(Press-News.org) Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a prevalent pregnancy complication posing significant health risks to both mothers and their newborns. Early detection and treatment of GDM are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes. Current screening methods, like glucose tolerance tests, are in after 24 weeks of pregnancy and have limitations in patient compliance and accuracy.
A new study led by Lijian Zhao, Pei Sun, Hui Huang, Nan Li at BGI Genomics in collaboration with the Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, recently published on Briefings in Bioinformatics aimed to develop a non-invasive method for early detection of GDM using cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and deep learning models.
Methods and Findings:
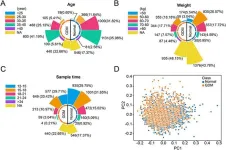
A deep learning model was developed using circulating cell-free DNA samples from 5,085 pregnant women, including 1,942 GDM patients and 3,143 healthy controls, to predict GDM status.
The researchers built a Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)-based deep neural network with a self-attention layer to analyze copy numbers of cfDNA sequencing data linked to gestational diabetes mellitus, focusing on identifying crucial genetic regions for accurate classification.
Key Points to Highlight:
1. The risk of gestational diabetes can be predicted non-invasively in the first trimester (12 weeks of pregnancy) which is earlier than the traditional method of glucose tolerance test performed late in pregnancy.
2. High accuracy of 93.5% in predicting GDM status, outperforming traditional methods.
3. Potential to improve patient compliance and accuracy in GDM screening, providing a promising approach for early detection of the gestational diabetes.
The study demonstrates the advantage of using cfDNA sequencing for early detection of GDM and highlights the importance of further investigating the use of deep learning models in precision medicine.
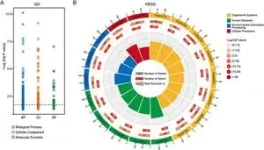
The analysis of cfDNA CNVs associated with diabetes genes and the use of a sophisticated model incorporating a self-attention layer to identify important genetic regions for accurate classification also allowed to identify:
•Essential genetic regions for accurate classification of GDM.
•CNV fragments covering 2190 genes, including known genes related to GDM like alpha- and beta-defensin genes (DEFA1, DEFA3, and DEFB1).
•Enriched biological processes and pathways linked to diabetes, such as glutamate signaling, forebrain development, and GTPase regulator activity.
Enhancing Research and Clinical Outcomes:
These findings provide a significant leap forward in understanding molecular mechanisms underlying GDM, offering insights for future research and therapeutic strategies.
About BGI Genomics:
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. Our services cover more than 100 countries and regions, involving more than 2,300 medical institutions. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
END
cfDNA sequencing enhances non-invasive early detection of gestational diabetes
2024-02-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising heart drugs ID'd by cutting-edge combo of machine learning, human learning
2024-02-01
University of Virginia scientists have developed a new approach to machine learning – a form of artificial intelligence – to identify drugs that help minimize harmful scarring after a heart attack or other injuries.
The new machine-learning tool has already found a promising candidate to help prevent harmful heart scarring in a way distinct from previous drugs. The UVA researchers say their cutting-edge computer model has the potential to predict and explain the effects of drugs for other diseases as well.
“Many common diseases such as heart disease, ...
Large multicenter clinical trial finds that antiseptic containing iodine reduces surgical-site infections in patients with extremity fractures
2024-02-01
A large multicenter clinical trial co-led by University of Maryland School of Medicine researchers large multicenter clinical trial co-led by University of Maryland School of Medicine researchers found that an antiseptic containing iodine resulted in about one-quarter fewer post-surgical infections in patients with limb fractures compared to another frequently used skin antiseptic. The results of the study of nearly 8,500 patients across the United States and Canada were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study – which compared the ...
Jealousy – we understand our own sex best
2024-02-01
We may not always fully understand why our partners get jealous, and women and men often get jealous for completely different reasons.
Two researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) decided to investigate whether people also know about these distinct differences between the sexes.
“What do people think triggers women’s and men’s jealousy? How well do women understand men’s jealousy, and men women’s jealousy? We wanted to find out,” says Professor Mons Bendixen at the Department of Psychology.
Men are more jealous ...
Hiring the most qualified candidate might be unfair
2024-02-01
WASHINGTON — Both liberals and conservatives are more likely to believe that merit-based hiring is unfair after learning about the impacts of socioeconomic disparities, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association.
People from across the political spectrum also are more likely to support programs that encourage socioeconomic diversity after learning about the effects of social class and low income, according to the research, published online in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
“Socioeconomic disadvantages early in life can undermine educational achievement, ...
Excavation of colossal caverns for Fermilab’s DUNE experiment completed
2024-02-01
Excavation workers have finished carving out the future home of the gigantic particle detectors for the international Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment. Located a mile below the surface, the three colossal caverns are at the core of a new research facility that spans an underground area about the size of eight soccer fields.
Hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, DUNE scientists will study the behavior of mysterious particles known as neutrinos to solve some of the biggest questions about our universe. Why is our ...
BIPOC individuals bear greater post-COVID health burdens, new research suggests
2024-02-01
Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) who were infected with COVID-19 experienced greater negative aftereffects in health and work loss than did similarly infected white participants, new research finds.
Despite similar symptom prevalence, BIPOC and Hispanic patients experienced greater negative impacts on their health status, activity levels, and ability to work compared with non-Hispanic and white patients participating in the ongoing multi-site INSPIRE clinical trial examining people with long COVID.
The findings are published in the journal Frontiers ...
National Academy of Medicine member new president of The Obesity Society
2024-02-01
ROCKVILLE, Md. — A member of the National Academy of Medicine is the new president of The Obesity Society (TOS), the organization announced today.
Jamy Ard, MD, FTOS, is professor in the Departments of Epidemiology and Prevention and Internal Medicine and vice dean of Clinical Research at Wake Forest University School of Medicine in Winston-Salem, N.C. He also co-directs the Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Weight Management Center, where he oversees medical weight management programs.
“I am honored to serve as president of ...
How to run a password update campaign efficiently and with minimal IT costs
2024-02-01
Updating passwords for all users of a company or institution’s internal computer systems is stressful and disruptive to both users and IT professionals. Many studies have looked at user struggles and password best practices. But very little research has been done to determine how a password update campaign can be conducted most efficiently and with minimal IT costs. Until now.
A team of computer scientists at the University of California San Diego partnered with the campus’ Information Technology Services to analyze the messaging for a campuswide mandatory ...
Five advances that could change heart health monitoring
2024-02-01
Chocolate valentines and candies with sweet sayings shouldn't be the only hearts you think about this February. It’s also American Heart Month, which puts a spotlight on cardiovascular health. According to the American Heart Association, heart disease is the leading cause of death for Americans, so it’s important to know the status of your own heart health. New methods for cardiac monitoring can be found in these five papers recently published in ACS journals. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
Future ...
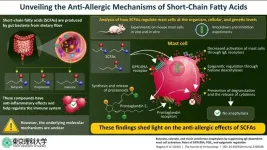
Gut bacteria can process dietary fiber into an anti-allergy weapon, finds new study
2024-02-01
The intricate relationship that exists between humans and the gut microbiome has become a hot research topic, and scientists are constantly uncovering new reasons why a healthy diet can lead to a healthier life. Dietary fibers are a particularly important aspect of this connection. When we ingest these compounds, which are mainly found in plant-based foods, our gut bacteria break them down into small molecules, called short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Over the past few years, studies have revealed various important anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating effects of SCFAs.
One of the ways SCFAs interact with ...