orthogonally to each other) can be greatly enhanced by applying magnetic fields or utilizing magnetism. In addition, the team developed a thermoelectric permanent magnet—a new functional material capable of thermoelectric cooling and power generation—by combining permanent magnets and thermoelectric materials into a hybrid structure. These results may guide in achieving thermal ...
Quantum computing and machine learning are effective tools in fluid dynamics
2024-01-16
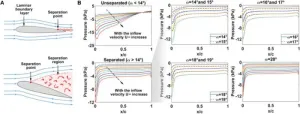
To prevent aircraft stalls, engineers have long studied the flow of air over airfoils such as airplane wings to detect the angles when flow separation occurs. Recently, a team of researchers at Shanghai Jiao Tong University including Xi-Jun Yuan and Zi-Qiao Chen investigated the use of quantum computing in connection with machine learning as a more accurate way of solving such problems. Their research was published Nov. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The use of a quantum support vector machine rather than a classical support vector machine increased the accuracy of classification of flow separation from 81.8% ...
Modified soft material promises better bioelectronics
2024-01-16
The scientific community has long been enamored of the potential for soft bioelectronic devices, but has faced hurdles in identifying materials that are biocompatible and have all of the necessary characteristics to operate effectively. Researchers have now taken a step in the right direction, modifying an existing biocompatible material so that it conducts electricity efficiently in wet environments and can send and receive ionic signals from biological media.
“We’re talking about ...
Study reveals key factors in surgeons' opioid prescribing patterns
2024-01-16
Key takeaways
Decreasing trend in opioid prescriptions: There was a notable nationwide reduction in opioid prescriptions after surgery from 2013 to 2017, reflecting a shift in the medical community's approach to pain management.
Social determinants affect opioid prescription rates: At the county level, lower median population age, higher education levels, insufficient sleep, higher health care costs, fewer mental health providers, and higher uninsured rates are linked to higher opioid prescription rates.
No ...
We need a staph vaccine: here’s why we don’t have one
2024-01-16
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is an extremely common bacterial infection; about 30% of people have colonies of SA living in their nose. SA is often harmless, but it is also a leading cause of hospital-acquired and community-associated infections. A vaccine for SA would be a game-changer for public health, but for decades, all vaccine candidates for SA have failed in clinical trials despite successful preclinical studies in mice. Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have finally explained why.
In a new study, published January ...
Analysis of breast cancer mortality in the US
2024-01-16
About The Study: Based on four simulation models, breast cancer screening, treatment of stage I to III breast cancer, and treatment of metastatic breast cancer were each associated with reduced breast cancer mortality between 1975 and 2019 in the U.S.
Authors: Sylvia K. Plevritis, Ph.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.25881)
Editor’s ...
Consumption of 100% fruit juice and body weight in children and adults
2024-01-16
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 eligible studies, including 17 among children (n = 45,851) and 25 among adults (n = 268,095), found a positive association between intake of 100% fruit juice and weight gain in children. Analysis of cohort studies in adults found a significant positive association among studies unadjusted for total energy, suggesting potential mediation by calories; an analysis of trials in adults found no significant association between 100% fruit juice consumption and body weight. The findings ...
Employer-sponsored health insurance premium cost growth and its association with earnings inequality among families
2024-01-16
About The Study: The findings of this study of U.S. families receiving employer-sponsored health insurance suggest that three decades of increasing health care premiums were likely associated with reduced annual earnings and increased earnings inequality by race and ethnicity and wage level and were meaningfully associated with wage stagnation.
Authors: Kurt Hager, Ph.D., M.S., of the UMass Chan Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Experiences of interpersonal violence in sport and perceived coaching style among college athletes
2024-01-16
About The Study: The results of this survey study involving 4,119 currently competing U.S. college athletes suggest that interpersonal violence is associated with marked changes in the psychosocial health and emotional well-being of college athletes, particularly those who identify as female and with non-heterosexual sexual orientations. Variations in coaching style have the potential to alter these associations. Ongoing efforts are needed to leverage the unique position that coaches hold to help reduce interpersonal violence and create safe places where all college athletes can thrive.
Authors: Yetsa A. Tuakli-Wosornu, M.D., ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
[Press-News.org] New study aims to unlock secrets of the human brainUniversity of Ottawa's Dr. Richard Naud’s work has important implications for theories of learning and memory and could potentially lead to future developments in AI