(Press-News.org)
“In the future, targeting of RBMX may be a novel method in cancer therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 1, entitled, “Aberrant RBMX expression is relevant for cancer prognosis and immunotherapy response.”
Cancer accounts for the highest rates of morbidity and mortality worldwide. RNA binding motif protein X-linked (RBMX) is a nuclear RNA-binding protein, associated with certain types of cancer by participating in the integration of sister chromatids and a combination of ribonucleoprotein complexes. However, the specific role of RBMX in cancer immunity remains unknown.
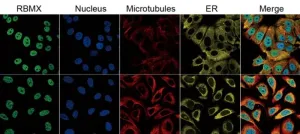
In this new study, researchers Yilei Sheng, Kunjian Lei, Chengpeng Sun, Jia Liu, Zewei Tu, Xingen Zhu, and Kai Huang from Nanchang University, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Neurological Tumors and Cerebrovascular Diseases, JXHC Key Laboratory of Neurological Medicine, and Yale School of Medicine present the aberrant expression levels, single-cell distributions, effective prognostic roles, immune cell infiltration associations, and immunotherapy responses of RBMX as a biomarker in various types of cancer. Moreover, they validate the aberrant expression of RBMX in clinical cancer samples.
“[...] a pan-cancer analysis is necessary for the identification of novel biological targets and biomarkers involved in carcinogenesis, cancer progression, and immunotherapy response. Such knowledge would improve the precision of cancer therapy.”
The researchers also evaluated the relationships between RBMX expression and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in clinical samples by immunofluorescent staining. Results showed that knockdown of RBMX can impair the proliferation, migration, and invasion of liver cancer cells. Finally, the team indicated that RBMX may play an immunoregulatory role in cancer progression, affecting the therapeutic effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with cancer.
“In conclusion, we performed an integrated analysis of RBMX, revealing its effective role in predicting cancer prognosis and response to immunotherapy. Abnormal expression of RBMX is associated with immune regulation, prognosis, the tumor microenvironment, immune cell infiltration, MSI, and TMB. The results of this study indicated that RBMX may play an independent role in clinical diagnosis and prediction.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205363
Corresponding Authors: Zewei Tu, Xingen Zhu, Kai Huang
Corresponding Emails: 401441619022@email.ncu.edu.cn, ndefy89006@ncu.edu.cn, kaihuang@ncu.edu.cn
Keywords: RBMX, cancer prognosis, immunotherapy response, proliferation, invasion
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205363
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
X, formerly known as Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
A team at HZB has developed a new measurement method that, for the first time, accurately detects tiny temperature differences in the range of 100 microkelvin in the thermal Hall effect. Previously, these temperature differences could not be measured quantitatively due to thermal noise. Using the well-known terbium titanate as an example, the team demonstrated that the method delivers highly reliable results. The thermal Hall effect provides information about coherent multi-particle states in quantum materials, based on their interaction with lattice vibrations (phonons).
The laws of quantum physics apply to all materials. However, in so-called ...
A new Roundtable discussion in the peer-reviewed journal Health Equity explores the results of a poll conducted by the National Collaborative for Health Equity (NCHE), called the “Heart of America Annual Survey.” The survey found that more than 80% of respondents want a national leader that unifies rather than divides us, suggesting that there is a readiness in the country to put polarization and division behind us so that we can solve our collective and common challenges and problems. Click here to read the Roundtable now.
Moderating ...
Jingrui He, professor of information sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has been awarded a two-year, $600,000 grant from the IBM-Illinois Discovery Accelerator Institute to improve modeling climate change and its impact across multiple application domains. He and a team of researchers from the University of Illinois and IBM will build Climate Runtime, a computational framework integrating cutting-edge capabilities from climate foundation models and multimodal fusion. This framework will allow for accurate prediction and quantification of weather and climate events and their impact in areas such as finance ...
Contacts:
David Hosansky, UCAR and NSF NCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
720-470-2073
Audrey Merket, UCAR and NSF NCAR Science Writer and Public Information Officer
amerket@ucar.edu
303-497-8293
The laws of thermodynamics dictate that a warmer atmosphere can hold more water vapor, but new research has found that atmospheric moisture has not increased as expected over arid and semi-arid regions of the world as the climate has warmed.
The findings are particularly puzzling because climate models have been predicting ...
Cleveland Clinic researchers have successfully developed a therapeutic peptide that blocks aggressive cancer cells from multiplying rapidly. The results highlight a potential new strategy for developing targeted treatments for triple-negative breast cancer, which currently has no approved options.
Targeted drugs attack cancer cell functions directly, offering a more precise approach to complement broader treatments like chemotherapy. A research team led by Ofer Reizes, PhD, and Justin Lathia, PhD, designed a peptide therapeutic that disrupts the molecular processes behind aggressive cancer growth when delivered into cells.
The ...
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology today named Mona V. Miller its next chief executive officer, effective April 1.
Miller is an experienced association leader with significant experience in strategic planning, advocacy and fundraising. Most recently, she was CEO of the American Society of Human Genetics. Before that she held multiple high-level positions at the Society for Neuroscience.
Miller said she was drawn to the ASBMB because “scientifically, biochemistry and molecular biology is at the forefront of knowledge that is transforming health and society.”
She said she looks forward to “focusing on the pivotal ...
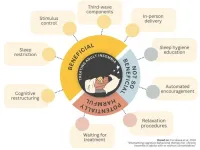
A combination of cognitive and behavioral strategies, ideally delivered in person by a therapist, maximizes the benefits of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), according to new research. CBT-I is a form of talk therapy, which can be delivered in person or through self-help guides. By analyzing 241 studies, involving over 30,000 adults, researchers identified the most beneficial components of CBT-I. These included: cognitive restructuring, third-wave components, sleep restriction, stimulus control and in-person delivery. Self-help with human encouragement could also be beneficial, while waiting for active treatment and enforcing ...
About The Study: Prenatal opioid exposure was associated with an increased risk of infection, eczema and dermatitis, and asthma, but not allergies and anaphylaxis or autoimmune conditions in this study of 401,000 neonates. These findings highlight the importance of further study of opioid-induced immune changes during pregnancy, the potential impact on long-term health in exposed children, and the mechanisms of opioid-induced immune dysregulation.
Authors: Erin Kelty, Ph.D., of the University of Western Australia in Crawley, Western Australia, ...
About The Study: In this comparative effectiveness trial of behavioral activation psychotherapy (BA) and antidepressant medication management (MEDS) in 416 patients with heart failure experiencing depression, both treatments significantly reduced depressive symptoms by nearly 50% with no statistically significant differences between treatments. BA recipients experienced better physical health-related quality of life, fewer emergency department visits, and fewer days hospitalized. The study findings suggest that patients with heart failure could be given the choice between BA or MEDS to ameliorate depression.
Authors: Waguih ...
A new study by Hebrew University is a significant breakthrough in understanding Tidal Disruption Events (TDEs) involving supermassive black holes. The new simulations, for the first time ever, accurately replicate the entire sequence of a TDE from stellar disruption to the peak luminosity of the resulting flare. This study has unveiled a previously unknown type of shockwave within TDEs, settling a longstanding debate about the energy source of the brightest phases in these events. It confirms that shock dissipation powers the brightest weeks ...