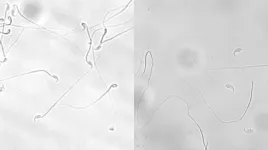
(Press-News.org) Mice lacking a certain gene are unable to produce offspring because their sperm lack the connection between the tail and the head. A new thesis from the University of Gothenburg indicates a probable cause of male infertility.
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have identified a new protein, dubbed by them as “MC2”, that plays a crucial part in the formation of swimmable sperm in mice. This protein is needed to create a functional connection between the head and the tail of the sperm.
“The connection is located in the ‘neck’ of the sperm head and facilitates coordinated movement and function as the sperm swims towards the egg. Certainly, the tail and head will each be created perfectly without such a connection – but to no avail, as they will be unable to reach their target,” says Kexin Zhang, a doctoral student at the Department of Chemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Gothenburg.
Gene of no importance for females
Experiments on mice indicated to Kexin Zhang and her research colleagues that production of the MC2 protein was controlled by a specific gene in the genome. When the gene was removed using genetic scissors, the researchers saw that the mice stopped producing the protein and became completely infertile. It is already known that genetic factors are responsible for 15 to 30 per cent of infertility in men. The gene is not on the sex chromosome and had no impact on the females’ ability to produce offspring.
“My research helped to enhance understanding of the causes of infertility due to the absence of the head of the sperm, which is known as acephalic spermatozoa syndrome. The underlying cause of this diagnosis has been unknown until now,” says Kexin Zhang.
Contraceptive
The discovery of the MC2 protein provides new insights into the molecular structure of sperm cells that then develop into spermatozoa. Researchers will be able to study these insights further.
“It is estimated that some 15 per cent of all heterosexual couples have problems with having children. The man is responsible for the problems in about half of these cases. I hope our research will eventually lead to new diagnostic methods and new treatments for male infertility. It may also be possible to create a male contraceptive by switching off this gene,” says Kexin Zhang.
END
Missing gene could explain infertility
2024-01-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists uncover new marine source of carbon emissions into atmosphere, finding bottom trawling contributes to global warming
2024-01-18
(WASHINGTON, DC) 18 JANUARY 2024 — Bottom trawling is a previously unaccounted for source of atmospheric carbon emissions, scientists reveal in a study published today. As the world scrambles to slash emissions caused by fossil fuels, deforestation and other sources, the study finds bottom trawling — the act of dragging a heavy fishing net across the ocean floor and resuspending some of the carbon in the seafloor sediment — to be a significant source of atmospheric carbon pollution. A previous study found that part of that disturbed ...
Light it up: reimagining the optical diode effect
2024-01-18
Osaka, Japan – At the heart of global internet connectivity, optical communications form an indispensable foundation. Key to this foundation are optical isolators, created by combining multiple components. The result is a complex structure that transmits light in only one direction, to prevent damage to lasers and minimize noise by avoiding the reversal of light. However, some magnetic materials have an optical diode effect – an unconventional nonreciprocal absorption of light manifested by the material itself. This effect leads to a change in transmittance depending ...
Machine learning method speeds up discovery of green energy materials
2024-01-18
Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers at Kyushu University, in collaboration with Osaka University and the Fine Ceramics Center, have developed a framework that uses machine learning to speed up the discovery of materials for green energy technology. Using the new approach, the researchers identified and successfully synthesized two new candidate materials for use in solid oxide fuel cells – devices that can generate energy using fuels like hydrogen, which don’t emit carbon dioxide. Their findings, which were reported in the journal, ...
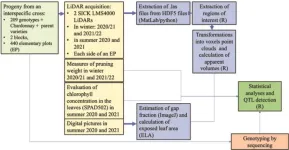
Revolutionizing grapevine phenotyping: harnessing LiDAR for enhanced growth assessment and genetic insights
2024-01-18
In response to the pressing need to reduce pesticide usage and adapt grapevine varieties to climate change, there's an unprecedented effort to phenotype new genotypes using high-throughput methods. Teams globally are developing advanced systems, employing technologies like multispectral cameras and LiDAR, to assess growth traits, photosynthetic capability, and other architectural parameters. However, traditional methods remain time-consuming and less efficient for large-scale studies. The current research gap lies in effectively employing LiDAR technology ...
AI-driven nutritional assessment of seed mixtures enhances sustainable farming practices
2024-01-18
Cultivating seed mixtures for local pastures is an age-old method to produce cost-effective and balanced animal feed, enhancing agricultural autonomy and environmental friendliness in line with evolving European regulations and organic consumer demands. Despite its benefits, farmers face adoption challenges due to the asynchronous ripening of cereals and legumes and the difficulty in assessing the nutritional value of heterogeneous seeds. Current practices rely on informal, empirical methods, and a proposed solution is to develop a mobile app or online service, similar to Pl@ntNet, for automated nutritional evaluation of seed mixtures, ...
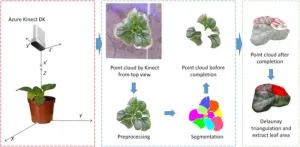
Revolutionizing plant phenotyping: deep learning and 3D point cloud technology in overcoming reconstruction challenges
2024-01-18
The 3-dimensional point cloud technology revolutionizes non-invasive measurement of plant phenotypic parameters, offering vital data for agriculture and research. Current research focuses on overcoming the limitations of 2.5D imaging and occlusions. Methods such as structure from motion, multi-view stereo, and advanced active 3D reconstruction techniques are being explored for this purpose. However, issues persist with incomplete data acquisition and the inaccuracy of phenotypic parameter extraction due ...
Revolutionizing grape yield predictions: the rise of semi-supervised berry counting with CDMENet
2024-01-18
To improve grape yield predictions, automated berry counting has emerged as a crucial yet challenging task due to the dense distribution and occlusion of berries. While grape cultivation is a significant global economic activity, traditional manual counting methods are inaccurate and inefficient. Recent research has shifted towards deep learning and computer vision, employing detection and density estimation techniques for more precise counts. However, these methods grapple with the variability of farmland and high occlusion rates, leading to significant counting errors. Additionally, creating high-performance ...
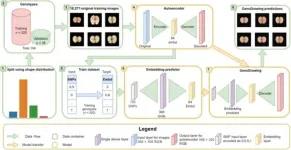
GenoDrawing: pioneering plant phenotyping with autoencoders and SNP markers
2024-01-18
Advancements in whole-genome sequencing have revolutionized plant species characterization, providing a wealth of genotypic data for analysis. The combination of genomic selection and neural networks, especially deep learning and autoencoders, has emerged as a promising method for predicting complex traits from this data. Despite the success in applications like plant phenotyping, challenges remain in accurately translating visual information from images into measurable data for genomic studies.
In November 2023, Plant ...
USC Office of Research and Innovation names new executive director for USC Stevens Center
2024-01-18
Erin Overstreet has been selected as the new executive director of the USC Stevens Center for Innovation where she will oversee the university’s commercialization of USC-driven intellectual property.
Overstreet’s expertise and experience embody technology transfer and innovation across the academic, educational, and venture capital sectors; such experience is critical for bridging USC research to a broadened, national technology transfer ecosystem, said Ishwar Puri, senior vice president of the Office of Research and Innovation.
“The university has the utmost confidence in Dr. Overstreet’s ability to ...
Can topography facilitate the refinement of landscape design methods?
2024-01-18
In the field of Landscape Architecture, Topography aims to study the complex and ongoing changing relationship between humans and the land through continuously updated and iterative tools and media. It maintains a balance between abstract concepts and concrete perceptions, which can both drive the development of science and technology in this field and hold on to openness to artistic expression. Thus, topographical design may be an effective way to help facilitate refining landscape design methods.
The work entitled “Can Topography ...