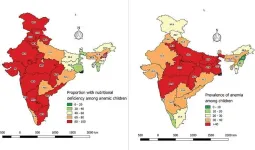
(Press-News.org) 6 in 10 sampled under-5s in India have micronutrient deficiencies, and 4 in 10 have anaemia, per survey of 17,230 children.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002095
Article Title: Prevalence and determinants of anemia due to micronutrient deficiencies among children aged 12–59 months in India–Evidence from Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey, 2016–18
Author Countries: India
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
6 in 10 sampled under-5s in India have micronutrient deficiencies, and 4 in 10 have anaemia, per survey of 17,230 children
2024-01-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
DNA becomes our ‘hands’ to construct advanced nanoparticle materials
2024-01-18
Evanston, IL In a paper to be published in Science Jan. 18, scientists Chad Mirkin and Sharon Glotzer and their teams at Northwestern University and University of Michigan, respectively, present findings in nanotechnology that could impact the way advanced materials are made.
The paper describes a significant leap forward in assembling polyhedral nanoparticles. The researchers introduce and demonstrate the power of a novel synthetic strategy that expands possibilities in metamaterial design. These are the unusual materials that underpin “invisibility cloaks” and ultrahigh-speed optical computing systems.
"We manipulate ...
Repeated sexual failures cause social stress in fruit flies
2024-01-18
Repeated failures to reproduce make fruit flies stressed and frustrated, which in turn makes them less resilient to other types of stress, Julia Ryvkin at Bar-Ilan University and colleagues report in the open-access journal PLOS Genetics, publishing January 18.
Animals are motivated to take actions that improve their survival and reproduction through reward systems in the brain, but failure causes stress. The reward systems have been extensively studied, but less attention has been paid to how animals respond to failure. To investigate, researchers compared ...
Complement system causes cell damage in Long Covid
2024-01-18
Most people infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus recover after the acute illness. However, a significant proportion of infected individuals develop long-lasting symptoms with a wide range of manifestations. The causes and disease mechanisms of Long Covid are still unknown, and there are no diagnostic tests or targeted treatments.
Part of the immune system active for too long
A team of researchers led by Onur Boyman, professor of immunology at the University of Zurich (UZH) and Director of the Department of Immunology at the University Hospital Zurich (USZ), has shown in a study that the complement system plays an important role in Long Covid. It is part of the innate immune system ...
Analysis of brain tumor blood vessels yields a candidate therapy—and a platform to find more
2024-01-18
JANUARY 18, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has generated a granular portrait of how the cellular and molecular components of the blood vessels that feed brain metastases of melanoma and lung and breast cancers differ from those of healthy brain tissue, illuminating how they help shape the internal environment of tumors to support cancer growth and immune evasion.
Led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Leire Bejarano and Johanna Joyce, researchers also developed a platform to identify potentially targetable vulnerabilities in the vasculature of brain metastases. They report in the current issue of Cancer ...
UChicago, Caltech study suggests that physical processes can have hidden neural network-like abilities
2024-01-18
We tend to separate the brain and the muscle—the brain does the thinking; the muscle does the doing. The brain takes in complex information about the world and makes decisions, and the muscle merely executes. This has also shaped how we think about a single cell; some molecules within cells are seen as ‘thinkers’ that take in information about the chemical environment and decide what the cell needs to do for survival; separately, other molecules are seen as the ‘muscle,’ building structures needed for survival.
But a new study shows how the molecules that build structures, i.e, the muscle, can themselves do both the thinking and the doing. The ...
Wireless drug patch shows promise as chronic disease treatment delivery system
2024-01-18
CHAPEL HILL, NC – University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientists created a new drug delivery system, called the Spatiotemporal On-Demand Patch (SOP), which can receive commands wirelessly from a smartphone or computer to schedule and trigger the release of drugs from individual microneedles. The patch’s thin, soft platform resembles a Band-Aid and was designed to enhance user comfort and convenience, since wearability is a crucial factor for chronically ill patients.
The research team, led by Juan Song, PhD, professor of pharmacology ...
AI can boost service for vulnerable customers
2024-01-18
AUSTIN, Texas –– Artificial intelligence has become the Swiss Army knife of the business world, a universal tool for increasing sales, optimizing efficiency, and interacting with customers. But new research from Texas McCombs explores another purpose for AI in business: to contribute to the social good.
It can do so by helping businesses better serve vulnerable consumers: anyone in the marketplace who experiences limited access to and control of resources.
“AI is widely recognized for its operational and ...
Structural study points the way to better malaria drugs
2024-01-18
Structural insights into a potent antimalarial drug candidate’s interaction with the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum have paved the way for drug-resistant malaria therapies, according to a new study by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Van Andel Institute.
The antimalarial molecule, TDI-8304, is one of a new class of experimental therapeutics that targets the proteasome, an essential, multiprotein complex in P. falciparum cells. Two years ago, the researchers showed in a preclinical study that TDI-8304 potently kills malaria parasites at multiple stages of their life cycle and ...
VCU research promotes a business paradigm shift that emphasizes people, not just profit
2024-01-18
RICHMOND, Va. (Jan. 18, 2024) – New research from Virginia Commonwealth University fundamentally challenges the paradigm that business organizations should promote profit above all else.
Christopher S. Reina, Ph.D., executive director of the VCU Institute for Transformative Leadership, lays out the foundation for transforming business to be much more people-centered and humanistic in “Humanistic Organizing: The Transformative Force of Mindful Organizational Communication.” ...
Towards the quantum of sound
2024-01-18
The quantum ground state of an acoustic wave of a certain frequency can be reached by completely cooling the system. In this way, the number of quantum particles, the so-called acoustic phonons, which cause disturbance to quantum measurements, can be reduced to almost zero and the gap between classical and quantum mechanics bridged.
Over the past decade, major technological advances have been made, making it possible to put a wide variety of systems into this state. Mechanical vibrations oscillating between ...