A new study in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health found that hypertension management via telehealth increased among Medicaid recipients regardless of race and ethnicity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Click here to read the article now.
Jun Soo Lee, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and coauthors, reported that from February-April 2023, the number of hypertension-related telehealth outpatient visits per 100 persons increased from 0.01 to 6.13, and the number of hypertension-related in-person visits decreased from 61.88 to 52.63.
The investigators found that Hispanic adults with hypertension had both the lowest cost per telehealth visit and the highest proportion of hypertension-related telehealth visits.
“Expanding telehealth use could potentially reduce existing disparities related to hypertension,” stated the investigators. “For example, Hispanic individuals have lower levels of hypertension awareness and treatment compared to non-Hispanic White and non-Hispanic Black adults. Telehealth offers an opportunity to address this through evidence-based practices like self-measured blood pressure monitoring, increased language concordance with a clinician, and culturally adapted lifestyle interventions.”
“The application of telehealth for patients with hypertension can enable better patient care and personal patient management,” says Charles R. Doarn, MBA, Editor-in-Chief of the Journal and Research Professor in the Department of Environmental and Public Health Sciences, and Director of the Space Research Institute for Discovery and Exploration at the University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio.
About the Journal
Telemedicine and e-Health is an Official Research Journal of the American Telemedicine Association (ATA) and an Official Journal of Digital Health Canada and the International Society for Telemedicine & e-Health. The Journal is led by Editor-in-Chief Charles R. Doarn, MBA, FATA, and is the leading peer-reviewed journal for cutting-edge telemedicine applications for achieving optimal patient care and outcomes. Complete tables of contents and a sample issue are available on the Telemedicine and e-Health website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. is a global media company dedicated to creating, curating, and delivering impactful peer-reviewed research and authoritative content services to advance the fields of biotechnology and the life sciences, specialized clinical medicine, and public health and policy. For complete information, please visit the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. website
END
Racial and ethnic differences in hypertension-related telehealth
2024-01-29
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Henry Ford Health helps advance precision medicine research in Michigan
2024-01-29
Michiganders will continue to have the opportunity to advance medical research aimed at advancing individualized health care through a renewed award to Henry Ford Health + Michigan State University Health Sciences from the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) All of Us Research Program. The award includes $18.3 million in initial funding to support a consortium of 8 health care provider organizations with a presence in 16 states.
Henry Ford has led the consortium since 2017. The renewed award allows participation to continue until at least 2028. The multimillion-dollar multi-year award represents the largest NIH research grant in Henry Ford’s 108-year history.
All ...
Jobs and geography may affect hearing: New study maps hearing loss by state and county across the US
2024-01-29
Chicago, IL – January 24, 2024 – The first study to map the prevalence of bilateral hearing loss in the United States by state and county finds that rates of hearing loss are higher among men, non-Hispanic Whites, and residents of rural areas. Bilateral hearing loss is hearing loss in both ears.
West Virginia, Alaska, Wyoming, Oklahoma, and Arizona had the highest rates of hearing loss, while the District of Columbia, New Jersey, New York, Maryland, and Connecticut had the lowest (see top ten highest and ...
UChicago engineer driving key role in Great Lakes water transformation
2024-01-29
The Chicago-based Great Lakes ReNEW coalition has been awarded one of the largest, if not the largest, climate awards in the city’s history – up to $160 million over 10 years as one of the inaugural U.S. National Science Foundation’s Regional Innovation Engines.
Authorized in the “CHIPS and Science Act of 2022,” the NSF Engines program is designed to support the development of diverse regional coalitions of universities, local governments, the private sector and nonprofits to create solutions to today’s pressing issues.
Selected from an initial pool of more ...
Hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia
2024-01-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- Clinical research led by Indiana University School of Medicine investigators and their collaborators in Uganda has revealed that hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia. Their latest findings enhance strong evidence of hydroxyurea’s effectiveness and could ultimately reduce death in children in Africa, the continent most burdened by the disease.
The group’s research, recently published in the journal Blood, revealed that hydroxyurea treatment resulted in a remarkable ...
University of Manchester and SPIE announce $1 million endowment for postgraduate scholarships
2024-01-29
The University of Manchester and SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics have announced the establishment of the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics.
The $500k gift from the SPIE Endowment Matching Program will be matched 100% by the University and will be used to support both early-career and returning researchers from the University’s Photon Science Institute in partnership with the Royce Institute, the UK’s national institute for advanced materials research and innovation.
The partnership was announced today (29 January) during the SPIE Photonics West conference in San Francisco.
Photonics is the study of light and its interactions ...
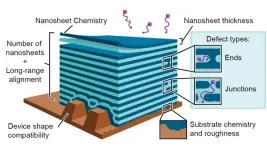
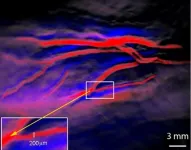
Argonne scientists help scale up nanomaterials for sustainable manufacturing
2024-01-29
New material is self-assembling, long-lasting and recyclable.
As electronic devices get smaller, the materials needed to create them get smaller as well. Nanoscience is the study of extremely small materials that find uses in energy storage, electronics, health and safety applications and more.
Now a team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has developed a new self-assembly method to fabricate multilayered 2D nanosheets. A nanosheet is an extremely small, lasagna-like material made of ultrathin layers of polymers and nanoparticles.
These nanosheets have significantly ...
OU scientists tests revolutionary imaging technique for pancreatic cancer
2024-01-29
Researchers at OU Health Stephenson Cancer Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences have embarked on a revolutionary new research study that could improve the detection of a deadly disease — pancreatic cancer — and give patients a chance to live longer, healthier lives.
The research focuses on an innovative combination of imaging techniques: a newly created contrast agent that recognizes pancreatic cancer cells, paired with Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography, or MSOT. Together, the approach can detect pancreatic cancer cells the width of an eyelash ...
Rising sea levels could lead to more methane emitted from wetlands
2024-01-29
As sea levels rise due to global warming, ecosystems are being altered. One small silver lining, scientists believed, was that the tidal wetlands found in estuaries might produce less methane – a potent greenhouse gas – as the increasing influx of seawater makes these habitats less hospitable to methane-producing microbes.
However, research from biologists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley indicates that these assumptions aren’t always true. After examining the microbial, chemical, and geological features of 11 wetland zones, the team found that a wetland region exposed ...
Study urges people to think twice before going on a diet
2024-01-29
A new qualitative study highlights the negative interpersonal and psychological consequences associated with “yo-yo dieting,” also known as weight cycling. The work underscores how toxic yo-yo dieting can be and how difficult it can be for people to break the cycle.
“Yo-yo dieting – unintentionally gaining weight and dieting to lose weight only to gain it back and restart the cycle – is a prevalent part of American culture, with fad diets and lose-weight-quick plans or drugs normalized as people pursue beauty ...
Astronomers spot 18 black holes gobbling up nearby stars
2024-01-29
Star-shredding black holes are everywhere in the sky if you just know how to look for them. That’s one message from a new study by MIT scientists, appearing today in the Astrophysical Journal.
The study’s authors are reporting the discovery of 18 new tidal disruption events (TDEs) — extreme instances when a nearby star is tidally drawn into a black hole and ripped to shreds. As the black hole feasts, it gives off an enormous burst of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Astronomers have detected previous tidal disruption events by looking for characteristic bursts in the optical and X-ray bands. To date, these searches have ...