(Press-News.org) In a study of nearly 5,000 North American first-year college students, those who were more extraverted, more agreeable, or less neurotic were more likely to feel a greater sense of belonging at school. Alexandria Stubblebine, an independent researcher in Ocala, Florida, USA, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 17, 2024.
Prior research has suggested that one’s personality traits are associated with one’s general sense of belonging. Within a college-specific context, other research has linked a secure sense of belonging to many positives, such as better academic performance and better mental health. Some studies have investigated relationships between students’ sense of belonging at school and their demographic traits, such as gender and race. However, very few studies have explored links between students’ personalities and sense of belonging at school.
To address that gap, Stubblebine and colleagues analyzed survey data from 4,753 first-year college students attending 12 different colleges and universities in the USA and Canada. The surveys evaluated each student’s sense of belonging at school and their levels of extraversion, agreeableness, openness, conscientiousness, and neuroticism—a collection of widely studied personality traits called “the Big Five.”
Statistical analysis of the survey responses showed that students with higher levels of extraversion or agreeableness tended to feel a greater sense of belonging after their first year at school. Those with greater neuroticism tended to feel a lower sense of belonging.
Additionally, students who were less neurotic, less open, and more extraverted had a higher likelihood of being enrolled in a large college. For students at large colleges, the statistical link between extraversion and belonging was stronger than for students at small schools.
These findings provide new insights into the links between personality and belonging at school, while also highlighting a potentially key role for school size. The authors call for more research to further deepen understanding, such as investigation of the potential influence of students’ race and ethnicity on these relationships, or the influence of other school characteristics beyond size. Such work could inform schools’ efforts to help students with different personalities and backgrounds build their sense of belonging and thrive at college.
The authors add: “Students who were more agreeable and more extraverted tended to have higher belonging in college, especially in big schools, and students who were more neurotic (that is, nervous and/or handle stress poorly) tended to have lower belonging in college. Additionally, and contrary to what many people might think, openness to new ideas and conscientiousness were unrelated to students' feelings of belonging.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295436
Citation: Stubblebine AM, Gopalan M, Brady ST (2024) Who feels like they belong? Personality and belonging in college. PLoS ONE 19(1): e0295436. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0295436
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
Certain personality traits linked to college students’ sense of belonging
Linkages between personality and belonging vary between big and small colleges, per new study
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Worldwide, we are living longer and the male-female longevity gap is shrinking
2024-01-17
When it comes to trends in mortality over the last thirty years, countries around the world can be grouped into five clusters, roughly representing the five continents, according to a new study published January 17, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David Atance of Universidad de Alcalá, Spain, and colleagues. While the clusters follow different trajectories, they share some commonalities, including longer life expectancies and fewer disparities between genders and groups of countries with different mortality and longevity indicators.
Most countries in the world have seen improvements in longevity over the last two centuries, ...
Mothers with high levels of dental plaque are 8 times more likely to transfer Candida albicans, involved in tooth decay, to their babies, underlining the need for moms to keep their own teeth clean
2024-01-17
Mothers with high levels of dental plaque are 8 times more likely to transfer Candida albicans, involved in tooth decay, to their babies, underlining the need for moms to keep their own teeth clean
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290938
Article Title: Multilocus sequence typing of Candida albicans oral isolates reveals high genetic relatedness of mother-child dyads in early life
Author Countries: Kuwait, USA
Funding: JX; grants K23DE027412 and R01DE031025 from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/ The funders ...
Dancing is an effective way for overweight and obese people to lose weight and fat, per meta-analysis
2024-01-17
Dancing is an effective way for overweight and obese people to lose weight and fat, per meta-analysis
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0296089
Article Title: Is dancing an effective intervention for fat loss? A systematic review and meta-analysis of dance interventions on body composition
Author Countries: China
Funding: We are sure that our funder is the Hunan Provincial Social Science Achievements Evaluation Committee project, the award number is XSP21YBZ163, and the Grant recipient is Longjun Jin. The funder had no role in study design, data collection ...
Arsenic concentrations are predicted to increase significantly in Bangladesh's drinking well water, consumed by around 97% of Bangladeshis, thanks to sea level rise from climate change
2024-01-17
Arsenic concentrations are predicted to increase significantly in Bangladesh's drinking well water, consumed by around 97% of Bangladeshis, thanks to sea level rise from climate change
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295172
Article Title: Sea level rise from climate change is expected to increase the release of arsenic into Bangladesh’s drinking well water by reduction and by the salt effect
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The fieldwork in Bangladesh was funded by the United States Agency of International Development (USAID; contract number US AID RE III 388-0070; https://www.usaid.gov/). ...
A third of surveyed United Nations staff working in Geneva report having personally experienced racial discrimination, and a third having witnessed colleagues being racially discriminated against
2024-01-17
A third of surveyed United Nations staff working in Geneva report having personally experienced racial discrimination, and a third having witnessed colleagues being racially discriminated against
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295715
Article Title: Racial discrimination within United Nations offices in Geneva: Results from an online survey
Author Countries: Germany, USA
Funding: The article was produced as part of the project "Racism and Mental Health: A Qualitative Study with Humanitarian Workers". The project is ...
Big dogs versus small dogs: Which sizes face higher risks of which diseases?
2024-01-17
A study of more than 25,000 U.S. dogs and 238 breeds has linked dog size to varying patterns of risk for health conditions over the course of a dog’s lifespan. Yunbi Nam of the University of Washington, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 17.
On average, smaller dogs tend to live longer than larger dogs. Evidence suggests that larger dogs do not tend to have more health conditions, but that dogs of different sizes may face different levels of risk for different conditions. However, more research is needed to clarify links between dog age, size, and disease prevalence.
To deepen understanding, ...
URI professor leads effort demonstrating success of new technology in conducting deep-sea research on fragile organisms
2024-01-17
KINGSTON, R.I. – Jan. 17, 2024 – A University of Rhode Island professor of Ocean Engineering and Oceanography, along with a multidisciplinary research team from multiple institutions, successfully demonstrated new technologies that can obtain preserved tissue and high-resolution 3D images within minutes of encountering some of the most fragile animals in the deep ocean.
URI Professor Brennan Phillips, the principal investigator on the project, and a team of 15 researchers from six institutions, including URI, have shown ...
Woolly mammoth movements tied to earliest Alaska hunting camps
2024-01-17
Researchers have linked the travels of a 14,000-year-old woolly mammoth with the oldest known human settlements in Alaska, providing clues about the relationship between the iconic species and some of the earliest people to travel across the Bering Land Bridge.
Scientists made those connections by using isotope analysis to study the life of a female mammoth, named Élmayųujey'eh, by the Healy Lake Village Council. A tusk from Elma was discovered at the Swan Point archaeological site in Interior Alaska. Samples from the tusk revealed details about Elma and the roughly 1,000-kilometer journey she took through Alaska ...
Researchers chronicle lifetime travels of a single woolly mammoth which wandered the north more than 14,000 years ago
2024-01-17
Attention editors: Embargoed by Science Advances until Wednesday, January 17th, 2 p.m. eastern
High resolution photos, background footage, video clips can be downloaded at this link: https://photos.app.goo.gl/Sn4unWFGHb5ULdeB9
Hamilton, ON, Jan. 17, 2024 – An international team of researchers from McMaster University, University of Alaska Fairbanks and the University of Ottawa has tracked and documented the movements and genetic connections of a female woolly mammoth that roamed the earth more than 14,000 years ago.
She travelled ...
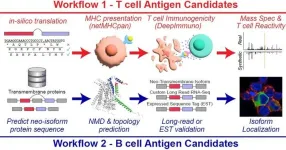
New research tool seeks to accelerate hunt for cancer immunotherapy targets
2024-01-17
An innovative computational tool dubbed “SNAF” may help the research world bring the emerging promise of cancer immunotherapy to a wider range of patients, according to a study published Jan. 17, 2024, in Science Translational Medicine.
The research tool, called the Splicing Neo Antigen Finder (SNAF), was developed by a multidisciplinary team of researchers from Cincinnati Children’s and the University of Virginia. The project was led by Guangyuan Li, PhD, and Nathan Salomonis, PhD, both with the Division of Biomedical Informatics at Cincinnati ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Certain personality traits linked to college students’ sense of belongingLinkages between personality and belonging vary between big and small colleges, per new study