(Press-News.org) Mothers with high levels of dental plaque are 8 times more likely to transfer Candida albicans, involved in tooth decay, to their babies, underlining the need for moms to keep their own teeth clean
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290938
Article Title: Multilocus sequence typing of Candida albicans oral isolates reveals high genetic relatedness of mother-child dyads in early life
Author Countries: Kuwait, USA
Funding: JX; grants K23DE027412 and R01DE031025 from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/ The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Mothers with high levels of dental plaque are 8 times more likely to transfer Candida albicans, involved in tooth decay, to their babies, underlining the need for moms to keep their own teeth clean
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dancing is an effective way for overweight and obese people to lose weight and fat, per meta-analysis
2024-01-17
Dancing is an effective way for overweight and obese people to lose weight and fat, per meta-analysis
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0296089
Article Title: Is dancing an effective intervention for fat loss? A systematic review and meta-analysis of dance interventions on body composition
Author Countries: China
Funding: We are sure that our funder is the Hunan Provincial Social Science Achievements Evaluation Committee project, the award number is XSP21YBZ163, and the Grant recipient is Longjun Jin. The funder had no role in study design, data collection ...
Arsenic concentrations are predicted to increase significantly in Bangladesh's drinking well water, consumed by around 97% of Bangladeshis, thanks to sea level rise from climate change
2024-01-17
Arsenic concentrations are predicted to increase significantly in Bangladesh's drinking well water, consumed by around 97% of Bangladeshis, thanks to sea level rise from climate change
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295172
Article Title: Sea level rise from climate change is expected to increase the release of arsenic into Bangladesh’s drinking well water by reduction and by the salt effect
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The fieldwork in Bangladesh was funded by the United States Agency of International Development (USAID; contract number US AID RE III 388-0070; https://www.usaid.gov/). ...
A third of surveyed United Nations staff working in Geneva report having personally experienced racial discrimination, and a third having witnessed colleagues being racially discriminated against
2024-01-17
A third of surveyed United Nations staff working in Geneva report having personally experienced racial discrimination, and a third having witnessed colleagues being racially discriminated against
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295715
Article Title: Racial discrimination within United Nations offices in Geneva: Results from an online survey
Author Countries: Germany, USA
Funding: The article was produced as part of the project "Racism and Mental Health: A Qualitative Study with Humanitarian Workers". The project is ...
Big dogs versus small dogs: Which sizes face higher risks of which diseases?
2024-01-17
A study of more than 25,000 U.S. dogs and 238 breeds has linked dog size to varying patterns of risk for health conditions over the course of a dog’s lifespan. Yunbi Nam of the University of Washington, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 17.
On average, smaller dogs tend to live longer than larger dogs. Evidence suggests that larger dogs do not tend to have more health conditions, but that dogs of different sizes may face different levels of risk for different conditions. However, more research is needed to clarify links between dog age, size, and disease prevalence.
To deepen understanding, ...
URI professor leads effort demonstrating success of new technology in conducting deep-sea research on fragile organisms
2024-01-17
KINGSTON, R.I. – Jan. 17, 2024 – A University of Rhode Island professor of Ocean Engineering and Oceanography, along with a multidisciplinary research team from multiple institutions, successfully demonstrated new technologies that can obtain preserved tissue and high-resolution 3D images within minutes of encountering some of the most fragile animals in the deep ocean.
URI Professor Brennan Phillips, the principal investigator on the project, and a team of 15 researchers from six institutions, including URI, have shown ...
Woolly mammoth movements tied to earliest Alaska hunting camps
2024-01-17
Researchers have linked the travels of a 14,000-year-old woolly mammoth with the oldest known human settlements in Alaska, providing clues about the relationship between the iconic species and some of the earliest people to travel across the Bering Land Bridge.
Scientists made those connections by using isotope analysis to study the life of a female mammoth, named Élmayųujey'eh, by the Healy Lake Village Council. A tusk from Elma was discovered at the Swan Point archaeological site in Interior Alaska. Samples from the tusk revealed details about Elma and the roughly 1,000-kilometer journey she took through Alaska ...
Researchers chronicle lifetime travels of a single woolly mammoth which wandered the north more than 14,000 years ago
2024-01-17
Attention editors: Embargoed by Science Advances until Wednesday, January 17th, 2 p.m. eastern
High resolution photos, background footage, video clips can be downloaded at this link: https://photos.app.goo.gl/Sn4unWFGHb5ULdeB9
Hamilton, ON, Jan. 17, 2024 – An international team of researchers from McMaster University, University of Alaska Fairbanks and the University of Ottawa has tracked and documented the movements and genetic connections of a female woolly mammoth that roamed the earth more than 14,000 years ago.
She travelled ...
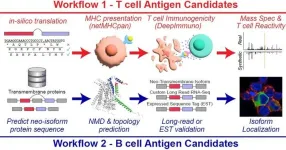
New research tool seeks to accelerate hunt for cancer immunotherapy targets
2024-01-17
An innovative computational tool dubbed “SNAF” may help the research world bring the emerging promise of cancer immunotherapy to a wider range of patients, according to a study published Jan. 17, 2024, in Science Translational Medicine.
The research tool, called the Splicing Neo Antigen Finder (SNAF), was developed by a multidisciplinary team of researchers from Cincinnati Children’s and the University of Virginia. The project was led by Guangyuan Li, PhD, and Nathan Salomonis, PhD, both with the Division of Biomedical Informatics at Cincinnati ...
SARS-CoV-2 can infect dopamine neurons causing senescence
2024-01-17
A new study reported that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, can infect dopamine neurons in the brain and trigger senescence—when a cell loses the ability to grow and divide. The researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons suggest that further research on this finding may shed light on the neurological symptoms associated with long COVID such as brain fog, lethargy and depression.
The findings, published in Cell Stem Cell on Jan. 17, show that dopamine neurons infected with SARS-CoV-2 stop working and send out chemical signals that cause ...
The metalens meets the stars
2024-01-17
Metalenses have been used to image microscopic features of tissue and resolve details smaller than a wavelength of light. Now they are going bigger.
Researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a 10-centimeter-diameter glass metalens that can image the sun, the moon and distant nebulae with high resolution. It is the first all-glass, large-scale metalens in the visible wavelength that can be mass produced using conventional CMOS fabrication technology.
The ...