(Press-News.org) WHAT:
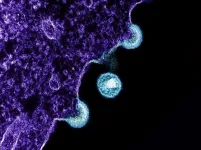
Three different HIV antibodies each independently protected monkeys from acquiring simian-HIV (SHIV) in a placebo-controlled proof-of-concept study intended to inform development of a preventive HIV vaccine for people. The antibodies—a human broadly neutralizing antibody and two antibodies isolated from previously vaccinated monkeys—target the fusion peptide, a site on an HIV surface protein that helps the virus fuse with and enter cells. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, was led by the Vaccine Research Center (VRC) at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Antibodies that target the fusion peptide can neutralize diverse strains of HIV in vitro, that is, in a test tube or culture dish outside of a living organism. The NIAID VRC isolated a fusion peptide-directed human antibody, called VRC34.01, from a person living with HIV who donated blood samples for research. They also isolated two antibodies from rhesus macaques—a species of monkey with immune systems like humans’—who previously had received a vaccine regimen designed to generate fusion peptide-directed antibodies. Demonstrating that these antibodies protect animals would validate the fusion peptide as a target for human vaccine design. SHIV challenge—administering an infective dose of SHIV—to rhesus macaques is a widely used animal model for assessing the performance of HIV antibodies and vaccines.
In this study, rhesus macaques in each of four groups received a single intravenous infusion of one type of antibody—a 2.5 or 10 mg/kg of bodyweight dose of VRC34.01, or one of the two vaccine-elicited rhesus macaque antibodies—and other monkeys received a placebo infusion. To determine the protective effect of the antibodies, each monkey was challenged five days after infusion with a strain of SHIV known to be sensitive to fusion peptide-directed antibodies.
All monkeys that received a placebo infusion acquired SHIV following the challenge. Among monkeys that received VRC34.01 infusions, none receiving the 10 mg/kg dose and 25% of those receiving the 2.5 mg/kg dose acquired SHIV. Of those that received the vaccine-elicited rhesus macaque antibodies, no monkeys receiving the antibody called DFPH-a.15 acquired SHIV, and 25% of those receiving the antibody called DF1W-a.01 acquired SHIV. Over time, the concentration of antibodies in the blood of animals that received DFPH-a.15 declined. Those animals were re-challenged 30 days later to see if the lower concentration of antibodies had a decreased protective effect, and half of them acquired SHIV.
The three antibodies studied each provided statistically significant protection from SHIV, and the effect was dose dependent, that is, highest in monkeys with greater antibody concentrations in their blood.
According to the authors, these findings represent the proof-of-concept that fusion peptide-directed antibodies can provide protection against SHIV and help determine the concentration of antibodies a vaccine would need to generate to be protective. They suggest that their findings on vaccine-elicited antibodies in some animals support further work to design preventive HIV vaccine concepts targeting the fusion peptide. They conclude that an effective HIV vaccine targeting the HIV fusion peptide likely will need to expand upon the concepts used in this study, by generating multiple varieties of fusion peptide-directed antibodies. This would increase the likelihood that the vaccine could maintain a preventive effect across the vastly diverse HIV variants in circulation.
ARTICLE:
A Pegu et al. Antibodies targeting the fusion peptide on the HIV envelope provide protection to rhesus macaques against mucosal SHIV challenge. Science Translational Medicine DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adh9039 (2024).
WHO:
Richard Koup, M.D., NIAID VRC Deputy Director and Immunology Section Chief, is available to discuss this research.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact the NIAID News & Science Writing Branch, (301) 402-1663, NIAIDNews@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
Social networks of sanctuary-living Grauer’s gorillas provide unique insights into the behavior of a critically endangered species and inform on their care and future release.
Adult female gorillas are at the centre of social networks in a sanctuary-living Grauer's Gorilla group, according to social network analysis which also finds them to be the most gregarious.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295561
Article Title: Group structure and individual relationships of sanctuary-living Grauer’s ...
In a study of nearly 5,000 North American first-year college students, those who were more extraverted, more agreeable, or less neurotic were more likely to feel a greater sense of belonging at school. Alexandria Stubblebine, an independent researcher in Ocala, Florida, USA, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 17, 2024.
Prior research has suggested that one’s personality traits are associated with one’s general sense of belonging. Within a college-specific context, other research has linked a secure sense of belonging to many positives, such as better academic performance and better mental health. Some studies have investigated ...
When it comes to trends in mortality over the last thirty years, countries around the world can be grouped into five clusters, roughly representing the five continents, according to a new study published January 17, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David Atance of Universidad de Alcalá, Spain, and colleagues. While the clusters follow different trajectories, they share some commonalities, including longer life expectancies and fewer disparities between genders and groups of countries with different mortality and longevity indicators.
Most countries in the world have seen improvements in longevity over the last two centuries, ...
Mothers with high levels of dental plaque are 8 times more likely to transfer Candida albicans, involved in tooth decay, to their babies, underlining the need for moms to keep their own teeth clean
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290938
Article Title: Multilocus sequence typing of Candida albicans oral isolates reveals high genetic relatedness of mother-child dyads in early life
Author Countries: Kuwait, USA
Funding: JX; grants K23DE027412 and R01DE031025 from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/ The funders ...
Dancing is an effective way for overweight and obese people to lose weight and fat, per meta-analysis
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0296089
Article Title: Is dancing an effective intervention for fat loss? A systematic review and meta-analysis of dance interventions on body composition
Author Countries: China
Funding: We are sure that our funder is the Hunan Provincial Social Science Achievements Evaluation Committee project, the award number is XSP21YBZ163, and the Grant recipient is Longjun Jin. The funder had no role in study design, data collection ...
Arsenic concentrations are predicted to increase significantly in Bangladesh's drinking well water, consumed by around 97% of Bangladeshis, thanks to sea level rise from climate change
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295172
Article Title: Sea level rise from climate change is expected to increase the release of arsenic into Bangladesh’s drinking well water by reduction and by the salt effect
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The fieldwork in Bangladesh was funded by the United States Agency of International Development (USAID; contract number US AID RE III 388-0070; https://www.usaid.gov/). ...
A third of surveyed United Nations staff working in Geneva report having personally experienced racial discrimination, and a third having witnessed colleagues being racially discriminated against
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295715
Article Title: Racial discrimination within United Nations offices in Geneva: Results from an online survey
Author Countries: Germany, USA
Funding: The article was produced as part of the project "Racism and Mental Health: A Qualitative Study with Humanitarian Workers". The project is ...
A study of more than 25,000 U.S. dogs and 238 breeds has linked dog size to varying patterns of risk for health conditions over the course of a dog’s lifespan. Yunbi Nam of the University of Washington, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 17.
On average, smaller dogs tend to live longer than larger dogs. Evidence suggests that larger dogs do not tend to have more health conditions, but that dogs of different sizes may face different levels of risk for different conditions. However, more research is needed to clarify links between dog age, size, and disease prevalence.
To deepen understanding, ...
KINGSTON, R.I. – Jan. 17, 2024 – A University of Rhode Island professor of Ocean Engineering and Oceanography, along with a multidisciplinary research team from multiple institutions, successfully demonstrated new technologies that can obtain preserved tissue and high-resolution 3D images within minutes of encountering some of the most fragile animals in the deep ocean.
URI Professor Brennan Phillips, the principal investigator on the project, and a team of 15 researchers from six institutions, including URI, have shown ...
Researchers have linked the travels of a 14,000-year-old woolly mammoth with the oldest known human settlements in Alaska, providing clues about the relationship between the iconic species and some of the earliest people to travel across the Bering Land Bridge.
Scientists made those connections by using isotope analysis to study the life of a female mammoth, named Élmayųujey'eh, by the Healy Lake Village Council. A tusk from Elma was discovered at the Swan Point archaeological site in Interior Alaska. Samples from the tusk revealed details about Elma and the roughly 1,000-kilometer journey she took through Alaska ...