(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found overactivation in many brain regions, including the frontal and parietal lobes and the amygdala, in unmedicated children with anxiety disorders. They also showed that treatment with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) led to improvements in clinical symptoms and brain functioning. The findings illuminate the brain mechanisms underlying the acute effects of CBT to treat one of the most common mental disorders. The study, published in the American Journal of Psychiatry, was led by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
“We know that CBT is effective. These findings help us understand how CBT works, a critical first step in improving clinical outcomes,” said senior author Melissa Brotman, Ph.D., Chief of the Neuroscience and Novel Therapeutics Unit in the NIMH Intramural Research Program.
Sixty-nine unmedicated children diagnosed with an anxiety disorder underwent 12 weeks of CBT following an established protocol. CBT, which involves changing dysfunctional thoughts and behaviors through gradual exposure to anxiety-provoking stimuli, is the current gold standard for treating anxiety disorders in children.
The researchers used clinician-rated measures to examine the change in children’s anxiety symptoms and clinical functioning from pre- to post-treatment. They also used task-based fMRI to look at whole-brain changes before and after treatment and compare those to brain activity in 62 similarly aged children without anxiety.
Children with anxiety showed greater activity in many brain regions, including cortical areas in the frontal and parietal lobes, which are important for cognitive and regulatory functions, such as attention and emotion regulation. The researchers also observed elevated activity in deeper limbic areas like the amygdala, which are essential for generating strong emotions, such as anxiety and fear.
Following three months of CBT treatment, children with anxiety showed a clinically significant decrease in anxiety symptoms and improved functioning. Increased activation seen before treatment in many frontal and parietal brain regions also improved after CBT, declining to levels equal to or lower than those of non-anxious children. According to the researchers, the reduced activation in these brain areas may reflect more efficient engagement of cognitive control networks following CBT.
However, eight brain regions, including the right amygdala, continued to show higher activity in anxious compared to non-anxious children after treatment. This persistent pattern of enhanced activation suggests some brain regions, particularly limbic areas that modulate responses to anxiety-provoking stimuli, may be less responsive to the acute effects of CBT. Changing activity in these regions may require a longer duration of CBT, additional forms of treatment, or directly targeting subcortical brain areas.
“Understanding the brain circuitry underpinning feelings of severe anxiety and determining which circuits normalize and which do not as anxiety symptoms improve with CBT is critical for advancing treatment and making it more effective for all children,” said first author Simone Haller, Ph.D., Director of Research and Analytics in the NIMH Neuroscience and Novel Therapeutics Unit.
In this study, all children with anxiety received CBT. For comparison purposes, the researchers also measured brain activity in a separate sample of 87 youth who were at high risk for anxiety based on their infant temperament (for example, showing a high sensitivity to new situations). Because these children were not diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, they had not received CBT treatment. Their brain scans were taken at 10 and 13 years.
In adolescents at temperamental risk for anxiety, higher brain activity was related to increased anxiety symptoms over time and matched the brain activity seen in children diagnosed with an anxiety disorder before treatment. This provides preliminary evidence that the brain changes in children with anxiety were driven by CBT and that they may offer a reliable neural marker of anxiety treatment.
Anxiety disorders are common in children and can cause them significant distress in social and academic situations. They are also chronic, with a strong link into adulthood when they become harder to treat. Despite the effectiveness of CBT, many children continue to show anxiety symptoms after treatment. Enhancing the therapy to treat anxiety more effectively during childhood can have short- and long-term benefits and prevent more serious problems later in life.
This study provides evidence—in a large group of unmedicated youth with anxiety disorders—of altered brain circuitry underlying treatment effects of CBT. The findings could, in time, be used to enhance treatment outcomes by targeting brain circuits linked to clinical improvement. This is particularly important for the subset of children who did not significantly improve after short-term CBT.
“The next step for this research is to understand which children are most likely to respond. Are there factors we can assess before treatment begins to make the most informed decisions about who should get which treatment and when? Answering these questions would further translate our research findings into clinical practice,” said Brotman.
Reference
Haller, S. P., Linke, J. O., Grassie, H. L., Jones, E. L., Pagliaccio, D., Harrewijn, A., White, L. K., Naim, R., Abend, R., Mallidi, A., Berman, E., Lewis, K. M., Kircanski, K., Fox, N. A., Silverman, W. K., Kalin, N. H., Bar-Haim, Y., & Brotman, M. A. (2024). Normalization of fronto-parietal activation by cognitive-behavioral therapy in unmedicated pediatric patients with anxiety disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry. https://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ajp.20220449
Grants
MH002969, MH002781
Clinical trials
NCT00018057, NCT03283930
###
About the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): The mission of NIMH is to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses through basic and clinical research, paving the way for prevention, recovery, and cure. For more information, visit the NIMH website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit the NIH website.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
Women who follow vegan diets during pregnancy may face higher risks of developing preeclampsia and of giving birth to newborns with lower birth weight, suggests a recent study published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica.
For the study, 65,872 women identified themselves as omnivorous, 666 as fish/poultry vegetarians, 183 as lacto/ovo vegetarians, and 18 as vegans. Based on a questionnaire completed mid-pregnancy, investigators found that protein intake was lower among lacto/ovo vegetarians (13.3%) and vegans (10.4%) compared with omnivorous participants (15.4%). Micronutrient intake was also ...
In a study published in Economic Inquiry, investigators compared wages of Black and white interracially married individuals with those of intraracially married individuals in the United States.
After controlling for other factors that influence wages, the researchers found a wage penalty for white males in interracial marriages and a wage premium for Black males in interracial marriages, compared with their same sex and race counterparts in intraracial marriages. There were no wage penalties or premiums for white or Black females in interracial marriages.
The study also ...
In an analysis of all relevant published studies that assessed atopic dermatitis (also known as eczema) associated with trends in climate-related hazards due to greenhouse gas emissions, investigators found that impacts include direct effects on eczema, like particulate matter-induced inflammation from wildfires, and indirect effects, such as stress resulting from drought-induced food insecurity.
In their research published in Allergy, the scientists created maps showing the past, ...
Rhizarthrosis, also known as trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis, is a type of osteoarthritis that affects the thumb, and treatments range from splints to surgery. Investigators have uncovered various genetic differences between individuals with rhizarthrosis who undergo surgery for their condition versus those who opt for nonsurgical treatments.
The study, which is published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, included 1,083 surgical patients and 1,888 nonsurgical patients with rhizarthrosis, as well as 205,371 controls ...
By Amy Norton
Alcoholics Anonymous has long been a cornerstone of treating alcohol use disorders in the United States. But even today, Americans are not accessing it equally, according to a new study in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Alcoholics Anonymous, or AA, got its start nearly 90 years ago and is famous for spurring the "12-step" approach to recovery -- which includes acknowledging powerlessness over alcohol and giving your life over to a "higher power."
Over the years, AA and similar "mutual-help groups" ...
Chopped carrot pieces are among the most universally enjoyed foods and a snacking staple – a mainstay of school lunchboxes, picnics and party platters year-round.
Now researchers from the University of Bath have uncovered the secret science of prepping the popular root veg and quantified the processes that make them curl up if left uneaten for too long.
Mechanical Engineering student Nguyen Vo-Bui carried out the research as part of his final-year studies, in the limited circumstances of Covid-19 lockdowns of 2021.
Without access to labs, Nguyen aimed to identify the geometrical ...
Bottom Line: Imaging the tumors of patients with advanced melanoma receiving pembrolizumab (Keytruda) after only one week—rather than the standard of around three months—identified metabolic changes that corresponded with treatment response and progression-free survival (PFS).
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Michael D. Farwell, MD, an associate professor of radiology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
Background: Cancer immunotherapy has helped ...
Social systems where influence is focused around one or a few individuals may create environments where new ideas are ignored, and innovation is hindered.
This is according to a study published today in People and Nature by researchers at the University of Sydney and Stockholm University. It looked at the social networks and fertiliser use of 30 rural, cocoa-producing villages in Sulawesi, to examine how innovative and sustainable farming practices are adopted among communities.
It found that when one or two farmers hold a disproportionate level of influence (often due to their roles as "model farmers" in official sustainability programs) ...
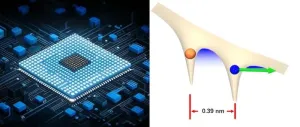
Tunnelling is one of most fundamental processes in quantum mechanics, where the wave packet could traverse a classically insurmountable energy barrier with a certain probability. Within the atomic scale, tunnelling effects play an important role in molecular biology, such as accelerating enzyme catalysis, prompting spontaneous mutations in DNA and triggering olfactory signaling cascades. Photoelectron tunnelling is a key process in light-induced chemical reactions, charge and energy transfer and radiation emission. The size of optoelectronic chips ...
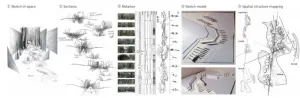
Replacing abstract form-making training with the perception of landscape site has been an important trend in the basic course of landscape architecture. Based on theoretical research and the authors’ teaching practice, this article aims to explore the significance, objects, and methods of site perception training. The authors argue that because landscape design is stemmed from the perception and interpretation of site characteristics, experiencing landscape sites must precede form-making training to become the foundation of design learning. Human-scale spaces that concern elements, structure, processes, and feelings for perception, representation, ...