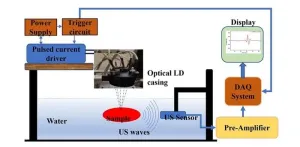
(Press-News.org) In the realm of biomedical sciences, the quest for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools is ever-evolving. One such promising innovation making waves is the photoacoustic (PA) technique. In the past decade, PA imaging has emerged as a viable imaging modality demonstrated in many clinical applications with promising outcomes. Unlike traditional methods, PA offers a noninvasive approach to probing biological tissues, yet the technique has still been limited in wide clinical applications, partially due to bulky and expensive laser sources.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology Indore unveiled a groundbreaking advancement—a compact and cost-effective PA sensing instrument designed specifically for biomedical tissue diagnosis. This proof-of-concept study employs low-cost diode laser. It represents a crucial step towards bridging the gap between laboratory research and clinical applications.
PA for breast tissue diagnosis
Focusing on the intricate landscape of breast tissue, the study delved into the complexities of fibrocystic changes—a condition often overshadowed by the looming specter of breast cancer. Fibrocystic changes can manifest as breast pain and palpable cystic masses, posing a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Moreover, these changes are frequently encountered in the peritumoral breast parenchyma, further complicating the diagnostic landscape.
Current diagnostic modalities, such as ultrasound and mammography, though commonly employed, often fall short in providing the accuracy and insight needed for precise diagnosis. Fine needle aspiration cytology, while a staple in diagnostic procedures, is hindered by sampling issues, necessitating further invasive procedures like core needle biopsies or surgical interventions.
Enter the PA technique—a beacon of hope in the realm of diagnostic uncertainty. This innovative approach harnesses the power of laser diodes to probe biological tissues, generating acoustic waves that unveil valuable insights into tissue composition and density. By analyzing the frequency spectra of the PA signals, researchers were able to discern distinct patterns between normal and diseased breast tissues.
Compact and cost-effective PA sensing
The newly developed instrument integrates multiple laser diodes within a compact casing, alongside a custom-built pulsed current supply unit. This setup ensures efficient PA excitation, generating precise 25 nanosecond pulses at a frequency of 20 kHz. Subsequent data analysis involved calculating frequency spectra to quantitatively assess tissue properties.
The results revealed distinct spectral patterns corresponding to different tissue types. For instance, fibrocystic breast disease exhibited a dominant frequency peak around 1.60 MHz, indicative of increased tissue density due to heightened glandular and stromal elements. In contrast, normal breast tissue showcased a lower peak frequency of 0.26 MHz, reflecting its fibrofatty composition.
Furthermore, histopathological examination validated these findings, affirming the correlation between spectral responses and tissue characteristics. Notably, the experimental setup successfully differentiated various tissue types based on quantitative spectral parameters like peak frequency, mean frequency, and spectral energy.
Promise for clinical practice
Crucially, the study underscores the potential of PA technology—not only to enhance diagnostic accuracy but also to streamline the sampling process for pathological breast tissues. With its ability to provide rapid and detailed tissue characterization, the compact PA sensing instrument holds promise for revolutionizing clinical practice.
In essence, this study represents a significant stride towards empowering clinicians with a fast, reliable, and cost-effective tool for diagnosing breast disease. By enabling cost-effective and rapid tissue diagnosis, the compact PA sensing instrument could potentially revolutionize biomedical practices, offering timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by S. Khan et al., "Development of a cost-effective compact diode-laser-based photoacoustic sensing instrument for breast tissue diagnosis," J. Biomed. Opt. 29(1) 017002 (2024) doi 10.1117/1.JBO.29.1.017002.
END
Advancing biomedical diagnostics: Compact photoacoustic sensing instrument for breast tissue characterization
A compact, cost-effective photoacoustic sensing instrument promises to enhance clinical diagnostics with greater speed and accuracy, for improved patient care and outcomes
2024-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Updating allocation algorithms could help donor hearts reach the transplant patients who need them most
2024-02-13
Receiving a heart transplant is a matter of life and death for many patients. Every time a heart becomes available, a “match run” is created to generate a list of transplant candidates ranked by an algorithm based on medical urgency, geography and pediatric status. Unfortunately, deceased donor organs are very scarce in the United States – so much so that some patients aren’t even placed on waitlists because it’s too unlikely that a heart will become available to them.
A research team led by experts at the University of Chicago Medicine developed a new risk score designed to predict the likelihood that ...
New study reveals dynamic impact of nicotine on brain regions responsible for reward and aversion
2024-02-13
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. – A new study led by researchers at the Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine sheds light on the intricate interplay of brain regions involved in nicotine's effects on the human brain.
The research, published in eNeuro, an open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Society for Neuroscience, explores how nicotine influences key areas associated with reward and aversion, showcasing a nuanced relationship that varies based on dosage, sex and distinct brain regions. The medial ...
New assay identifies clinically relevant gene fusions in pediatric tumors more accurately and efficiently
2024-02-13
Philadelphia, February 13, 2024 – Identification of specific gene fusions is critical for the successful targeted treatment of pediatric cancer patients. Researchers at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles have developed a novel assay that automatically integrates the data from multiple fusion identification tools (callers) and efficiently and accurately identifies clinically relevant gene fusions in pediatric tumors. Their results are reported in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by ...
Pediatric sickle cell disease team uses pain screening to improve care
2024-02-13
CLEVELAND -- A recent study from researchers at University Hospitals (UH) Connor Whole Health and UH Rainbow Babies & Children’s Hospital describes a quality improvement project where pain screening procedures were embedded within an outpatient pediatric sickle cell disease (SCD) clinic. The study examined (1) the feasibility of routine pain screening, (2) the prevalence of various clinical pain presentations, and (3) what integrative health and medicine modalities were preferred by youth aged 8 to 18 with SCD.
The study, entitled “Pain Screening in Youth with Sickle Cell Disease: A Quality Improvement ...
Grantees selected for The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research and the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation Aging and Cancer Initiative
2024-02-13
New York, NY – February 13, 2024 – The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research and the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation (SWCRF) have selected six investigators to receive three grants for their collaborative, two-year program aimed at improving our understanding of the links between aging and cancer. With additional support from the Melanoma Research Alliance (MRA), $1.5 million will fund three innovative projects, each pairing one lab focused on aging with another working on cancer research.
Aging is a major risk factor for developing and dying of cancer. In fact, 90 percent of cancer diagnoses and deaths occur in people ...
Benefits of heat pumps detailed in new NREL report
2024-02-13
Millions of U.S. households would benefit from heat pumps, but the cost of installing the technology needs to come down to make their use a more attractive proposition, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
The findings, detailed in the journal Joule, quantify the costs and benefits of air-source heat pumps across the United States and consider various climates, heating sources, and types of homes. The researchers based their conclusions on simulations of 550,000 statistically ...
School Of Public Health team receives funding for mobile app to prevent dementia In Asian Americans
2024-02-13
By Ann Kellett, Texas A&M University School of Public Health
A research team led by Junhyoung “Paul” Kim, Ph.D., an associate professor of health behavior in the School of Public Health at Texas A&M University, has been awarded a two-year grant from a Korean foundation to design mobile technology to help older Chinese American and Korean American adults in the United States prevent dementia.
The project is in line with the National Institute on Aging’s priority on increasing participation by Asian Americans in dementia care. This cohort is the nation’s ...
Road features that predict crash sites identified in new machine-learning model
2024-02-13
AMHERST, Mass. – Issues such as abrupt changes in speed limits and incomplete lane markings are among the most influential factors that can predict road crashes, finds new research by University of Massachusetts Amherst engineers. The study then used machine learning to predict which roads may be the most dangerous based on these features.
Published in the journal Transportation Research Record, the study was a collaboration between UMass Amherst civil and environmental engineers Jimi Oke, assistant ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine-led study shows rapid COVID-19 tests done at home are reliable
2024-02-13
In a study involving nearly 1,000 patients seen at the Baltimore Convention Center Field Hospital (BCCFH) during a five-month period in 2022 — researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine, the University of Maryland School of Medicine and five other collaborators report that a rapid antigen test (RAT) for detecting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can be used at home with accuracy comparable to the same test being administered by a health care professional.
The study was first posted online Feb. 13, 2024, in the American Society ...
Researchers learn how nectar-laden honey bees avoid overheating
2024-02-13
Honey bees carrying nectar have the remarkable ability to adjust their flight behavior to avoid overheating when air temperatures increase, according to research led by a University of Wyoming scientist.
Jordan Glass, a postdoctoral research associate in UW’s Department of Zoology and Physiology, conducted the study to determine how high air temperatures may limit the ability of honey bees to forage for nectar. His research findings appear in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, one of the world’s most prestigious multidisciplinary scientific journals covering the biological, physical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Advancing biomedical diagnostics: Compact photoacoustic sensing instrument for breast tissue characterizationA compact, cost-effective photoacoustic sensing instrument promises to enhance clinical diagnostics with greater speed and accuracy, for improved patient care and outcomes