COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy protects infants for six months
2024-02-14
(Press-News.org) WHAT:
Women who receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination or booster during pregnancy can provide their infants with strong protection against symptomatic COVID-19 infection for at least six months after birth, according to a study from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. These findings, published in Pediatrics, reinforce the importance of receiving both a COVID-19 vaccine and booster during pregnancy to ensure that infants are born with robust protection that lasts until they are old enough to be vaccinated.
COVID-19 is especially dangerous for newborns and young infants, and even healthy infants are vulnerable to COVID-19 and are at risk for severe disease. No COVID-19 vaccines currently are available for infants under six months old. Earlier results from the Multisite Observational Maternal and Infant COVID-19 Vaccine (MOMI-Vax) study revealed that when pregnant volunteers received both doses of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, antibodies induced by the vaccine could be found in their newborns’ cord blood. This suggested that the infants likely had some protection against COVID-19 when they were still too young to receive a vaccine. However, researchers at the NIAID-funded Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium (IDCRC), which conducted the study, did not know how long these antibody levels would last or how well the infants would actually be protected. The research team hoped to gather this information by following the infants through their first six months of life.
In this portion of the study, researchers analyzed data from 475 infants born while their pregnant mothers were enrolled in the MOMI-Vax study. The study took place at nine sites across the United States. It included 271 infants whose mothers had received two doses of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy. The remaining 204 infants in the study were born to mothers who had received both doses of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine as well as a COVID-19 booster. To supplement data gathered during pregnancy and at birth, the infants were evaluated during at least one follow-up visit during their first six months after birth. Parents also reported whether their infants had become infected or had demonstrated COVID-19 symptoms.
Based on blood samples from the infants, the researchers found that newborns with high antibody levels at birth also had greater protection from COVID-19 infection during their first six months. While infants of mothers who received two COVID-19 vaccine doses had a robust antibody response at birth, infants whose mothers had received an additional booster dose during pregnancy had both higher levels of antibodies at birth and greater protection from COVID-19 infection at their follow-up visits.
While older children and adults should continue to follow guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to stay up-to-date on their COVID-19 vaccines and boosters, this study highlights how much maternal vaccination can benefit newborns too young to take advantage of the vaccine: During the course of this study, none of the infants examined required hospitalization for COVID-19. Researchers will continue to evaluate the data from the MOMI-Vax study for further insights concerning COVID-19 protection in infants.
ARTICLE:
CV Cardemil et al. Maternal COVID-19 Vaccination and Prevention of Symptomatic Infection in Infants. Pediatrics DOI: 10.1542/peds.2023-064252 (2024).
WHO:
Cristina Cardemil, M.D., a medical officer in NIAID’s Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, is available to comment.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Elizabeth Deatrick, (301) 402-1663, NIAIDNews@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-14
Skywalker gibbon couples wake up each morning and sing to each other, their voices echoing across the forest canopy of their home. The primate’s endearing love song helped scientists confirm what was formerly a strong hunch: Myanmar has the largest population of endangered Skywalker gibbons on Earth.
When Star Wars-loving scientists identified Skywalker gibbons as a distinct species in 2017, fewer than 200 individuals were known to exist, all in southwestern China. A study published today in the International Journal of Primatology is the first in the past century to confirm living Skywalker gibbons in ...
2024-02-14
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 14, 2024 – It was a last-ditch effort. For years doctors had tried to keep a patient’s recurrent drug-resistant bacterial blood infection at bay, but it kept coming back and antibiotics were no longer working.
The family agreed to try an experimental treatment that uses viruses to kill bacteria. The patient’s Enterococcus faecium bacterial strain, which had become zombie-like and was almost impossible to treat with currently available antibiotics, was tested against wastewater collected from across the country to find a virus – called a bacteriophage – that scientists theorized would specifically target the drug-resistant bacteria.
It worked ...
2024-02-14
ETRI’s researchers have developed an AI-powered e-sports analysis platform that provides real-time win rate prediction services by analyzing gameplay screens. This platform was notably applied to the highly popular League of Legends (LoL) during a recent international e-sports tournament, garnering positive feedback.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) has developed a technology that recognizes real-time game situations by analyzing play elements extracted from game videos and automatically generates highlights by identifying key play events in the game.
Also, this e-sports service platform, based ...
2024-02-14
Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) and the University of California, Davis have reached a new breakthrough in pancreatic cancer research—eight years in the making. It could help slow the disease’s deadly spread.
In 2017, as a postdoc in CSHL’s Tuveson lab, Chang-il Hwang and collaborators from the Vakoc lab uncovered a protein essential for jumpstarting metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Now an assistant professor at UC Davis, Hwang recently reunited with CSHL Professors David Tuveson and Christopher Vakoc. The trio once again set their sights on PDAC. The disease is known for its aggressiveness. ...
2024-02-14
While pesticides protect crops from hungry animals, pesky insects, or even microbial infections, they also impact other vital organisms, including bees and earthworms. And today, research published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters reveals that worms are affected by the relatively small amounts of chemicals that can leach out of pesticide-treated seeds. Exposure to nonlethal amounts of these insecticides and fungicides resulted in poor weight gain and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage in the worms.
Pesticide treatment can be introduced at several different ...
2024-02-14
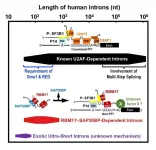
In humans, the length of pre-mRNA varies extensively (from 30 to 1,160,411 nucleotides by recent studies). The fundamental mechanism of splicing has been studied with model pre-mRNAs including 158- and 231-nt introns, for historical instance, that are spliced very efficiently in vitro and in vivo. Such an ideal pre-mRNA contains good splicing signal sequences, i.e., the 5′ splice site, the branch-site (BS) sequence, and the polypyrimidine tract (PPT) followed by the 3′ splice site that are recognized by U1 snRNP, U2 snRNP and U2AF2–U2AF1, respectively. Prof. Mayeda says, “Given the diverse lengths ...
2024-02-14
Corals searching for food in the cold and dark waters of the deep sea are building higher and higher mountains to get closer to the source of their food. But in doing so, they may find themselves trapped when the climate changes. That is shown in the thesis that theoretical ecologist Anna van der Kaaden of NIOZ in Yerseke and the Copernicus Institute for Sustainable Development in Utrecht will defend on Feb. 20 at the University of Groningen. “When the water gets warmer, these creatures prefer to be deeper, but a coral doesn’t just walk down the mountain,” Van der Kaaden said.
Deep and dark
Unlike the famous, colorful tropical corals, cold-water corals live ...
2024-02-14
Surgeons who routinely change surgical gloves and instruments are incurring similar costs to those using the same equipment, a new study has found.
The economic evaluation funded by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) follows a clinical trial conducted at 80 hospitals in Benin, Ghana, India, Mexico, Nigeria, Rwanda, and South Africa which established that routine change of gloves and instruments reduces surgical site infections (SSIs) by 13%.
The evaluation, published by the Lancet Global ...
2024-02-14
Scientists have long thought of the fluid-filled sac around our lungs merely as a cushion from external damage. Turns out, it also houses potent virus-eating cells that rush into the lungs during flu infections.
Not to be confused with phages, which are viruses that infect bacteria, these cells are macrophages, immune cells produced in the body.
“The name macrophage means ‘big eater.’ They gobble up bacteria, viruses, cancer cells, and dying cells. Really, anything that looks foreign, they take it up and destroy it,” said UC Riverside virologist Juliet Morrison, who led the discovery team. “We were surprised to find them in the lungs ...
2024-02-14
USC, together with Leonard and his late wife Pamela Schaeffer, is launching a new institute with a $59 million gift from the Schaeffers to be anchored in Los Angeles and in the university’s new Capital Campus in Washington, D.C. The mission of the Leonard D. Schaeffer Institute for Public Policy & Government Service is to strengthen democracy by training generations of public leaders and advancing evidence-based research to shape policy that addresses the nation’s most pressing issues, USC President Carol Folt announced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy protects infants for six months