Diverse forests are best at standing up to storms
2024-01-25
(Press-News.org) European forests with a greater diversity of tree species are more resilient to storms, according to new research published in the British Ecological Society journal, Functional Ecology.
A new study by researchers at the French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE) reveals that in Europe, the forests that are most resilient to storms are those with a greater diversity of tree species and dominated by slow growing species with high wood density, like oaks.
The researchers also found that the positive effect of tree diversity on storm resistance was more pronounced under extreme climatic conditions, such as the hot-dry conditions of the Mediterranean region and the cold-wet conditions of northern Scandinavia.
The study used simulations to model how forests with different characteristics, such as tree species diversity, resist and recover from storm damage.
In recent decades, Europe has experienced more frequent and severe windstorms that put forests and the ecosystem services they provide, such as habitat, carbon storage and timber, at risk. The researchers say their findings can aid in predicting the impact of increased storm frequency and intensity on forests and point to how we can make forests more resilient.
Dr Julien Barrere, researcher at INRAE and lead author of the study said: “An important takeaway from our study is that monocultures of fast growing species such as pine, although valuable from an economic point of view, are more susceptible to storm damage. In a context of increasing storm losses across the continent, our study therefore argues for forest management practices that promote diversity and slow growing tree species such as oak.”
In the study, the researchers created a model to simulate the dynamics of hundreds of forests after a storm, calibrating the model with data from 91,528 real-life forest plots in Europe. “Our simulated forests varied in both climate conditions, ranging from Mediterranean to Boreal, and in composition, i.e. in tree species diversity and identity.” explained Dr Barrere. “This allowed us to quantify the relationship between forest composition and resilience to storm disturbance, and how this relationship changes along the European climatic gradient.”
The researchers caution that because this is a modelling study, field work is still needed to support the findings. Dr Barrere said: “Although modelling studies like ours are essential for drawing conclusions about forest dynamics due to the long timescales in nature, the results must be interpreted with a clear understanding of the model hypotheses and complemented by field studies.”
-ENDS-
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-25
While sustainability reporting is a widespread practice in the private sector, new research shows that the same cannot be said for Ontario municipalities.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo studied 38 municipalities in Ontario, representing more than two-thirds of the population, and discovered that almost all municipalities publish their sustainability and climate change goals, but under half are formally reporting on their progress.
Municipalities are a key part of the equation ...
2024-01-25
A collaborative research team co-led by Professor Shuang ZHANG, the Interim Head of the Department of Physics, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), along with Professor Qing DAI from National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, China, has introduced a solution to a prevalent issue in the realm of nanophotonics – the study of light at an extremely small scale. Their findings, recently published in the prestigious academic journal Nature Materials, propose a synthetic complex frequency wave (CFW) approach to address optical loss in polariton propagation. These findings offer practical solutions such as more efficient light-based devices for faster and ...
2024-01-25
Two innovative teaching and learning projects led by The University of Hong Kong (HKU) earned honours in the Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) Reimagine Education Awards, presented in Abu Dhabi in December 2023.
Often referred to as the "Oscars of Education," the awards are designed to honour the most innovative and effective approaches to enhancing student learning experiences and employability outcomes.
The 2023 QS Reimagine Education Awards received a record number of more than 1,200 submissions across 17 categories. HKU has garnered ...
2024-01-25
The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, triggered by the earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011, resulted in a severe release of radioactive materials, including cesium, from the damaged nuclear reactors. The loss of cooling capabilities led to partial meltdowns in the reactor cores, releasing a substantial amount of cesium-137 (Cs-137) and cesium-134 (Cs-134) into the environment. The release of Cs-137, in particular, poses environmental and human health hazards due to its long half-life and high mobility in the environment. Environmentally, Cs-137 contributes ...
2024-01-25
This essay writes on a building project in the remote southwestern China that is built in uninhabited and is inspired and informed by its landscape context. The essay discusses how an extraordinary building project reacts to three different dimensions about landscape–architecture—a natural terrain being manipulated and recast. A small building needs to find its precise connecting point to a much larger historical and environmental context. A practical project needs to reach a balance between architectural pursuits and engineering concerns. Initially, artificial works might be isolated from and in conflict with the terrain, which requires architectural approaches ...
2024-01-25
Flinders University researchers say that cohesive and collaborative action from preventive health communicators and organisations is needed to inform young people about the devastating harms of vaping.
“Despite awareness of the potential harms, recreational vaping is increasing among younger people with our South Australian participants seeing vaping as ‘cleaner’ and less harmful than cigarettes,” says Flinders University’s Dr Joshua Trigg.
“We know that nicotine vapes are highly addictive and expose people to harmful chemicals, respiratory irritants, and toxic substances. In order to discourage ...
2024-01-25
Kyoto, Japan -- Our understanding of the world relies greatly on our knowledge of its constituent materials and their interactions. Recent advances in materials science technologies have ratcheted up our ability to identify chemical substances and expanded possible applications.
One such technology is infrared spectroscopy, used for molecular identification in various fields, such as in medicine, environmental monitoring, and industrial production. However, even the best existing tool -- the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer or FTIR -- utilizes a heating element as its light source. Resulting detector noise in the infrared region limits the devices' ...
2024-01-25
According to a new analysis, almost a quarter of Australians with disabilities smoke when compared to just 12.6% of the wider population.
While the number of Australians smoking is declining, the barriers for people with disabilities mean targeted support is needed to develop healthier habits.
Flinders University and Cancer Council NSW health experts are recommending new strategies to tackle the alarming smoking rate through targeted government policies, data collection on smoking and training for disability support workers on tobacco prevention ...
2024-01-25
A Rutgers Health analysis of millions of Medicare records has laid the groundwork for improving end-of-life care by demonstrating that nearly all older Americans follow one of nine trajectories in their last three years of life.
“Identifying which paths people actually take is a necessary precursor to identifying which factors send different people down different paths and designing interventions that send more people down whatever path is right for them,” said Olga Jarrín, the Hunterdon Professor of Nursing Research at Rutgers and corresponding author of the study published in BMC Geriatrics.
The team pulled the final three years of clinical records ...
2024-01-25
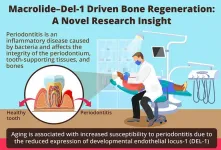
Niigata, Japan - Scientists from Niigata University discover macrolide-based molecules that increase the expression of DEL-1 protein and help in bone regeneration
Periodontitis is characterized by the loss of teeth resulting from inflammation of gums due to bacterial infections. The susceptibility to such bone loss disorders increases with age. The expression of the developmental endothelial locus-1 protein, crucial for bone regeneration, declines with age. Recently, researchers from Niigata University, University of Pennsylvania team identified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diverse forests are best at standing up to storms