(Press-News.org) (BOSTON: Thursday, February 8, 2024) – Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) will award up to US$1.8 million to biotechnology company, Visby Medical, to develop a portable rapid polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnostic to detect the presence of the pathogen that causes gonorrhea, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG), and its susceptibility to ciprofloxacin, a former frontline oral antibiotic that can no longer treat resistant NG. A rapid result on when ciprofloxacin may be effective could enable physicians to treat gonorrhea patients with confidence, while reserving ceftriaxone, the only antibiotic that remains effective against resistant NG.
Visby Medical is a leading innovator in rapid and accurate PCR testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) as well as COVID and the flu. The CARB-X award will help the company drive the next phase of development to meet the urgent challenges facing today's healthcare system.
In addition to the development of a rapid test for NG and susceptibility to ciprofloxacin, funding will support development of a test for NG as well as Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Trichomonas vaginalis (TV) in men based on urine samples. Currently, Visby Medical provides healthcare professionals with a second generation Sexual Health Test for the three most common STIs in women; the test is 510(k) cleared and has received a CLIA waiver from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Additional CARB-X funding will be awarded in separate phases covering feasibility testing and development of both the antimicrobial resistance and male STI testing uses. Funding will be triggered by the completion of specific project goals. Visby Medical intends to supplement the CARB-X award with additional funding sources.
Gonorrhea is the second most reported bacterial STI. Approximately 82 million people were infected globally in 2020. Patients with gonorrhea can face serious health effects, including pelvic inflammatory disease, chronic pelvic pain, and infertility. If left untreated, gonorrhea can spread to the bloodstream, which can be life threatening, and increase the risk of HIV infection. Since patients do not always exhibit symptoms, reported cases may only capture a fraction of the true burden.
“Following a year-long funding call for diagnostics that aim to identify gonorrhea and determine its susceptibility to antibiotics, Visby Medical joins SpeeDx, making two diagnostic developers in the CARB-X portfolio that focus on this infection,” said Erin Duffy, PhD, R&D Chief of CARB-X. “Our goal is to deliver diagnostics that are effective at all levels of the healthcare system. Given the portability of the envisioned Visby Medical PCR platform, which fits in the palm of your hand, we see this as rapidly and highly deployable in low-resourced and hard-to-reach settings. Additionally, for regions where ciprofloxacin remains a viable treatment, the Visby Medical diagnostic gives confidence that the physician is making the correct treatment decision.”
“The sexually transmitted infections epidemic continues to increase. That is why healthcare providers in ERs, urgent care clinics, community health centers and physicians’ offices need accurate and rapid diagnostic tests to enable same-visit, data-driven treatment based on a test result that identifies the pathogen and its antibiotic susceptibility," said Gary Schoolnik, MD, Chief Medical Officer of Visby Medical. “The CARB-X award will allow Visby Medical to enhance the only instrument-free PCR platform by adding the capacity to detect ciprofloxacin-resistant gonorrhea immediately and at the point-of-care. This has the potential to redefine best practice for patient care, infection control, and antibiotic stewardship.”
An estimated 1.27 million people died due to drug-resistant bacterial infections in 2019, a death toll that exceeded HIV/AIDS (864,000) and malaria (643,000) in that same year. CARB-X is building a pipeline of high-value products to prevent, diagnose and treat bacterial infections, including those that have become resistant to antibiotics. CARB-X emphasizes performance characteristics that will allow the broadest use of these products against infections driving the greatest global morbidity and mortality.
When CARB-X was founded in 2016, the early-stage antibiotic pipeline was stalled. Since then, CARB-X has supported 95 R&D projects in 13 countries, and CARB-X product developers have made tremendous progress: 18 projects have advanced into or completed clinical trials; 12 remain active in clinical development, including late-stage clinical trials; and two diagnostic products have reached the market. Additionally, at least 9 product developers with active R&D projects have already secured advanced development partnerships which can help support their clinical development after leaving the CARB-X portfolio.
In 2022, CARB-X launched new funding rounds to support R&D projects and fill critical gaps in the antibacterial pipeline. These include oral therapeutics to replace the workhorse antibiotics that are failing; vaccines for neonatal sepsis, which kills 2.5 million infants annually; and oral therapeutics, vaccines and rapid diagnostics for gonorrhea. Visby Medical’s diagnostic is the first diagnostic and fourth project to receive a CARB-X award as part of the 2022-2023 funding call. Additional projects are under review, and new product developers will be announced this year. Register for the CARB-X newsletter to learn more about upcoming funding calls that will be announced this year.
CARB-X funding for this research is supported by federal funds from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS); Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response; Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority; under agreement number 75A50122C00028, and by awards from Wellcome (WT224842), Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), the UK Department of Health and Social Care as part of the Global Antimicrobial Resistance Innovation Fund (GAMRIF), the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and the Novo Nordisk Foundation. The U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in HHS, provides support in the form of in-kind services through access to a suite of preclinical services for product development. The content of this press release is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of any CARB-X funders.
CARB-X Contact: Genevieve Holmes, carbxpr@bu.edu
Visby Medical Contact: Harry Wade, harry.wade@visby.com
About CARB-X
CARB-X (Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator) is a global non-profit partnership dedicated to supporting early-stage antibacterial research and development to address the rising threat of drug-resistant bacteria. CARB-X supports innovative therapeutics, preventatives and rapid diagnostics. CARB-X is led by Boston University and funded by a consortium of governments and foundations. CARB-X funds only projects that target drug-resistant bacteria highlighted on the CDC’s Antibiotic Resistant Threats list, or the Priority Bacterial Pathogens list published by the WHO, with a priority on those pathogens deemed Serious or Urgent on the CDC list or Critical or High on the WHO list. https://carb-x.org/ | X (formerly Twitter) @CARB_X
About Visby Medical
Visby Medical is transforming the order of diagnosis and treatment for infectious diseases so clinicians can test, talk with, and treat the patient in a single visit. The company developed a proprietary technology platform that is the world’s first instrument-free, single-use PCR platform that fits in the palm of your hand and rapidly tests for serious infections.
The Visby Medical Sexual Health Test for women is the first step in a robust pipeline that is accelerating the delivery of fast and accurate, palm-sized PCR diagnostics to the point of care, and eventually for use at home. https://www.visbymedical.com/ | LinkedIn
About BARDA and NIAID
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services works to enhance and protect the health and well-being of all Americans, providing for effective health and human services and fostering advances in medicine, public health, and social services. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) leads the nation’s medical and public health preparedness for, response to and recovery from disaster and other public health emergencies. Within ASPR,the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) invests in innovation, advanced research and development, acquisition, and manufacturing of medical countermeasures – vaccines, drugs, therapeutics, diagnostic tools, and non-pharmaceutical products – needed to combat health security threats and is one of the leading public sector funders of advanced development of antimicrobial therapeutics and diagnostics.
As part of HHS, NIH is the primary U.S. federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. NIAID conducts and supports research — at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide — to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About Wellcome
Wellcome supports science to solve the urgent health challenges facing everyone. We support discovery research into life, health and wellbeing, and we’re taking on three worldwide health challenges: mental health, infectious disease and climate and health.
About the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF)
Education and research are crucial foundations for our future. Thus, the promotion of education, science and research is a policy priority of the German Federal Government. The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) strengthens education at all stages of life and provides support for scientific research and innovation.
About the Global AMR Innovation Fund (GAMRIF)
The Global AMR Innovation Fund (GAMRIF) is a One Health UK aid fund that supports research and development around the world to reduce the threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in humans, animals and the environment for the benefit of people in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). GAMRIF core objectives are to develop innovative One Health solutions to tackle AMR; increase availability of context-specific, accessible, and affordable innovations for LMICs; establish international research partnerships with industry, academia, and governments; and collaborate with and leverage additional funding from other global donors.
About the Public Health Agency of Canada
The Public Health Agency of Canada is an agency of the Government of Canada that is responsible for public health, emergency preparedness and response, and infectious and chronic disease control and prevention. Created in 2004 with a mission to promote and protect the health of Canadians through leadership, partnership, innovation and action in public health, the Agency’s activities focus on preventing disease and injuries, responding to public health threats, promoting good physical and mental health, and providing information to support informed decision making. The Agency has a long history of working with domestic and international partners on combatting health threats, including AMR. Most recently, the Agency released the Pan-Canadian Action Plan on AMR, a multijurisdictional effort that emphasizes One Health collaboration to make progress on AMR.
About the Novo Nordisk Foundation
Established in Denmark in 1924, the Novo Nordisk Foundation is an enterprise foundation with philanthropic objectives. The vision of the Foundation is to improve people’s health and the sustainability of society and the planet. The Foundation’s mission is to progress research and innovation in the prevention and treatment of cardiometabolic and infectious diseases as well as to advance knowledge and solutions to support a green transformation of society.
www.novonordiskfonden.dk/en
About Boston University
Founded in 1839, Boston University is an internationally recognized institution of higher education and research. With nearly 37,000 students, it is the third-largest independent university in the United States. BU consists of 17 schools and colleges and the interdisciplinary Faculty of Computing & Data Sciences, along with a number of multi-disciplinary centers and institutes integral to the University’s research and teaching mission. In 2012, BU joined the Association of American Universities (AAU), a consortium of 65 leading research universities in the United States and Canada. For further information, please contact Kim Miragliuolo at kmira@bu.edu. www.bu.edu
END
CARB-X funds Visby Medical to develop a portable rapid diagnostic for gonorrhea including antibiotic susceptibility
Visby Medical aims to improve patients’ health outcomes and increase the lifespan of the last remaining antibiotic for resistant gonorrhea
2024-02-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fusion research facility JET’s final tritium experiments yield new energy record
2024-02-08
GARCHING and OXFORD (8 February 2024) –
The Joint European Torus (JET), one of the world’s largest and most powerful fusion machines, has demonstrated the ability to reliably generate fusion energy, whilst simultaneously setting a world-record in energy output.
These notable accomplishments represent a significant milestone in the field of fusion science and engineering.
In JET's final deuterium-tritium experiments (DTE3), high fusion power was consistently produced for 5 seconds, resulting in a ground-breaking record of 69 megajoules using a mere 0.2 milligrams of fuel.
JET is a tokamak, a design which uses powerful ...
A new “metal swap” method for creating lateral heterostructures of 2D materials
2024-02-08
Electronically conducting two-dimensional (2D) materials are currently hot topics of research in both physics and chemistry owing to their unique properties that have the potential to open up new avenues in science and technology. Moreover, the combination of different 2D materials, called heterostructures, expands the diversity of their electrical, photochemical, and magnetic properties. This can lead to innovative electronic devices not achievable with a single material alone.
Heterostructures can be fabricated in two ways: vertically, with materials ...
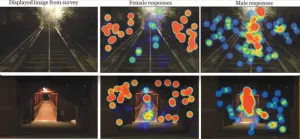
Study visually captures a hard truth: Walking home at night is not the same for women
2024-02-08
An eye-catching new study shows just how different the experience of walking home at night is for women versus men.
The study, led by Brigham Young University public health professor Robbie Chaney, provides clear visual evidence of the constant environmental scanning women conduct as they walk in the dark, a safety consideration the study shows is unique to their experience.
Chaney and co-authors Alyssa Baer and Ida Tovar showed pictures of campus areas at four Utah universities — Utah Valley University, ...
Ice cores provide first documentation of rapid Antarctic ice loss in the past
2024-02-08
Researchers from the University of Cambridge and the British Antarctic Survey have uncovered the first direct evidence that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet shrunk suddenly and dramatically at the end of the Last Ice Age, around eight thousand years ago.
The evidence, contained within an ice core, shows that in one location the ice sheet thinned by 450 metres — that’s more than the height of the Empire State Building — in just under 200 years.
This is the first evidence anywhere in Antarctica for such a fast loss of ice. Scientists are worried that today’s rising temperatures ...
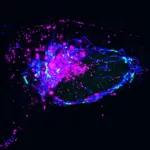
Faulty DNA disposal system causes inflammation
2024-02-08
LA JOLLA (February 8, 2024)—Cells in the human body contain power-generating mitochondria, each with their own mtDNA—a unique set of genetic instructions entirely separate from the cell’s nuclear DNA that mitochondria use to create life-giving energy. When mtDNA remains where it belongs (inside of mitochondria), it sustains both mitochondrial and cellular health—but when it goes where it doesn’t belong, it can initiate an immune response that promotes inflammation.
Now, Salk scientists ...
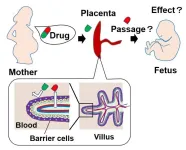
Breaking through barriers
2024-02-08
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) overcome scientific roadblocks and develop a model to assess the biology of the human placental barrier
Tokyo, Japan – During pregnancy, the human placenta plays multiple essential roles, including hormone production and nutrient/waste processing. It also serves as a barrier to protect the developing fetus from external toxic substances. However, the placental barrier can still be breached by certain drugs. In a recent article published in Nature Communications, a team led by researchers ...
Patterns of brain connectivity differ between pre-term and term babies
2024-02-08
Under strict embargo until 10.00 GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
A new King’s College London scanning study of 390 babies has shown distinct patterns between term and pre-term babies in the moment-to-moment activity and connectivity of brain networks.
Supported by Wellcome and the National institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre, this is the first study to analyse how the communication between brain areas changes moment-to-moment in the first few weeks of life.
Published in Nature Communications, the study also found that these dynamic ...
Social science: White actors featured more than non-white actors on American film posters
2024-02-08
White actors are featured more frequently and more prominently on posters for American-produced films than non-white actors despite recent increases in the representation of actors from other ethnic groups, according to a study published in Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.
Galit Fuhrmann Alpert and colleagues investigated trends in the ethnic diversity of actors featured on over 45,000 posters advertising over 24,000 English-speaking films produced in the USA between 1960 and 2021. Actors were assigned to one of four ethnic groups; white, Black, Indian, or Asian using an algorithm trained on the FairFace image dataset, which contains equal numbers ...
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
2024-02-08
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 01:00hrs GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals and cells
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute have found a new treatment target for CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), one of the most common types of genetic epilepsy.
CDD causes seizures and impaired development in children, and medications are limited to managing symptoms rather than tackling the root cause of the disease. The disorder involves losing the function of a gene producing the CDKL5 enzyme, which ...
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies
2024-02-08
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies are presented in the peer-reviewed Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (JICM). Biofield therapies (BFTs), such as External Qigong, Healing Touch, Reiki, and Therapeutic Touch, are a related group of integrative medicine interventions in which practitioners use their hands on or above a client’s body to stimulate healing and well-being. Click here to read the article now.
The guidelines call for including details of the intervention protocols relevant to biofield therapy trials. The Reporting Evidence Guidelines comprises ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] CARB-X funds Visby Medical to develop a portable rapid diagnostic for gonorrhea including antibiotic susceptibilityVisby Medical aims to improve patients’ health outcomes and increase the lifespan of the last remaining antibiotic for resistant gonorrhea