(Press-News.org) An eye-catching new study shows just how different the experience of walking home at night is for women versus men.
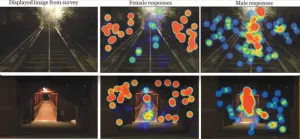
The study, led by Brigham Young University public health professor Robbie Chaney, provides clear visual evidence of the constant environmental scanning women conduct as they walk in the dark, a safety consideration the study shows is unique to their experience.
Chaney and co-authors Alyssa Baer and Ida Tovar showed pictures of campus areas at four Utah universities — Utah Valley University, Westminster, Brigham Young University and University of Utah — to participants and asked them to click on areas in the photos that caught their attention. Women focused significantly more on potential safety hazards — the periphery of the images — while men looked directly at focal points or their intended destination.
“The resulting heat maps represent perhaps what people are thinking or feeling or doing as they are moving through these spaces,” Chaney said. “Before we started the study, we expected to see some differences, but we didn’t expect to see them so contrasting. It’s really visually striking.”
Nearly 600 individuals took part in the study, published recently in the journal Violence and Gender, with 56% of participants being female and 44% being male. Each participant looked at 16 images and were told to imagine themselves walking through those areas. They used a Qualtrics heat map tool to click on the areas of the image that stood out the most to them.
While men tended to focus on the path or a fixed object (like a light, the walking path or a garbage can), the women's visual pattern represented a scanning of the perimeter (bushes, dark areas next to a path).
Chaney, along with Baer and Tovar — both BYU undergrads at the time of the study’s inception — say the findings provide some insight into what it is like to walk home as a woman, which could be multiplied through years or a lifetime of experiences.
“This project has been a fantastic conversation starter to bring awareness to lived experiences, particularly of women in this case,” said Baer, who recently finished graduate school at George Washington University and now works in Washington, D.C. “My hope is that in having concrete data we are able to start conversations that lead to meaningful action.”
Authors said the data suggests that because environment is perceived and experienced differently by women and men, decision makers in building campus and community environments should consider the varied experiences, perceptions and safety of both.
“Why can’t we live in a world where women don’t have to think about these things? It’s heartbreaking to hear of things women close to me have dealt with,” Chaney said. “It would be nice to work towards a world where there is no difference between the heat maps in these sets of images. That is the hope of the public health discipline.”
END
Study visually captures a hard truth: Walking home at night is not the same for women
Heat maps show men look straight ahead; women scan periphery
2024-02-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ice cores provide first documentation of rapid Antarctic ice loss in the past
2024-02-08
Researchers from the University of Cambridge and the British Antarctic Survey have uncovered the first direct evidence that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet shrunk suddenly and dramatically at the end of the Last Ice Age, around eight thousand years ago.
The evidence, contained within an ice core, shows that in one location the ice sheet thinned by 450 metres — that’s more than the height of the Empire State Building — in just under 200 years.
This is the first evidence anywhere in Antarctica for such a fast loss of ice. Scientists are worried that today’s rising temperatures ...
Faulty DNA disposal system causes inflammation
2024-02-08
LA JOLLA (February 8, 2024)—Cells in the human body contain power-generating mitochondria, each with their own mtDNA—a unique set of genetic instructions entirely separate from the cell’s nuclear DNA that mitochondria use to create life-giving energy. When mtDNA remains where it belongs (inside of mitochondria), it sustains both mitochondrial and cellular health—but when it goes where it doesn’t belong, it can initiate an immune response that promotes inflammation.
Now, Salk scientists ...
Breaking through barriers
2024-02-08
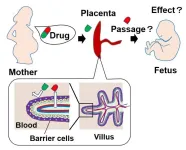
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) overcome scientific roadblocks and develop a model to assess the biology of the human placental barrier
Tokyo, Japan – During pregnancy, the human placenta plays multiple essential roles, including hormone production and nutrient/waste processing. It also serves as a barrier to protect the developing fetus from external toxic substances. However, the placental barrier can still be breached by certain drugs. In a recent article published in Nature Communications, a team led by researchers ...
Patterns of brain connectivity differ between pre-term and term babies
2024-02-08
Under strict embargo until 10.00 GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
A new King’s College London scanning study of 390 babies has shown distinct patterns between term and pre-term babies in the moment-to-moment activity and connectivity of brain networks.
Supported by Wellcome and the National institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre, this is the first study to analyse how the communication between brain areas changes moment-to-moment in the first few weeks of life.
Published in Nature Communications, the study also found that these dynamic ...
Social science: White actors featured more than non-white actors on American film posters
2024-02-08
White actors are featured more frequently and more prominently on posters for American-produced films than non-white actors despite recent increases in the representation of actors from other ethnic groups, according to a study published in Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.
Galit Fuhrmann Alpert and colleagues investigated trends in the ethnic diversity of actors featured on over 45,000 posters advertising over 24,000 English-speaking films produced in the USA between 1960 and 2021. Actors were assigned to one of four ethnic groups; white, Black, Indian, or Asian using an algorithm trained on the FairFace image dataset, which contains equal numbers ...
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
2024-02-08
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 01:00hrs GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals and cells
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute have found a new treatment target for CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), one of the most common types of genetic epilepsy.
CDD causes seizures and impaired development in children, and medications are limited to managing symptoms rather than tackling the root cause of the disease. The disorder involves losing the function of a gene producing the CDKL5 enzyme, which ...
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies
2024-02-08
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies are presented in the peer-reviewed Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (JICM). Biofield therapies (BFTs), such as External Qigong, Healing Touch, Reiki, and Therapeutic Touch, are a related group of integrative medicine interventions in which practitioners use their hands on or above a client’s body to stimulate healing and well-being. Click here to read the article now.
The guidelines call for including details of the intervention protocols relevant to biofield therapy trials. The Reporting Evidence Guidelines comprises ...
Wayne State University awarded $1.4 million from Department of Defense to expand on research findings surrounding prostate cancer
2024-02-08
DETROIT– A team of researchers from Wayne State University was awarded a $1.4 million, three-year grant from the U.S. Department of Defense for the study, “Cytochrome c acetylation drives prostate cancer aggressiveness and Warburg effect.”
The study, led by Maik Hüttemann, Ph.D., professor of molecular medicine and genetics, and biochemistry, microbiology and immunology at Wayne State University’s School of Medicine, aims to establish the role of the protein cytochrome c, which the team proposes is ...
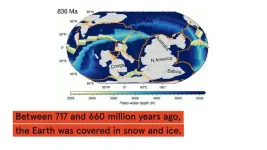
What turned Earth into a giant snowball 700m years ago? Scientists now have an answer
2024-02-08
Australian geologists have used plate tectonic modelling to determine what most likely caused an extreme ice-age climate in Earth’s history, more than 700 million years ago.
The study, published in Geology, helps our understanding of the functioning of the Earth's built-in thermostat that prevents the Earth from getting stuck in overheating mode. It also shows how sensitive global climate is to atmospheric carbon concentration.
“Imagine the Earth almost completely frozen over,” said the study’s lead author, ARC Future Fellow ...
Researchers estimate survival chances during CPR for cardiac arrest
2024-02-08
A person’s chance of surviving while receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for cardiac arrest in hospital declines rapidly from 22% after one minute to less than 1% after 39 minutes, finds a US study published by The BMJ today.
Similarly, the likelihood of leaving hospital with no major brain damage declines from 15% after one minute of CPR to less than 1% after 32 minutes with no heartbeat.
The researchers say the findings provide insights that may help guide hospital teams, patients and their families in deciding how long to continue resuscitation.
In-hospital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Study visually captures a hard truth: Walking home at night is not the same for womenHeat maps show men look straight ahead; women scan periphery