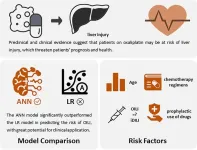
Predictive model of oxaliplatin-induced liver injury based on artificial neural network and logistic regression
2024-02-08
(Press-News.org)
Since 2004, several clinical studies have reported that patients with OXA frequently experienced adverse effects of liver injury (LI), typically characterized by hepatic sinusoidal injury, splenomegaly, decreased platelet count and noncirrhotic portal hypertension, which can progress to nodular regenerative hyperplasia with long-term treatment. LI also decreased hepatic functional reserve and aggravated the postoperative course of colorectal cancer patients after hepatectomy, and may affect intraoperative bleeding, postoperative morbidity, and overall survival. LI can further progress to liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis, both of which would be detrimental to the patients’ health. The risk of OXA-induced LI (OILI) can be greatly reduced if people potentially at high risk of OILI can be identified and then treated and prevented accordingly in advance.
Although there is a preliminary understanding of the clinical features and disease characteristics, studies on OILI's prediction or risk factors are rare. There is a lack of exploration in terms of patient and medication characteristics, and there is also a lack of clinical prediction tools for OILI. Based on a previous safety evaluation of OXA, OILI was explored in depth. Artificial Neural Network(Ann) and logistic regression (LR) models were selected to predict the risk of OILI, and the performance of the two models was evaluated and compared, in the expectation of identifying patients at high risk of OILI, achieving timely intervention and appropriate management, and improving the safety of OXA administration.
The medical information of patients treated with oxaliplatin between May and November 2016 at 10 hospitals was collected prospectively. We used the updated Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method (RUCAM) to identify cases of OILI and summarized the patient and medication characteristics. Furthermore, the ANN and LR models for predicting the risk of OILI were developed and evaluated.
The incidence of OILI was 3.65%. The median RUCAM score with interquartile range was 6 (4, 9). The ANN model performed similarly to the LR model in sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. In discrimination, the area under the curve of the ANN model was larger (0.920>0.833, p=0.019). In calibration, the ANN model was slightly improved. The important predictors of both models overlapped partially, including age, chemotherapy regimens and cycles, single and total dose of OXA, glucocorticoid drugs, and antihistamine drugs.
When discriminative and calibration abilities were given priority, the ANN model significantly outperformed the traditional LR model in predicting the risk of OILI. It. has great potential for clinical application. A comprehensive analysis found that age, chemotherapy regimens, prophylactic use of glucocorticoids, and prophylactic use of antihistamines were associated with the risk of OILI. Other chemotherapy drugs in OXA-based chemotherapy regimens may have different degrees of impact on OILI and deserve further attention. We suspect that OILI may be an iDILI, and chemotherapy dose factors may be weakly correlated. Decision making on prophylactic medications needs to be carefully considered, and the actual preventive effect also needs to be supported by more evidence. Based on the ANN model and potential risk factors, early screening of high-risk groups can be carried out. Medical decision making can be optimized. Timely intervention and nursing can be realized. The ultimate goal is to reduce the adverse effects of OILI and promote drug safety in cancer patients.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-08
Natural scientist and author Robert Rothman takes readers on a reptillian tour of the Galápagos Islands in his new book, A Paradise for Reptiles: Lizards, Snakes, and Giant Tortoises of the Galápagos Islands Vol. 1: Tortoises, Geckos, and Snakes, published by RIT Press.
For more than 30 years, Rothman has led hundreds of Rochester Institute of Technology students on tours to the Galápagos Islands to observe the wildlife and landscape that inspired Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. Rothman’s A Paradise for Reptiles, an homage to the 19th century scientist, is an accessibly written guide for anyone interested in Darwin, the Galápagos, ...
2024-02-08
Language use in social media can be a useful tool for social scientists, because it reflects living conditions in areas the posts originate from.
“There is a correlation between social inequalities and language patterns in social media,” says Associate Professor Lucas M. Bietti at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Psychology.
Researchers studied 30 million X/Twitter posts from the United States. They compared the language used in the tweets to the living conditions in the counties from which the ...
2024-02-08
For some leukemia patients, the only potential chemotherapy option is a drug that also carries a high risk of heart failure. This means that some patients who recover from their cancer will end up dying of heart disease brought on by the cure.
In a new study, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago and other universities have identified mechanisms that cause the drug, ponatinib, to harm the heart. They also identified a promising treatment that could reverse this process. The paper, with senior author Sang Ging Ong, assistant professor of pharmacology and medicine at UIC, is published in Circulation Research. The study is part of a growing field called cardio-oncology ...
2024-02-08
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a tiny worm species that infects and kills insects. These worms, called nematodes, could control crop pests in warm, humid places where other beneficial nematodes are currently unable to thrive.
This new species is a member of a family of nematodes called Steinernema that have long been used in agriculture to control insect parasites without pesticides. Steinernema are not harmful to humans or other mammals and were first discovered in the 1920s.
“We spray trillions of them on crops every year, and they’re ...
2024-02-08
In a study that signals potential reproductive and health complications in humans, now and for future generations, researchers from McGill University, the University of Pretoria, Université Laval, Aarhus University, and the University of Copenhagen, have concluded that fathers exposed to environmental toxins, notably DDT, may produce sperm with health consequences for their children.
The decade-long research project examined the impact of DDT on the sperm epigenome of South African Vhavenda and Greenlandic ...
2024-02-08
UPTON, NY—Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have demonstrated a new way to boost the oil content of plant leaves and seeds. As described in the journal New Phytologist, the scientists identified and successfully altered key portions of a protein that protects newly synthesized oil droplets. The genetic alterations essentially protect the oil-protector protein so more oil can accumulate.
“Implementing this strategy in bioenergy or oil crop plants could ...
2024-02-08
Québec, February 8, 2024 - Contrary to popular belief, the benefits of physical activity do not outweigh the risks of cardiovascular disease associated with drinking sugar-sweetened beverages, according to a new study led by Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health. Jean-Philippe Drouin-Chartier, professor at Université Laval’s Faculty of Pharmacy, was a co-author.
Sugar-sweetened beverages are the largest source of added sugars in the North American diet. Their consumption is associated with ...
2024-02-08
(BOSTON: Thursday, February 8, 2024) – Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) will award up to US$1.8 million to biotechnology company, Visby Medical, to develop a portable rapid polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnostic to detect the presence of the pathogen that causes gonorrhea, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG), and its susceptibility to ciprofloxacin, a former frontline oral antibiotic that can no longer treat resistant NG. A rapid result on when ciprofloxacin may be effective could enable physicians to treat gonorrhea patients with confidence, while reserving ceftriaxone, the only antibiotic that remains effective against resistant NG.
Visby ...
2024-02-08
GARCHING and OXFORD (8 February 2024) –
The Joint European Torus (JET), one of the world’s largest and most powerful fusion machines, has demonstrated the ability to reliably generate fusion energy, whilst simultaneously setting a world-record in energy output.
These notable accomplishments represent a significant milestone in the field of fusion science and engineering.
In JET's final deuterium-tritium experiments (DTE3), high fusion power was consistently produced for 5 seconds, resulting in a ground-breaking record of 69 megajoules using a mere 0.2 milligrams of fuel.
JET is a tokamak, a design which uses powerful ...
2024-02-08
Electronically conducting two-dimensional (2D) materials are currently hot topics of research in both physics and chemistry owing to their unique properties that have the potential to open up new avenues in science and technology. Moreover, the combination of different 2D materials, called heterostructures, expands the diversity of their electrical, photochemical, and magnetic properties. This can lead to innovative electronic devices not achievable with a single material alone.
Heterostructures can be fabricated in two ways: vertically, with materials ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Predictive model of oxaliplatin-induced liver injury based on artificial neural network and logistic regression