(Press-News.org) UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 8AM EST ON FEB. 13, 2024
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have created a new version of a microbe to compete economically with E. coli – a bacteria commonly used as a research tool due to its ability to synthesize proteins – to conduct low-cost and scalable synthetic biological experiments.
As an inexpensive multiplier – much like having a photocopier in a test tube – the bacteria Vibrio natriegens could help labs test protein variants for creation of pharmaceuticals, synthetic fuels and sustainable compounds that battle weeds or pests. The microbe can work effectively without costly incubators, shakers or deep freezers and can be engineered within hours.
The research publishes Feb. 13 in PNAS Nexus.
“It’s really easy to produce,” said lead author David Specht, a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Buz Barstow, assistant professor of biological and environmental engineering.
To study proteins for creating medical cures or fashioning fuels, researchers use a plasmid (a small piece of DNA) that acts as the instruction manual to make the molecular machine – a protein – of interest. Currently, when researchers place a plasmid into E. coli, they can create many copies to test several variants.
E. coli cells help molecular biologists multiply and manipulate plasmids for protein engineering, but the process is expensive since they often purchase the bacteria from manufacturers, must keep it cold and maintain rooms of expensive equipment to sustain it. A modified E. coli, used for this purpose, is also very fragile.
“As scientists, we don’t often know precisely what those regulatory or molecular sequences should be to achieve our goals,” said Barstow. “So, we must test a lot of variants, and Vibrio natriegens allows researchers to scale up that process of testing.”
The microbe V. natriegens is not complicated, Specht said. “It’s so simple to make that someone with limited resources – like high school labs, home inventors or startup biological businesses – can do it,” he said.
Researcher Timothy Sheppard compared the simplicity of V. natriegens in conducting synthetic and molecular experiments to using a simple writing instrument hundreds of years old: “We’ve found nature’s pencil for cloning and conducting synthetic biology,” he said.
The process is inexpensive with V. natriegens, as it requires no capital equipment purchases and it can work at room temperature. The cells produced from V. natriegens grow quickly: According to the paper, a transformation started at 9 a.m. yields visible colonies by 5 p.m., each filled with masses of proteins.
“The microbe is a radically simple solution to a hard problem,” Barstow said.
Funding for this research came from the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (U.S. Department of Energy); a Cornell 2030 Project Fast Grant; and a gift from Mary Fernando Conrad ’83 and Tony Conrad.
-30-
END
Low-cost microbe can speed biological discovery
2024-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Determining who gets blamed when cars hit pedestrians
2024-02-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study examines the circumstances behind who is found at fault when cars hit pedestrians in an urban area.
Results showed that the environment where the crash took place – especially the types of roads and the amount of access to marked crosswalks – played a key role in whether the pedestrian or the driver was blamed for the collision.
In the study, done in Columbus, pedestrians were more likely to be blamed when they were crossing roads with a high volume of cars traveling at faster speeds, and where crosswalks were few and far between.
In areas of the city – such as downtown – ...
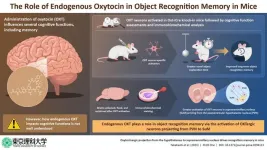
Oxytocin: the love hormone that holds the key to better memory
2024-02-13
Oxytocin (OXT) is a hormone that is known for its effects on psychological well-being and emotional bonding in animals. Interestingly, research has shown that this natural chemical in the brain plays a crucial role in other cognitive processes as well, including learning and memory. Now, scientists may have discovered exactly how OXT influences memory in animals by studying “OXT neurons” that contain OXT receptors and function differently based on the availability of the chemical in the brain.
In a recent study published on 16 November 2023, in PLOS One, a group ...
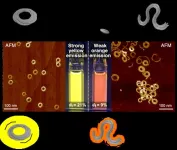
Exploring the effect of ring closing on fluorescence of supramolecular polymers
2024-02-13
In supramolecular chemistry, the self-assembly state of molecules plays a significant role in determining their tangible properties. Controlling the self-assembled state has garnered significant attention as it can be exploited to design materials with desired properties like charge transport capability and fluorescence wavelength. For years, scientists have been trying to decipher how molecular organization impacts the properties of supramolecular assemblies that are in the nano (<10 nm) and mesoscopic (10–1000 nm) scales. However, the study of structures with supramolecular polymer assemblies derived from the same monomer is often hindered by dynamic structural ...
Frequent marine heatwaves in the Arctic Ocean will be the norm
2024-02-13
Marine heatwaves will become a regular occurrence in the Arctic in the near future and are a product of higher anthropogenic greenhouse-gas emissions – as shown in a study just released by Dr. Armineh Barkhordarian from Universität Hamburg’s Cluster of Excellence for climate research CLICCS.
Since 2007, conditions in the Arctic have shifted, as confirmed by data recently published in the journal Nature Communications Earth & Environment. Between 2007 and 2021, the marginal zones ...
Greenland’s ice sheet is melting - and being replaced by vegetation
2024-02-13
University of Leeds Press Release
Under embargo until 10:00 GMT on 13 February
There are graphics and photographic images that help explain this story – see under Note to editors
Greenland’s ice sheet is melting - and being replaced by vegetation
An estimated 11,000 sq miles or 28,707 sq kilometres of Greenland’s ice sheet and glaciers have melted over the last three decades, according to a major analysis of historic satellite records.
The total area of ice loss is equivalent to the size of Albania, and represents about 1.6 % of Greenland’s ...
New Durham University research opens avenues for more efficient and stable blue OLED displays
2024-02-13
-With pictures-
A new research from scientists at Durham University reveals an unexpected pathway towards brighter, more efficient, and more stable blue organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
The findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics could help enable the next generation of energy-saving display technologies.
OLED displays, used in most modern smartphones and TVs, rely on light emission from specialised organic molecules.
Obtaining stable, efficient blue emission suitable for displays remains a key challenge.
Now, Durham ...
Study finds childhood bullying linked to distrust and mental health problems in adolescence
2024-02-13
A new study, co-led by UCLA Health and the University of Glasgow, found that young teenagers who develop a strong distrust of other people as a result of childhood bullying are substantially more likely to have significant mental health problems as they enter adulthood compared to those who do not develop interpersonal trust issues.
The study, published in the journal Nature Mental Health on Feb. 13, is believed to be the first to examine the link between peer bullying, interpersonal distrust, and the subsequent development of mental health problems, such as anxiety, depression, hyperactivity and anger.
Researchers ...
Compounds released by bleaching reefs promote bacteria, potentially stressing coral further
2024-02-13
On healthy reefs around the world, corals, algae, fishes and microbes live interconnected and in balance—exchanging nutrients, resources, and chemical signals. New research led by the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa and and the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) revealed that when coral bleaching occurs, corals release unique organic compounds into the surrounding water that not only promote bacterial growth overall, but select for opportunistic bacteria that may further stress reefs.
“Our results demonstrate how the impacts of both short-term thermal ...
Short corrective comments can help social media user to spot false information, study shows
2024-02-13
Short and simple comments from ordinary social media users can help others online to spot fake news, a new study shows.
Research shows reading corrections from others online can reduce the perceived accuracy of and engagement with incorrect content.
Experts found the format and strength of corrective comments do not matter much. Social media users do not need to write long and detailed comments to flag false content.
While the study shows the general effectiveness of social correction, it also finds ...
Biomarker-directed combination effective in immunotherapy-resistant lung cancer
2024-02-13
HOUSTON ― A specific combination of targeted therapy and immunotherapy may better help patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) overcome inherent immune resistance and reinvigorate anti-tumor activity, according to a new study led by a researcher from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase II umbrella HUDSON study, published today in Nature Medicine, demonstrated that the anti PD-L1 antibody, durvalumab, coupled with the ATR inhibitor, ceralasertib, provided the greatest clinical benefit of four combinations evaluated.
This pair had an objective response ...