(Press-News.org) A major challenge to developing better neural prostheses is sensory encoding: transforming information captured from the environment by sensors into neural signals that can be interpreted by the nervous system. But because the number of electrodes in a prosthesis is limited, this environmental input must be reduced in some way, while still preserving the quality of the data that is transmitted to the brain.
Demetri Psaltis (Optics Lab) and Christophe Moser (Laboratory of Applied Photonics Devices) collaborated with Diego Ghezzi of the Hôpital ophtalmique Jules-Gonin – Fondation Asile des Aveugles (previously Medtronic Chair in Neuroengineering at EPFL) to apply machine learning to the problem of compressing image data with multiple dimensions, such as color, contrast, etc. In their case, the compression goal was downsampling, or reducing the number of pixels of an image to be transmitted via a retinal prosthesis.
“Downsampling for retinal implants is currently done by pixel averaging, which is essentially what graphics software does when you want to reduce a file size. But at the end of the day, this is a mathematical process; there is no learning involved,” Ghezzi explains.
“We found that if we applied a learning-based approach, we got improved results in terms of optimized sensory encoding. But more surprising was that when we used an unconstrained neural network, it learned to mimic aspects of retinal processing on its own.”
Specifically, the researchers’ machine learning approach, called an actor-model framework, was especially good at finding a “sweet spot” for image contrast. Ghezzi uses Photoshop as an example. “If you move the contrast slider too far in one or the other direction, the image becomes harder to see. Our network evolved filters to reproduce some of the characteristics of retinal processing.”
The results have recently been published in Nature Communications.
Validation both in-silico and ex-vivo
In the actor-model framework, two neural networks work in a complementary fashion. The model portion, or forward model, acts as a digital twin of the retina: it is first trained to receive a high-resolution image and output a binary neural code that is as similar as possible to the neural code generated by a biological retina. The actor network is then trained to downsample a high-resolution image that can elicit a neural code from the forward model that is as close as possible to that produced by the biological retina in response to the original image.
Using this framework, the researchers tested downsampled images on both the retina digital twin and on mouse cadaver retinas that had been removed (explanted) and placed in a culture medium. Both experiments revealed that the actor-model approach produced images eliciting a neuronal response more akin to the original image response than an image generated by a learning-free computation approach, such as pixel-averaging.
Despite the methodological and ethical challenges involved in using explanted mouse retinas, Ghezzi says that it was this ex-vivo validation of their model that makes their study a true innovation in the field.
“We cannot only trust the digital, or in-silico, model. This is why we did these experiments – to validate our approach.”
Other sensory horizons
Because the team has past experience working on retinal prostheses, this was their first use of the actor-model framework for sensory encoding. But Ghezzi sees potential to expand the framework’s applications within and beyond the realm of vision restoration. He adds that it will be important to determine how much of the model, which was validated using mice retinas, is applicable to humans.
“The obvious next step is to see how can we compress an image more broadly, beyond pixel reduction, so that the framework can play with multiple visual dimensions at the same time. Another possibility is to transpose this retinal model to outputs from other regions of the brain. It could even potentially be linked to other devices, like auditory or limb prostheses,” Ghezzi says.
END
A machine learning framework that encodes images like a retina
EPFL researchers have developed a machine learning approach to compressing image data with greater accuracy than learning-free computation methods, with applications for retinal implants and other sensory prostheses.
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
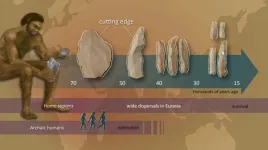
Innovation in stone tool technology involved multiple stages at the time of modern human dispersals
2024-02-07
A study led by researchers at the Nagoya University Museum in Japan may change how we understand the cultural evolution of Homo sapiens at the time of their dispersal across Eurasia about 50,000 to 40,000 years ago. These findings challenge traditional beliefs about the timing and nature of cultural transitions during this critical period in human history.
Published in Nature Communications, the researchers’ insights into stone tool technology suggest that the commonly held view of a ‘revolution’ in culture and technology that allowed anatomically modern humans to outcompete ...
New study sheds new light on forests' role in climate and water cycle
2024-02-07
Forests, which cover a third of Earth's land surface, are pivotal in carbon storage and the water cycle, though the full scope of their impact remains to be fully understood. In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Stockholm University and international colleagues provide new insights into the complex role forests play in the climate system and water cycle.
The research, involving scientists from 11 institutions across five countries, including Sweden, the UK, Finland, Germany, and Brazil, highlights the intricate relationship between forests, particularly their emission ...
Repetitive high concentration capsaicin patch applications for nerve pain in a real-world setting
2024-02-07
Capsaicin, derived from hot chili pepper plants, has been used to treat various types of pain, and a high concentration capsaicin patch (HCCP) is approved for the treatment of nerve (or neuropathic) pain. In a real-world study published in Pain Practice that included 97 outpatients in Germany diagnosed primarily with neuropathic back pain, postoperative/posttraumatic neuropathic pain, or postherpetic neuralgia (shingles pain), patients appeared to benefit from multiple HCCP applications.
Among the ...
Does gender affect food allergy’s impact on quality of life?
2024-02-07
An analysis of relevant published studies indicates that across all ages, food allergy negatively affects individuals’ quality of life to a greater extent in females than in males.
The analysis, which is published in Clinical and Experimental Allergy, included 34 studies. In the studies, women and the parents of girls tended to report a greater impact of food allergy on health-related quality of life than men or parents of boys.
Evidence also showed that improvements in quality of life over the course of treatment for food allergy can be different for males and females, with weak evidence suggesting that male children may experience more improvements ...
Does air pollution contribute to global cardiovascular disease–related deaths?
2024-02-07
A recent analysis of data from nearly all World Health Organization member states clearly demonstrates a link between air pollution and mortality from cardiovascular diseases, with more of such deaths associated with air pollution in low-income countries compared with high-income countries.
In all 183 countries included in the Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine study, ischemic heart disease-related deaths attributed to air pollution were higher than stroke-related deaths caused by air pollution. In 2019, outdoor air pollution caused 16 ischemic heart disease-related deaths per 100,000 people in high-income countries compared with 70 per 100,000 in low-income countries.
Also, in ...
Researchers develop and test the first unmanned forestry machine
2024-02-07
A study published in the Journal of Field Robotics assessed the world’s first unmanned machine designed for autonomous forestry operations. Investigators demonstrated that using computer vision, autonomous navigation, and manipulator control algorithms, their newly developed machine can safely, accurately, and efficiently pick up logs from the ground and maneuver through various forest terrains without the need for human intervention.
The research represents a significant milestone in the field of autonomous outdoor robotics, which could reduce the need for human labor, thereby increasing productivity and reducing labor costs, while ...
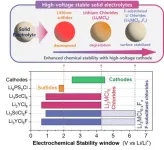
KIST-LLNL raises expectations for commercialization of high-energy-density all-solid-state batteries
2024-02-07
Researchers are actively working on non-flammable solid electrolytes as a safer alternative to liquid electrolytes commonly found in lithium-ion batteries, which are vulnerable to fires and explosions. While sulfide-based solid electrolytes exhibit excellent ionic conductivity, their chemical instability with high-voltage cathode materials necessary for high-energy-density batteries has impeded their commercial viability. Consequently, there has been a growing interest in chloride-based solid electrolytes, which are stability in high-voltage conditions due to their strong bonding ...
Survey finds most don’t know the numbers that help predict heart disease
2024-02-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Keeping track of blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels can help identify risk factors for heart disease. However, a national survey by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center found that while many adults know their childhood address or best friend’s birthday, less than half know their blood pressure or ideal weight, and fewer than 1 in 5 know their cholesterol or blood sugar levels.
“Recognizing heart disease risk factors early and adequately treating ...
Artificial intelligence helps predict whether antidepressants will work in patients
2024-02-07
In patients with major depression disorder it is, thanks to use of artificial intelligence, now possible to predict within a week whether an antidepressant will work. With the help of an AI algorithm, a brain scan and an individual's clinical information, researchers from Amsterdam UMC and Radboudumc could see up to 8 weeks faster whether or not the medication would work. The results of this study are published today in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
"This is important news for patients. Normally, ...
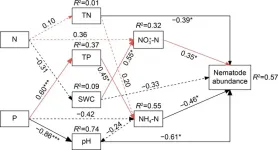
Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil nematode community of soybean farmland
2024-02-07
As a predator of soil microorganisms, nematodes respond rapidly to changes in soil environment, which can reflect climate conditions, ecosystem succession status, nutrient cycling and soil ecosystem health. In agroecosystems, nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers are often applied in large quantities. Therefore, studying the effect of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil nematode communities is helpful to understand how nitrogen and phosphorus addition affects the growth and development of crops in farmland ecosystems. This study demonstrates that the addition of nitrogen and phosphorus significantly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
[Press-News.org] A machine learning framework that encodes images like a retinaEPFL researchers have developed a machine learning approach to compressing image data with greater accuracy than learning-free computation methods, with applications for retinal implants and other sensory prostheses.