(Press-News.org) Clinical trials and medical research have been historically lacking in diversity among all groups.
But recent trends have been turning the tide at least a little bit toward equity and inclusivity, according to a new meta-analysis published by a team of investigators from the Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine (HMSOM) and the Hackensack Meridian Health Research Institute (HMHRI).
The meta-analysis of clinical trials which included New Jersey patients from 2017 to 2022 show a snapshot of more diverse representation - and better reporting of race and ethnicity factors, according to the new paper in the Elsevier journal Global Epidemiology.
“The past five years have seen an overall uptick in the equity of race/ethnicity reporting and inclusivity of clinical trials, as compared to previously reported data, presaging the potential acquisition of ever more powerful and meaningful results of such intervention studies going forward,” write the authors, including three HMSOM students.
The team used the Clinicaltrials.gov registry to identify nearly 500 clinical trials which took place at least in part in New Jersey.
Of this group of trials, greater than 97 percent reported on race and/or the ethnicity of the enrollees, according to the findings. The participation in the trials assessed collectively still showed a majority 76.7 percent White participants; but the Black participants made up about 14.1 percent of the enrollees, which is slightly higher than the 2020 U.S. Census figure (which was used as a reference standard.)
The proportion of Asian and Hispanic descent, however, was slightly lower than the corresponding Census figures.
Thus, more inclusivity work needs to be done, according to the authors.
“Our 5-year snapshot reveals that a very large percentage of trials report on race/ethnicity - and inclusivity is improving,” the authors conclude. “While there is still some way to go to have the demographic numbers in these trials match U.S. Census values, our results suggest that recent efforts are having an effect.”
END
HMSOM researchers: Data shows clinical trials becoming more inclusive
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CAR T cells show promise against age-related diseases in mice
2024-02-02
Highlights
Laboratory research led by MSK and Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory demonstrates the potential for CAR T cells to improve “healthspan” by eliminating senescent cells associated with aging-related diseases.
Not only was the treatment able to improve the metabolic function of aging mice and mice fed a high-fat diet, but it also proved protective against metabolic decline when given to younger mice.
The CAR T cell-based approach offers a powerful alternative to more traditional small-molecule drugs target senescent cells, supported by its long-lasting effects and the potential to fine-tune ...
Clinique partners with Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai to establish the Mount Sinai-Clinique Healthy Skin Dermatology Center
2024-02-02
New York, NY (February 2, 2024) – Clinique and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai today announced a philanthropic partnership to establish the Mount Sinai-Clinique Healthy Skin Dermatology Center. The Center will develop forward-thinking research in dermatology, exploring the biological underpinnings of how skin ages, skin allergies and inflammatory or eczematous skin conditions, including eczema (or atopic dermatitis) and contact dermatitis. Rooted in a shared mission to conduct dermatological research that improves patients’ lives, the partnership will focus on applicable scientific discovery and leading-edge innovation to modernize allergy science in order to ...
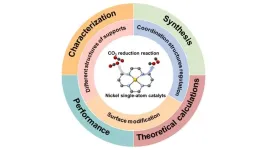
Strategies for enhancing the performance of nickel single-atom catalysts for the electroreduction of CO2 to CO
2024-02-02
Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) is considered as an effective strategy for mitigating the energy crisis and the greenhouse effect. Among the multiple reduction products, CO is regarded as having the highest market value as it is a crucial feedstock for Fischer-Tropsch process which can synthesize high-value long-chain hydrocarbons. Since the carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2RR) has complex intermediates and multiple proton-coupled electron transfer processes, improving the reaction activity and products selectivity remain two great challenges.
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have the advantages of high atom utilization, tunable coordination structure ...
Brexit-induced spatial restrictions reveal alarming increase of fishing fleet’s carbon footprint
2024-02-02
In a study published today in Marine Policy, researchers have unveiled striking evidence that fisheries management decisions such as spatial fisheries restrictions can increase greenhouse gas emissions. The study, conducted by a team of scientists led by postdoctoral researcher Kim Scherrer at the University of Bergen, sheds light on the unforeseen consequences of policy changes on fishing fleets and their carbon footprint.
In the North Atlantic, international agreements often allow fleets to follow the fish across national borders. This allows fishers to catch the fish where it is most efficient. But when the UK left the EU (Brexit), ...
Scammed! Animals ‘led by the nose’ to leave plants alone
2024-02-02
University of Sydney researchers have shown it is possible to shield plants from the hungry maws of herbivorous mammals by fooling them with the smell of a variety they typically avoid.
Findings from the study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution show tree seedlings planted next to the decoy smell solution were 20 times less likely to be eaten by animals.
“This is equivalent to the seedlings being surrounded by actual plants that are unpalatable to the herbivore. In most cases it does trick the animals into leaving the plants alone,” said PhD student Patrick ...
Why are people climate change deniers?
2024-02-02
Do climate change deniers bend the facts to avoid having to modify their environmentally harmful behavior? Researchers from the University of Bonn and the Institute of Labor Economics (IZA) ran an online experiment involving 4,000 US adults, and found no evidence to support this idea. The authors of the study were themselves surprised by the results. Whether they are good or bad news for the fight against global heating remains to be seen. The study is being published in the journal Nature Climate Change. STRICTLY EMBARGOED: Do not publish before Friday, February 02, 11 a.m. CET!
A surprisingly large number of people ...
Epigenetic status determines metastasis
2024-02-02
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and Heidelberg University investigated in mice how spreading tumor cells behave at the site of metastasis: Some tumor cells immediately start to form metastases. Others leave the blood vessel and may then enter a long period of dormancy. What determines which path the cancer cells take is their epigenetic status. This was also confirmed in experiments with human tumor cells. The results of the study could pave the way for novel diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
What makes cancer so dangerous? ...
Prehistoric mobility among Tibetan farmers, herders shaped highland settlement patterns, cultural interaction, study finds
2024-02-02
The 1 million-square-mile Tibetan Plateau — often called the “roof of the world” — is the highest landmass in the world, averaging 14,000 feet in altitude. Despite the extreme environment, humans have been permanent inhabitants there since prehistoric times.
Farming and herding play major roles in the economy of the Tibetan Plateau today — as they have throughout history. To make the most of a difficult environment, farmers, agropastoralists and mobile herders interact and move in conjunction with one another, which in turn shapes ...
World Wetlands Day: Bogs hold an important key to the climate crisis
2024-02-02
World Wetlands Day: Bogs hold an important key to the climate crisis
Peat bogs store twice as much CO2 as all of the world's forests combined. A new research center at the University of Copenhagen will map Earth’s wetlands and provide important knowledge about the greenhouse gas budgets of these areas. The Global Wetland Center will teach us how to contain carbon from plants and trees in bogs and other wetlands – and preserve it as well as the ancient bog bodies also found there.
He is world-renowned ...
Natural therapy shows promise for dry-eye disease
2024-02-02
Researchers at the University of Auckland are running a trial of castor oil as a potential safe and natural treatment for dry-eye disease following a successful pilot study.
While exact figures aren’t available for New Zealand, in Australia, it is estimated dry-eye disease affects around 58 percent of the population aged over 50.
Advancing age, menopause, increased screen time, contact lens wear are just some of the risk factors for developing dry eye disease.
Blepharitis is the most common cause of dry-eye disease, accounting for more than 80 percent of cases. It is a chronic condition with no known cure.
“Currently, patients ...