(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Biological systems can behave as siblings in several ways, including by borrowing something and never giving it back. That appears to be what the human immune system did with a protein that now helps bind and regulate the subunits that make up antibodies, according to a multi-institute research collaboration. They found that, before the immune system evolutionarily co-opted it, the protein originally belonged to gene family responsible for directing cells to move to the right location at the right time to address specific functional needs.
The researchers, including Kazuhiko Kawasaki, associate research professor of anthropology at Penn State, published their findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. According to the team, while this work primarily informs a fundamental understanding of one feature of the immune system and associated genes, it may also help open design pathways future therapeutics, such as personalized immune responses.
“Everything comes from somewhere, and we believe we found the origin of immunoglobin Joining chain (J chain), an important immune molecule,” said corresponding author Martin F. Flajnik, department of microbiology and immunology, University of Maryland, who led the study. Flajnik also earned his undergraduate degree in biology from Penn State in 1978 before completing his graduate degrees at the University of Rochester.
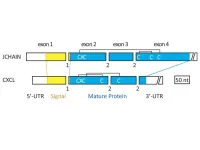
The J chain assembles and stabilizes two types of antibodies, called immunoglobin M (IgM) and immunoglobin A (IgA). It specifically regulates the structures of the IgM and IgA molecules, which have several subunits, and is required for their movement across the mucus-producing tissue lining body structures with external exposure, like the intestine, nasal cavity and lungs. The researchers found that the J chain originated from the CXCL chemokines, a specific family of proteins that regulate the ability of white blood cells to move throughout the body.
“Like immunoglobin itself and human-like adaptive immunity, the J chain emerged in jawed vertebrates, but its origin has remained mysterious since its discovery over 50 years ago,” Flajnik said. “This finding was never anticipated. Chemokine-driven locomotion is a vital function of the immune system, but a totally different function as compared to the J chain!”
Evolutionarily, new genes are often generated from genes that reside physically close together on the chromosome, and those genes typically remain clustered together even as they evolve different yet similar functions, but Kawasaki said location isn’t the only deciding factor to determine origin.
“The evolutionary relationship of genes can usually be detected when two genes retain similar nucleotide sequences or encoded amino acid sequences,” Kawasaki said, referring to the materials comprising an organism’s genetic code. “But previous studies could not detect any genes that show sequence similarities to the J chain gene, probably because the J chain gene sequence was quickly changed at its origin.”
Flajnik said he had a hunch that the J chain was related to a group of secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein (SCPP) genes due to their similar charges and levels of proline, an amino acid. He knew Kawasaki was an expert on SCPP genes, so he emailed him to assess the idea.
“He told me that, for various good reasons, the SCPPs and J chain were not related,” Flajnik said. “That was sad, as it was my favorite hypothesis.”
However, Kawasaki had noticed that genes on the opposite side of the J chain gene, away from the SCPP genes, did appear to be related to the J chain. Those were the CXCL chemokine genes.
“I immediately checked these CXCL chemokine genes and found that, though these genes do not show sequence similarities to the J chain genes, these genes and the J chain gene resemble each other with other various characteristics,” Kawasaki said.
Those characteristics include the same number of exons, which encode the protein, and phases of introns, which act as interrupters to stop or start splicing of the RNA molecules transcribed from the gene. The second exon encodes the same sequence, which is known as the classical tripeptide Cysteine-X-Cysteine, for both genes. The lengths of three of the exons are also similar.
“No other gene encoding the human secretome, which encompasses all proteins that can be secreted by cells of an organism, shares all three characteristics,” Kawasaki said.
The bonds between the Cysteine molecules encoded by the second exon in each gene are completely different from one another, though, the researchers said.
“This means that a chemokine can change its structure, to a large extent, and take on a new function,” Flajnik said.
Next, the researchers said they plan to investigate if chemokines have taken on other functions, specifically in the immune system. They also want to study if chemokines are pliable in their structure, which could indicate the ability to take on an entirely new secondary structure, adapting in response to different biological needs as required.
“I've been around for a long time, for 44 years in science, but this experience was one of the most incredibly satisfying and lucky,” Flajnik said. “I doubt that this similarity would have been uncovered for a long time without the serendipitous interaction between Kazuhiko and me.”
Other co-authors include Yuko Ohta, assistant professor of microbiology and immunology at the University of Maryland, and Caitlin D. Castro, a research fellow in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Chicago.
The National Institutes of Health supported this research.
END
Evolutionary origin of mysterious immune system molecule in humans revealed
The human immune system appears to have evolutionarily co-opted a molecule from another biological process, researchers report
2024-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCSF scientist wins Barancik Prize for Innovation in MS Research
2024-01-30
[New York, January 30, 2024] – Sergio E. Baranzini, PhD, a geneticist, neuroimmunologist and data scientist at the University of California, San Francisco, is the winner of this year’s Barancik Prize for Innovation in MS Research. Dr. Baranzini is being recognized for his pioneering efforts to integrate vast pools of information to understand complex mechanisms that cause MS and to develop more precise approaches to stop the disease and end it by prevention.
Baranzini is a Distinguished Professor and holds the Heidrich Friends and Family endowed chair in Neurology at the University of California, San Francisco ...
Salk Professor Joanne Chory honored with Benjamin Franklin Medal in Life Science
2024-01-30
LA JOLLA (January 30, 2024)—Salk Institute Professor Joanne Chory has been selected by the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia to receive a Benjamin Franklin Medal in Life Science for her achievements in plant science. She will receive a 14-karat gold medal and a $10,000 honorarium at the Franklin Institute Awards Ceremony in April 2024. Chory joins other extraordinary scientists and engineers as a Franklin laureate, including Nikola Tesla, Marie and Pierre Curie, Thomas Edison, Albert Einstein, and Jane Goodall, among others.
“Joanne’s contributions to the field of plant biology have impacted and will continue to impact scientists around the world,” ...
Study finds gut microbiota influence severity of respiratory viral infection
2024-01-30
The composition of microbiota found in the gut influences how susceptible mice are to respiratory virus infections and the severity of these infections, according to researchers from the Center for Translational Antiviral Research in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University.
The findings, published in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, report that segmented filamentous bacteria, a bacterial species found in the intestines, protected mice ...
Smartphone-based shopping mall walking program and daily walking steps
2024-01-30
About The Study: This study found that the use of a smartphone-based mall walking program combined with physical shopping mall facilities and lottery-based digital incentive coupons may motivate people to increase their daily number of walking steps.
Authors: Masamichi Hanazato, Ph.D., of Chiba University in Chiba-shi, Chiba, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53957)
Editor’s ...
Comparison of sleeve gastrectomy vs Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
2024-01-30
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial of 1,735 patients undergoing primary bariatric surgery found that both laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass were performed with a low perioperative risk without clinically significant differences between groups.
Authors: Suzanne Hedberg, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Gothenburg in Gothenburg, Sweden is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53141)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Worries about costs, time off work and COVID-19 kept some older adults from having surgery
2024-01-30
When it comes to having surgery, older adults don’t just base their decision on how much pain they’ll feel and how quickly they’ll recover, a new study finds.
Many also have serious concerns about how much they’ll have to pay out of their own pockets, how much work they’ll miss, and whether they’ll catch COVID-19 in the hospital or surgery center.
And a majority of those who called themselves very concerned about these issues ended up not having an operation that they had considered having, the study finds. The percentage who didn’t go through with surgery was much lower among those who said they’d been very concerned about pain or the ...
JMIR Perioperative Medicine invites submissions on perioperative blood management
2024-01-30
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue titled “Perioperative Blood Management” in JMIR Perioperative Medicine. The premier, peer-reviewed journal is indexed in PubMed and focuses on how technology and data science can improve care delivery and surgical patient outcomes. The new theme issue aims to explore the latest advancements, challenges, and patient-centered innovative approaches in optimizing blood-related practices before, during, and after surgical procedures.
JMIR Perioperative Medicine welcomes contributions from global researchers, clinicians, and experts in ...
Structural color ink: Printable, non-iridescent and lightweight
2024-01-30
A new way of creating color uses the scattering of light of specific wavelengths around tiny, almost perfectly round silicon crystals. This Kobe University development enables non-fading structural colors that do not depend on the viewing angle and can be printed. The material has a low environmental and biological impact and can be applied extremely thinly, promising significant weight improvements over conventional paints.
An object has color when light of a specific wavelength is reflected. With traditional pigments, this happens by molecules absorbing other colors from white light, but over time this interaction makes the molecules degrade and the color fades. ...
A faster, more efficient imaging system for nanoparticles
2024-01-30
Teams led by professors Jinyang Liang and Fiorenzo Vetrone from the Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre at the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) have developed a new system for imaging nanoparticles. It consists of a high-precision, short-wave infrared imaging technique capable of capturing the photoluminescence lifetimes of rare-earth doped nanoparticles in the micro- to millisecond range.
This groundbreaking discovery, which was published in the journal Advanced Science, paves the way for promising applications, particularly in the biomedical and information security fields.
Rare-earth ...
Lifetime of ‘biodegradable’ straws in the ocean is 8-20 months, study finds
2024-01-30
Plastic drinking straws that get into marine ecosystems make beaches unsightly and pose problems for turtles and seabirds. So, people increasingly favor alternatives marketed as biodegradable or compostable. But do marine microorganisms break apart those straws? Researchers conducted experiments with seawater and report in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering that some commercial bioplastic or paper straws might disintegrate within eight to 20 months in coastal ocean systems and switching to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
[Press-News.org] Evolutionary origin of mysterious immune system molecule in humans revealedThe human immune system appears to have evolutionarily co-opted a molecule from another biological process, researchers report