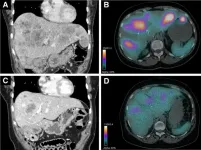
(Press-News.org) Reston, VA—Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is effective for clinical control of symptomatic metastatic insulinomas, according to new research published in the February issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In the largest study to date of metastatic insulinoma patients treated with PRRT, more than 80 percent of patients had long-lasting symptom control, and nearly 60 percent were able to reduce the use of other drugs to treat the disease.
Metastatic insulinoma is a rare malignant neuroendocrine tumor characterized by inappropriate insulin secretion. This results in life-threatening hypoglycemia, which is often difficult to treat. The severity of symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening hypoglycemic events, leading to coma and death. Most insulinomas are benign, but approximately six percent -develop metastases and are therefore considered malignant.
“Because of the rarity of the disease, the treatment strategies for malignant metastatic disease are ill-defined,” stated Damian Wild, MD, PhD, nuclear medicine physician at University Hospital Basel, in Basel, Switzerland. “There is currently limited data available about the efficacy of PRRT in patients with malignant insulinomas. Our research aimed to evaluate whether PRRT could improve symptoms and if it had an impact on medication needed to control hypoglycemia.”
The retrospective study included 26 patients with malignant insulinomas who were treated with a total of 106 cycles of 90Y-DOTATOC or 177Lu-DOTATOC. A scoring system was used to quantify the severity and frequency of hypoglycemic episodes, and the score before and after PRRT was analyzed. Information on medication needed to control hypoglycemia before and after PRRT was also collected, an overall and progression-free survival was recorded.
PRRT was effective in controlling hypoglycemia in 81 percent of the study population and enabled 58 percent of patients to reduce the use of other drugs to control hypoglycemic episodes, resulting in reduced potential drug side effects. Overall and progression-free survival were 19.7 and 11.7 months, respectively.
“Compared to the effectiveness of other drugs commonly used to control hypoglycemia, the results of PRRT are promising and will likely have an impact on guidelines for the treatment of metastatic insulinoma,” noted Wild. “They also imply that PRRT is indicated at an earlier time point, for example as a first or second line of therapy, for the treatment of metastatic insulinomas.”
This study was made available online in December 2023.
The authors of “Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy Is Effective for Clinical Control of Symptomatic Metastatic Insulinoma: A Long-Term Retrospective Analysis” include Liene Friebe, Martin Braun, and Andreas Baumann, Clinic of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland; Martin T. Freitag, Clinic of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland, ENETS Center of Excellence for Neuroendocrine and Endocrine Tumors, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland, and Clinic of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany; Guillaume Nicolas and Damian Wild, Clinic of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland and ENETS Center of Excellence for Neuroendocrine and Endocrine Tumors, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland; David Bushnell, Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City, Iowa; and Emanuel Christ, ENETS Center of Excellence for Neuroendocrine and Endocrine Tumors, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland and Department of Endocrinology, Diabetology, and Metabolism, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland.
Visit the JNM website for the latest research, and follow our new Twitter and Facebook pages @JournalofNucMed or follow us on LinkedIn.
###
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center for more information about molecular imaging and precision imaging. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Rebecca Maxey at (703) 652-6772 or rmaxey@snmmi.org.
About JNM and the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) is the world’s leading nuclear medicine, molecular imaging and theranostics journal, accessed more than 16 million times each year by practitioners around the globe, providing them with the information they need to advance this rapidly expanding field. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.snmjournals.org.
JNM is published by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging—precision medicine that allows diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes. For more information, visit www.snmmi.org.
END
The American College of Cardiology’s newest registry offers data-driven insights on cardiac procedures performed in the ambulatory surgery setting through its first-of-its-kind dashboard. The number of cardiac procedures being performed in ambulatory surgery centers has grown significantly in the last decade, leading ACC’s NCDR to create the CV ASC Registry Suite to fit into the established workflow and allow these facilities to measure and compare their patient care and outcomes to similar procedures performed in the hospital outpatient setting.
Ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) are health care facilities that provide same-day surgical care, ...
Timothy Frawley has spent the better of the past two decades working in and around commercial fisheries. Born and raised in Casco Bay, Maine, he grew up packing lobsters and pitching bait on Portland’s working waterfront. He has worked in commercial fisheries in California, Alaska and the Mexican state of Baja California Sur.
Throughout his years spent on working waterfronts, Frawley, a postdoctoral researcher affiliated with the University of Maine’s Darling Marine Center, closely observed the ways in which fishermen conducted their business, making decisions about what and how they fished, and how it affected their operations and profit.
“While ...
Heart failure remains the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. During a heart attack blood stops flowing into the heart. Without oxygen, part of the heart muscle dies. The heart muscle does not regenerate, instead it replaces dead tissue with a scar made of cells called fibroblasts that do not help the heart pump. If there is too much scarring, the heart progressively enlarges, or dilates, weakens and eventually stops working.
“The current thought is that advanced or chronic heart failure, a stage in which the cardiac muscle has become too weak, is a point of no return. The present ...
As the world gradually transitions to making meaningful reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, one of the most crucial questions that needs to be answered is how much that change is going to cost.
The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has put out reports on this potential cost that showed global greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by at least half in 2030 at a cost of less than $100 per ton of CO2 equivalent. A new study from the University of Delaware, Yale University and Columbia University, however, points out that these estimates do not consider some hidden, underlying frictions ...
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL: Feb. 13, 2024, 3:00 PM EST
Media Contacts: Karen Addis, APR, karen@addispr.com, +1 (301) 787-2394; Kerri Wade, MPA, kwade@smfm.org, +1 (202) 236-1780
National Harbor, Md. -- Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is one of the most common developmental disorders and is increasingly diagnosed worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated one in 100 children has autism. In the U.S., those numbers are much higher, with an estimated one in 36 children being diagnosed with autism, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Research into the causes of autism, specifically whether there is ...
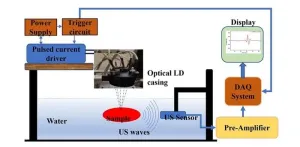
In the realm of biomedical sciences, the quest for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools is ever-evolving. One such promising innovation making waves is the photoacoustic (PA) technique. In the past decade, PA imaging has emerged as a viable imaging modality demonstrated in many clinical applications with promising outcomes. Unlike traditional methods, PA offers a noninvasive approach to probing biological tissues, yet the technique has still been limited in wide clinical applications, partially due to bulky and expensive laser sources.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology Indore ...
Receiving a heart transplant is a matter of life and death for many patients. Every time a heart becomes available, a “match run” is created to generate a list of transplant candidates ranked by an algorithm based on medical urgency, geography and pediatric status. Unfortunately, deceased donor organs are very scarce in the United States – so much so that some patients aren’t even placed on waitlists because it’s too unlikely that a heart will become available to them.
A research team led by experts at the University of Chicago Medicine developed a new risk score designed to predict the likelihood that ...
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. – A new study led by researchers at the Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine sheds light on the intricate interplay of brain regions involved in nicotine's effects on the human brain.
The research, published in eNeuro, an open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Society for Neuroscience, explores how nicotine influences key areas associated with reward and aversion, showcasing a nuanced relationship that varies based on dosage, sex and distinct brain regions. The medial ...
Philadelphia, February 13, 2024 – Identification of specific gene fusions is critical for the successful targeted treatment of pediatric cancer patients. Researchers at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles have developed a novel assay that automatically integrates the data from multiple fusion identification tools (callers) and efficiently and accurately identifies clinically relevant gene fusions in pediatric tumors. Their results are reported in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by ...
CLEVELAND -- A recent study from researchers at University Hospitals (UH) Connor Whole Health and UH Rainbow Babies & Children’s Hospital describes a quality improvement project where pain screening procedures were embedded within an outpatient pediatric sickle cell disease (SCD) clinic. The study examined (1) the feasibility of routine pain screening, (2) the prevalence of various clinical pain presentations, and (3) what integrative health and medicine modalities were preferred by youth aged 8 to 18 with SCD.
The study, entitled “Pain Screening in Youth with Sickle Cell Disease: A Quality Improvement ...