(Press-News.org) Sudden impacts or jolts to the head can cause skull fractures and traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). TBIs can cause bleeding, unconsciousness, and potential changes to the brain leading to memory loss, mood and personality changes and lack of concentration - sometimes many years after the initial injury.
However, very little research has been done to ascertain the extent and mechanism by which turbans might mitigate impacts to the head during cycling incidents.
Now, researchers from Imperial and the Sikh Scientists Network have studied the performance of turban styles worn by male and female Sikhs under the types of impacts common to cycling incidents. The findings allowed them to make evidence-based recommendations so that Sikhs who wear turbans might benefit from the best head protection possible.
The research is published today in Annals of Biomedical Engineering.
Using crash test dummy heads, the researchers tested five different turbans, distinguished by two wrapping styles and two different fabrics with size variations. They then compared their findings of injury risk with conventional cycle helmets and with bare heads.
They found that turbans greatly reduced the risk of skull fractures in areas covered with a thick layer of fabric, compared to bare heads. Also, the style of the turban greatly affected the risk of head injury.
For impacts to the front of the head, the Dastaar turban style with 3 metre long and 2m wide Rubia Voile fabric performed the best, with a 23 per cent reduction in the force applied to the head compared to the worst performing turban style.
For impacts to the side of the head, the Dumalla turban style with 10m long and 1m wide Full Voile fabric performed the best, with a 59 per cent reduction in the force applied to the head compared to the worst performing turban style.
They also found that although the risk of skull fractures and brain injuries was higher with all turbans than conventional bicycle helmets, the risk might be reduced using the following recommendations:
Covering a larger area of the head with a thick layer of fabric.
Placing energy absorbing materials between the layers of the fabric to increase impact duration and reduce force, reducing the risk of skull fractures.
Reducing the friction between the layers of fabric to reduce the rotational force transmitted to the head, thus the risk of brain injuries.
Lead author Dr Mazdak Ghajari, from Imperial’s Dyson School of Design Engineering, said: “From our previous work, we have a good understanding of which types of impacts are common in cyclists and how we should assess the efficacy of head protection equipment in the lab. This project was a great opportunity for us to apply this expertise to empower Sikhs to protect themselves from head injury.”
Co-author Dr Gurpreet Singh, from the Sikh Scientists Network and Imperial’s Department of Materials, said: “Sikhs have earned the right to wear the sacred turban with pride for centuries now. However, being just 0.5% of the world population, very little has been done to scientifically empower Sikhs to continue practicing their faith with advanced, protective materials that are in-line with their religious requirements. Due to a lack of research into advanced fabrics, Sikhs currently face varying degrees of risk.
“Our findings show that simple Sikh turbans have the potential to mitigate head impacts. This provides important evidence that we hope will point the wider scientific community to invest in the best headgear fabrics to absorb shock, which indeed will open commercial markets to people from all walks of life that deal with concussions and head impacts.”
The researchers now plan to use their findings to develop a force-absorbing turban material to offer Sikhs who wear turbans better head protection in situations where helmets might otherwise be worn.
The findings could also be used to benefit Sikhs in other areas where head protection is worn. For example, due to religious tenets, Sikhs who wear turbans are exempt from wearing hard hats and motorcycle helmets in several countries where it is a legal requirement, including the UK, India, some Canadian states, Denmark, New Zealand, Sweden and Thailand.
Ruth Purdie OBE, chief executive of The Road Safety Trust, which funded the research, said: “Cyclists are classed as vulnerable road users, and therefore it is important to think about different ways to improve their safety.
“The findings of this study could really support Sikh cyclists and help reduce their risks of head injury.”
This work was funded by The Road Safety Trust and supported by the Sikh Scientists Network. The research was undertaken with Rehat Maryada – the Code of Sikh Conduct and Conventions – in mind.
END
Turban style and thickness affects head injury risk in Sikh cyclists
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists successfully simulate protein complex that initiates fertilization
2024-02-02
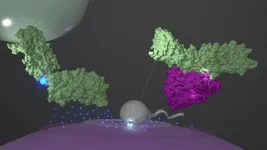
Who hasn't seen it before: the view through the microscope in which a sperm penetrates an egg cell and fertilises it. This fundamental step in procreation happens dynamically and seemingly without problems. However, if you zoom in on the processes that take place during fertilisation at a molecular level, it becomes highly complex and it is thus not surprising that 15 percent of couples worldwide struggle to conceive. No microscope, however modern, can illuminate the countless interactions between the proteins involved. Therefore, the exact trigger for the fertilisation process and the molecular events that transpire just before the fusion of the sperm and egg have ...
Immune cells lose ‘killer instinct’ in cancerous tumors – but functionality can be re-awakened
2024-02-02
Some immune cells in our bodies see their ‘killer instinct’ restricted after entering solid tumours, according to new research.
In a new paper published in Nature Communications, a team led by researchers from the University of Birmingham and the University of Cambridge found how immune cells called natural killer cells (NK cells) rapidly lose their functionality when entering and residing in tumours.
Using tumour cells grown from mice models, the team established that NK cells adopt a dormant state when entering solid tumours through the loss of production of key effector mechanisms used to promote immune ...
Did climate change trigger pandemics in antiquity?
2024-02-02
For their study in Science Advances, the researchers reconstructed temperatures and precipitation for the period from 200 BC to 600 AD, with a resolution of three years. This means that two data points cover a period of three years – an extremely high resolution for paleoclimate researchers. The period extends from the so-called Roman Climatic Optimum to the Late Antique Little Ice Age. This period also includes three major pandemics known from historians’ records: the Antonine Plague (around 165 to 180 AD), the Cyprian Plague (around 251 to 266) and the Justinian ...
Outstanding success in the Excellence Strategy: TU Dresden enters the next round with three new Clusters of Excellence initiatives
2024-02-02
As a result, TUD ranks second overall in the number of calls for proposals in the current competition nationwide. This is according to today’s joint announcement (February 2, 2024) by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the German Science and Humanities Council (WR). An international panel of experts appointed by the DFG and the WR through the Joint Science Conference (GWK) has assessed a total of 143 draft proposals over the last few days and selected 41 as valuable funding opportunities.
In addition, TUD's three existing Clusters of Excellence have expressed their intent to the DFG that they wish to continue their outstanding research work. TUD, therefore, ...
HMSOM researchers: Data shows clinical trials becoming more inclusive
2024-02-02
Clinical trials and medical research have been historically lacking in diversity among all groups.
But recent trends have been turning the tide at least a little bit toward equity and inclusivity, according to a new meta-analysis published by a team of investigators from the Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine (HMSOM) and the Hackensack Meridian Health Research Institute (HMHRI).
The meta-analysis of clinical trials which included New Jersey patients from 2017 to 2022 show a snapshot of more diverse representation - and better reporting of race and ethnicity factors, according to the new paper in the Elsevier ...
CAR T cells show promise against age-related diseases in mice
2024-02-02
Highlights
Laboratory research led by MSK and Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory demonstrates the potential for CAR T cells to improve “healthspan” by eliminating senescent cells associated with aging-related diseases.
Not only was the treatment able to improve the metabolic function of aging mice and mice fed a high-fat diet, but it also proved protective against metabolic decline when given to younger mice.
The CAR T cell-based approach offers a powerful alternative to more traditional small-molecule drugs target senescent cells, supported by its long-lasting effects and the potential to fine-tune ...
Clinique partners with Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai to establish the Mount Sinai-Clinique Healthy Skin Dermatology Center
2024-02-02
New York, NY (February 2, 2024) – Clinique and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai today announced a philanthropic partnership to establish the Mount Sinai-Clinique Healthy Skin Dermatology Center. The Center will develop forward-thinking research in dermatology, exploring the biological underpinnings of how skin ages, skin allergies and inflammatory or eczematous skin conditions, including eczema (or atopic dermatitis) and contact dermatitis. Rooted in a shared mission to conduct dermatological research that improves patients’ lives, the partnership will focus on applicable scientific discovery and leading-edge innovation to modernize allergy science in order to ...
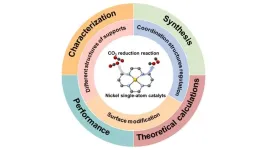
Strategies for enhancing the performance of nickel single-atom catalysts for the electroreduction of CO2 to CO
2024-02-02
Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) is considered as an effective strategy for mitigating the energy crisis and the greenhouse effect. Among the multiple reduction products, CO is regarded as having the highest market value as it is a crucial feedstock for Fischer-Tropsch process which can synthesize high-value long-chain hydrocarbons. Since the carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2RR) has complex intermediates and multiple proton-coupled electron transfer processes, improving the reaction activity and products selectivity remain two great challenges.
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have the advantages of high atom utilization, tunable coordination structure ...
Brexit-induced spatial restrictions reveal alarming increase of fishing fleet’s carbon footprint
2024-02-02
In a study published today in Marine Policy, researchers have unveiled striking evidence that fisheries management decisions such as spatial fisheries restrictions can increase greenhouse gas emissions. The study, conducted by a team of scientists led by postdoctoral researcher Kim Scherrer at the University of Bergen, sheds light on the unforeseen consequences of policy changes on fishing fleets and their carbon footprint.
In the North Atlantic, international agreements often allow fleets to follow the fish across national borders. This allows fishers to catch the fish where it is most efficient. But when the UK left the EU (Brexit), ...
Scammed! Animals ‘led by the nose’ to leave plants alone
2024-02-02
University of Sydney researchers have shown it is possible to shield plants from the hungry maws of herbivorous mammals by fooling them with the smell of a variety they typically avoid.
Findings from the study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution show tree seedlings planted next to the decoy smell solution were 20 times less likely to be eaten by animals.
“This is equivalent to the seedlings being surrounded by actual plants that are unpalatable to the herbivore. In most cases it does trick the animals into leaving the plants alone,” said PhD student Patrick ...