(Press-News.org) New research finds that individual behavioural flexibility and not evolutionary selection is driving the northward shift of Balearic shearwaters.
The findings were revealed through a decade-long study which tagged individual birds.
The results indicate that individual animals may have greater behavioural flexibility to respond to climate change impacts than previously thought.
How individual animals respond to climate change is key to whether populations will persist or go extinct. Many species are shifting their ranges as the environment warms, but up to now the mechanisms underlying this have been unclear. For Europe’s most endangered seabird, the Balearic shearwater (Puffinus mauretanicus), new research has revealed that individual behavioural flexibility and not evolutionary selection is driving this species’ rapid migratory range shift. The study, led by University of Oxford biologists, has been published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The findings could help inform conservation strategies for vulnerable migratory bird species. The results also suggest that individual animals may have greater behavioural flexibility to respond to climate change impacts than previously thought, although this behavioural adaptation may have hidden costs, making the long-term impact on this species unclear.
Balearic shearwaters are long-lived but Critically Endangered mainly because of declines driven by fisheries by-catch, as they can get caught on baited longline hooks and gill nets. They breed in remote corners of the Mediterranean’s Balearic Islands, then migrate to spend the summer off the Atlantic coasts of Spain, France, and increasingly the UK.
Since 2010, researchers from Oxford University’s Biology Department and from the University of Liverpool, together with collaborators working in Ibiza, have been tracking colonies in Mallorca using miniature on-board geolocation devices. This revealed that the birds have been migrating further and further north once they leave the Mediterranean.
It was unknown, however, whether this change was being driven by individual birds altering their behaviour, or through natural selection favouring birds that travel further.
To answer this, the researchers compared the migration tracks of the same individuals tagged in multiple years. This revealed that individual birds were shifting their range northwards by an average of 25km per year.
Co-lead author Joe Wynn (Department of Biology, University of Oxford & Institute of Avian Research "Vogelwarte Helgoland"), said: ‘We found that the best predictor of this change in migratory behaviour was the average sea surface temperature in the summering-grounds, suggesting that the birds may well be following changes in underlying marine resources. The fact that individuals can be this flexible in the face of rapid climate change is encouraging.’
But despite this flexibility in their summer destination, Balearic shearwaters are much more constrained in where they breed, so that migrating further north means they have further to fly back in the autumn.
Co-author Professor Tim Guilford (Department of Biology, University of Oxford) added: ‘We found that individuals speed up their return migration the further north they have gone, but this only partially compensates for the extra distance and they still arrive back in the Mediterranean late. We don’t yet know how such delays may affect their breeding success or survival.’
This raises the intriguing question of how the birds know how far away from home they are, when they set off back for the colony. To investigate this, the researchers compared the distance estimates of the different kinds of map that shearwaters might use to guide their migration decisions.
Co-lead author Patrick Lewin (Department of Biology, University of Oxford), said: ‘We found that the route individual birds took on previous migratory journeys was a much better predictor of return speed than an estimate of the straight line distance back to the colony. This suggests that birds do not rely on a large-scale navigational map on migration, but instead have some memory of the route they have flown in the past.’
‘It is possible that individual route memory plays an important role in the migration of many other long-lived seabirds, but further research is needed to clarify this’ he added.
Balearic shearwaters belong to one of the most threatened groups of birds on earth, and are themselves facing potential extinction as a species. This includes both land-based threats, such as predation by invasive species and habitat degradation, and at-sea threats, such as fisheries bycatch, overfishing, pollution, and windfarm development.
Collaborator Pep Arcos from SEO/Birdlife said: ‘In addition to direct threats both on land and at sea, the increasing threat of climate change poses a challenge for a species that breeds in such a restricted habitat. Results from this study suggest that individual flexibility might help with distribution shifts driven by climate change outside the breeding season, but the question is still open about what might be the consequences of climate change for the birds during breeding, when their movements are constrained by the location of the colony.
Notes to editors:
For media requests, contact the Communications team in the Department of Biology, University of Oxford – comms@biology.ox.ac.uk
The study ‘Climate change drives migratory range shift via individual plasticity in shearwaters’ will be published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Monday 29 January at 20:00 GMT/ 15:00 ET at doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2312438121. To view a copy of the paper before this under embargo, contact the Communications team in the Department of Biology, University of Oxford – comms@biology.ox.ac.uk
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the eighth year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2024. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 300 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past five years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
The Department of Biology is a University of Oxford department within the Maths, Physical, and Life Sciences Division. It utilises academic strength in a broad range of bioscience disciplines to tackle global challenges such as food security, biodiversity loss, climate change and global pandemics. It also helps to train and equip the biologists of the future through holistic undergraduate and graduate courses. For more information visit www.biology.ox.ac.uk.
END
Endangered seabird shows surprising individual flexibility to adapt to climate change
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Spacing characteristics between vegetation could be a warning sign of degrading dryland ecosystems - study
2024-01-29
Scientists have found that the spatial arrangement of plants in drylands can be a sign of the environment degrading, according to a new study.
One of the iconic features of drylands is the striking appearance of islands of plants surrounded by bare soil. This spatial structure of arid vegetation has long fascinated scientists, but now a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, has shed new light on why these plants group in this way.
An international team of scientists, including from the University of Birmingham, combined field data from 115 sites around the world, and used mathematical models and remote sensing to build a picture of how the ...
Researchers spying for signs of life among exoplanet atmospheres
2024-01-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The next generation of advanced telescopes could sharpen the hunt for potential extraterrestrial life by closely scrutinizing the atmospheres of nearby exoplanets, new research suggests.
The next generation of advanced telescopes could sharpen the hunt for potential extraterrestrial life by closely scrutinizing the atmospheres of nearby exoplanets, new research suggests.
Published recently in The Astronomical Journal, a new paper details how a team of astronomers from The Ohio State University examined upcoming telescopes’ ability to detect chemical ...
People are inclined to hide a contagious illness while around others, research shows
2024-01-29
A startling number of people conceal an infectious illness to avoid missing work, travel, or social events, new research at the University of Michigan suggests.
The findings are reported in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. Across a series of studies involving healthy and sick adults, 75% of the 4,110 participants said they had either hidden an infectious illness from others at least once or might do so in the future. Many participants reported boarding planes, going on dates, and engaging in other social interactions while secretly sick. More than 61% of healthcare workers participating in the study also ...
Racial and ethnic differences in hypertension-related telehealth
2024-01-29
A new study in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health found that hypertension management via telehealth increased among Medicaid recipients regardless of race and ethnicity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Click here to read the article now.
Jun Soo Lee, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and coauthors, reported that from February-April 2023, the number of hypertension-related telehealth outpatient visits per 100 persons increased from 0.01 to 6.13, and the number of hypertension-related in-person visits decreased from 61.88 to 52.63.
The investigators ...
Henry Ford Health helps advance precision medicine research in Michigan
2024-01-29
Michiganders will continue to have the opportunity to advance medical research aimed at advancing individualized health care through a renewed award to Henry Ford Health + Michigan State University Health Sciences from the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) All of Us Research Program. The award includes $18.3 million in initial funding to support a consortium of 8 health care provider organizations with a presence in 16 states.
Henry Ford has led the consortium since 2017. The renewed award allows participation to continue until at least 2028. The multimillion-dollar multi-year award represents the largest NIH research grant in Henry Ford’s 108-year history.
All ...
Jobs and geography may affect hearing: New study maps hearing loss by state and county across the US
2024-01-29
Chicago, IL – January 24, 2024 – The first study to map the prevalence of bilateral hearing loss in the United States by state and county finds that rates of hearing loss are higher among men, non-Hispanic Whites, and residents of rural areas. Bilateral hearing loss is hearing loss in both ears.
West Virginia, Alaska, Wyoming, Oklahoma, and Arizona had the highest rates of hearing loss, while the District of Columbia, New Jersey, New York, Maryland, and Connecticut had the lowest (see top ten highest and ...
UChicago engineer driving key role in Great Lakes water transformation
2024-01-29
The Chicago-based Great Lakes ReNEW coalition has been awarded one of the largest, if not the largest, climate awards in the city’s history – up to $160 million over 10 years as one of the inaugural U.S. National Science Foundation’s Regional Innovation Engines.
Authorized in the “CHIPS and Science Act of 2022,” the NSF Engines program is designed to support the development of diverse regional coalitions of universities, local governments, the private sector and nonprofits to create solutions to today’s pressing issues.
Selected from an initial pool of more ...
Hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia
2024-01-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- Clinical research led by Indiana University School of Medicine investigators and their collaborators in Uganda has revealed that hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia. Their latest findings enhance strong evidence of hydroxyurea’s effectiveness and could ultimately reduce death in children in Africa, the continent most burdened by the disease.
The group’s research, recently published in the journal Blood, revealed that hydroxyurea treatment resulted in a remarkable ...
University of Manchester and SPIE announce $1 million endowment for postgraduate scholarships
2024-01-29
The University of Manchester and SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics have announced the establishment of the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics.
The $500k gift from the SPIE Endowment Matching Program will be matched 100% by the University and will be used to support both early-career and returning researchers from the University’s Photon Science Institute in partnership with the Royce Institute, the UK’s national institute for advanced materials research and innovation.
The partnership was announced today (29 January) during the SPIE Photonics West conference in San Francisco.
Photonics is the study of light and its interactions ...
Argonne scientists help scale up nanomaterials for sustainable manufacturing
2024-01-29
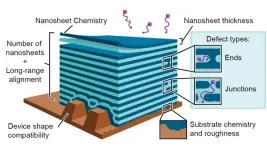
New material is self-assembling, long-lasting and recyclable.
As electronic devices get smaller, the materials needed to create them get smaller as well. Nanoscience is the study of extremely small materials that find uses in energy storage, electronics, health and safety applications and more.
Now a team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has developed a new self-assembly method to fabricate multilayered 2D nanosheets. A nanosheet is an extremely small, lasagna-like material made of ultrathin layers of polymers and nanoparticles.
These nanosheets have significantly ...