(Press-News.org) Forty-three million Americans lack access to municipal water, and 1 in 10 people globally do not have access to safe drinking water. Rice University’s new WaTER Institute, launched today, aims to address this and other complex water-related challenges.
“Clean water can save more lives than doctors,” said Pedro J. Alvarez , the institute’s director and the George R. Brown Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering.
The institute’s researchers will also predict and prevent diseases by monitoring wastewater; decrease the amount of energy used to move and treat water in large municipal water systems; predict water-related natural disasters; extract high-value metals with high energy efficiency and low water consumption, and more.
The institute will lead cutting-edge, multidisciplinary research and technological innovation focusing on three key areas: public health, energy transitions and resilient infrastructure. Its full name is the Institute for Clean Water Technologies, Entrepreneurship and Research.
“Rice has strategically increased its investment in research that will positively impact the community, region, nation and world,” said President Reginald DesRoches, “As university president and a civil engineer, I am confident that Rice scientists will make discoveries that transform lives and communities through innovation.”
Researchers will tackle seven major challenges related to water:
Safe water quality for a growing population
Distribution between humans and their environment
Water disaster protection
Water infrastructure (distribution and collection)
Enough food for all
Water to produce energy
Solutions for water conflicts and a fair share for all
“I’m excited to see how the WaTER Institute, drawing from the expertise of institutes and disciplines across campus, develops transformative solutions that economically produce clean water while minimizing energy and chemical requirements,” said Ramamoorthy Ramesh , executive vice president for research. “This institute brings together fundamental science, technological innovations and policy. It also promotes a culture of entrepreneurship around water.”
“The WaTER Institute builds on longstanding partnerships and existing strengths that Rice has in wastewater monitoring, water treatment, nanomaterials development and environmental research,” said Rafael Verduzco , professor and associate chair of chemical and biomolecular engineering and professor of materials science and nanoengineering.
For example, the Houston Health Department, partnering with Rice and Houston Public Works, is a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Wastewater Surveillance System Center of Excellence. The wastewater monitoring effort, led by Lauren Stadler, Rice assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering; Loren Hopkins, chief environmental science officer for the Houston Health Department and a professor in the practice of statistics at Rice and Katherine Ensor, the Noah G. Harding Professor of Statistics, helps predict and prevent pandemics by detecting diseases in sewage. The center, dubbed Houston Wastewater Epidemiology, will provide training on wastewater epidemiology to other state and local health departments as well as research on developing statistical tools and metrics to enhance surveillance interpretation.
Qilin Li , one of the institute leaders, has been leading a collaboration with the city to develop decision-making tools to optimize water supply systems, including wastewater reuse for potable water supply to alleviate shortages. Rice scientists also plan to develop virtual testing to improve resilience, minimize energy requirements and prevent degrading water quality associated with water distribution through large, centralized systems.
“The Rice WaTER Institute will provide a much-needed platform for researchers, practitioners, entrepreneurs and policymakers to work together toward a long-term vision for water management that is supported by sound technological solutions,” said Li, professor of civil and environmental engineering and co-director of the Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment with Alvarez.
The researchers will also protect public health through the technologies they are developing to remove contaminants such as endocrine disruptors and PFAS (perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances) or “forever chemicals” that are breaking through traditional water treatment systems.
“Like other toxic things in our water and environment, PFAS is not going away by itself,” said Mike Wong, a Rice researcher and one of the institute’s leaders. “We need better understanding and better solutions, but we also need better plans on how to get the technology off campus and into the homes, communities and businesses that need help the most. I am excited about all the ways the WaTER Institute can speed up our collective work to create low-cost, no-fuss methods to destroy PFAS.”
Wong is the Tina and Sunit Patel Professor in Molecular Nanotechnology, chair and professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and professor of chemistry, materials science and nanotechnology, and civil and environmental engineering.
The institute will promote entrepreneurship, specifically startups, for water technologies, Alvarez said. Researchers will collaborate with the Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship, the Liu Idea Lab for Innovation and Entrepreneurship and The Ion.
The WaTER Institute’s work will cut across the natural sciences, social sciences, humanities and engineering and connect with Rice’s other research institutes . “Our collaborative structures and culture are a major competitive advantage,” Alvarez said.
This marks the fifth institute Rice has launched over the past year and the eighth to receive additional funding from the university. The other new institutes include the Rice Advanced Materials Institute, Rice Synthetic Biology Institute, Medical Humanities Research Institute and the Rice Sustainability Institute.
END
Potential to ‘save more lives than doctors’: Rice launches WaTER Institute to develop accessible clean water technology
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New guidelines aim to elevate comprehensive care for people with severe epilepsy
2024-02-02
(February 2, 2024) The National Association of Epilepsy Centers (NAEC) has developed updated guidelines that outline the comprehensive services and resources epilepsy centers should provide to improve quality of care for people whose epilepsy is not well-controlled.
An Executive Summary of the 2023 Guidelines for Specialized Epilepsy Centers: Report of the National Association of Epilepsy Centers Guideline Panel was published online on February 2, 2024, in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The complete NAEC guidelines are published as an eAppendix on the journal’s website.
Epilepsy is one of the most ...
Welch Foundation supports Johnson-Winters' TB research
2024-02-02
With a $300,000 grant, the Welch Foundation is supporting University of Texas at Arlington research into why some types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the bacteria that causes the lung disease tuberculosis (TB), do not respond to treatments.
Since its founding in 1954, the Houston-based Welch Foundation has contributed to the advancement of chemistry through research grants, departmental programs, endowed chairs and other special projects in Texas.
“As one of the nation’s largest private funding sources for chemical research, it is our job ...
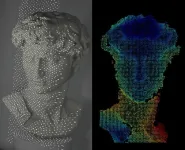
A sleeker facial recognition technology tested on Michelangelo’s David
2024-02-02
Many people are familiar with facial recognition systems that unlock smartphones and game systems or allow access to our bank accounts online. But the current technology can require boxy projectors and lenses. Now, researchers report in ACS’ Nano Letters a sleeker 3D surface imaging system with flatter, simplified optics. In proof-of-concept demonstrations, the new system recognized the face of Michelangelo’s David just as well as an existing smartphone system.
3D surface imaging is a common tool used in smartphone facial recognition, as well as in computer vision and autonomous driving. These systems typically consist of a dot projector that contains multiple components: ...
Plant groupings in drylands support ecosystem resilience
2024-02-02
Many complex systems, from microbial communities to mussel beds to drylands, display striking self-organized clusters. According to theoretical models, these groupings play an important role in how an ecosystem works and its ability to respond to environmental changes. A new paper in PNAS focused on the spatial patterns found in drylands offers important empirical evidence validating the models.
Drylands make up 40 percent of the Earth’s landmass and are places where water is the limiting resource for life. They often display a characteristic ...
Scientists see an ultra-fast movement on surface of HIV virus
2024-02-02
DURHAM, N.C. – As the HIV virus glides up outside a human cell to dock and possibly inject its deadly cargo of genetic code, there’s a spectacularly brief moment in which a tiny piece of its surface snaps open to begin the process of infection.
Seeing that structure snap open and shut in mere millionths of a second is giving Duke Human Vaccine Institute (DHVI) investigators a new handle on the surface of the virus that could lead to broadly neutralizing antibodies for an AIDS vaccine. Their findings appear Feb. 2 in Science Advances.
Being able to attach an antibody specifically to ...
Gene editing precisely repairs immune cells
2024-02-02
Some hereditary genetic defects cause an exaggerated immune response that can be fatal. Using the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool, such defects can be corrected, thus normalizing the immune response, as researchers led by Klaus Rajewsky from the Max Delbrück Center now report in “Science Immunology.”
Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) is a rare disease of the immune system that usually occurs in infants and young children under the age of 18 months. The condition is severe and has a high mortality rate. It is caused by various gene mutations that prevent cytotoxic T cells from functioning normally. These ...
COPD: The effect of low-dose cadmium, a highly toxic metal, on airway epithelial cells
2024-02-02
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Cigarette smoke exposure is associated with the development and severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, which is the third leading cause of death worldwide.
Cigarette smoke contains 2 to 3 micrograms of cadmium, a highly toxic metal and environmental pollutant, per cigarette. Burning tobacco releases cadmium oxide that can be adsorbed onto microparticles in smoke that travel deep into the lungs. Furthermore, the body is not able to remove cadmium, which accumulates in longtime smokers.
In ...
Regulation makes crypto markets more efficient
2024-02-02
First-of-its-kind research on cryptocurrency finds that the most regulated coins create the most efficient markets.
That crypto regulation, often provided by cryptocurrency exchanges like Binance, can also help protect investors by providing reliable, public information.
“Both small and institutional investors should know, if they invest in coins without any regulation, they may suffer from price manipulation or a severe lack of insider information,” said Liangfei Qiu, a University of Florida professor of business and one of the authors of the new study.
“Instead, they may want to invest in coins listed with platforms ...
Centuries-old texts penned by early astronomers Copernicus and Sacrobosco find new home at RIT
2024-02-02
The ancient astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus was the first scientist to document the theory that the sun is the center of the universe in his book, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres). That first edition book, along with a delicate manuscript from astronomer Johannes de Sacrobosco, that is contrary to Copernicus’ groundbreaking theory, has now found a permanent home at Rochester Institute of Technology.
The texts were donated to RIT’s Cary Graphic Arts Collection, one of the world’s premier libraries on graphic communication history and practices. The donor is Irene ...
Mechanism discovered that protects tissue after faulty gene expression
2024-02-02
The genetic material, in the form of DNA, contains the information that is crucial for the correct functioning of every human and animal cell. From this information repository, RNA, an intermediate between DNA and protein, the functional unit of the cell, is generated. During this process, the genetic information must be tailored for specific cell functions. Information that is not needed (introns) is cut out of the RNA and the important components for proteins (exons) are preserved. A team of researchers led by Professor Dr Mirka Uhlirova at the University of Cologne’s CECAD Cluster of ...