(Press-News.org) Nearly 150 years ago, scientists discovered that specialized blood cells serve a vital role in immune system protection against infection and illness.
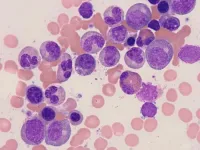
Certain groups of these white blood cells, now known as neutrophils, feature a nucleus that is structured strikingly different than most nuclei. The majority of cells feature round- or oval-shaped nuclei that are rigid, but neutrophils differ in that their nuclei adopt multiple lobular structures akin to that of flower petal arrangements.
These unique nuclear shapes permit neutrophils to travel all over the body to identify and combat invading pathogens. While much is now known about the role of neutrophils in combatting infection, how such peculiar nuclear structures are assembled has remained enigmatic since the 1880s.
Reporting in Nature, University of California San Diego School of Biological Sciences Postdoctoral Scholar Indumathi Patta and Professor Cornelis Murre, in collaboration with Dr. Ming Hu at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, have deciphered the shapeshifting puzzle of the neutrophil nucleus.
“We now know how these nuclear shapes are assembled and it’s a beautiful process,” said Murre, a distinguished professor in the Department of Molecular Biology.
Using a combination of ancient staining procedures combined with advanced techniques, named chromosome-conformation-capture studies, the researchers unveiled how flower-like nuclei are assembled. While chromosomes of rounded cells fold into stacked bundles of DNA loops, neutrophil genomes lack such loops. Remarkably, when the researchers removed chromatin loops, progenitor cells swiftly converted round nuclear shapes into flower petal arrangements like those found in neutrophils. This simple conversion also sufficed to activate thousands of genes associated with an inflammatory gene program that allows neutrophils to combat invading bacteria.
After unveiling the neutrophil loop assembly question, the researchers now believe they have the instructions to guide the development of new nuclear shapes.
“This potentially opens an exciting new chapter in immune therapeutics since theoretically it should be possible to change the nuclear structure of killer immune cells so that they can more easily invade complex, solid environments, such as tumors,” said Murre. “Essentially, this could lead to engineering novel nuclear shapes in effector immune cells, which is a new concept in therapeutics development.”
The authors of the study include: Indumathi Patta, Maryam Zand, Lindsay Lee, Shreya Mishra, Alexandra Bortnick, Hanbin Lu, Arpita Prusty, Sara McArdle, Zbigniew Mikulski, Huan-You Wang, Christine Cheng, Kathleen Fisch, Ming Hu and Cornelis Murre.
END
Researchers uncover mechanisms behind enigmatic shapes of nuclei
Scientists may be able to direct immune cells toward diseased areas
2024-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Online images may be turning back the clock on gender bias
2024-02-14
A picture is worth a thousand words, as the saying goes, and research has shown that the human brain does indeed better retain information from images than from text. These days, we are taking in more visual content than ever as we peruse picture-packed news sites and social media platforms.
And much of that visual content, according to new Berkeley Haas research published in the journal Nature, is reinforcing powerful gender stereotypes.
Through a series of experiments, observations, and the help of large language models, professors Douglas Guilbeault and Solène Delecourt found that female and male gender associations are more extreme among Google Images than within text ...
Smoking has long-term effects on the immune system
2024-02-14
Like other factors such as age, sex and genetics, smoking has a major impact on immune responses. This is the finding recently made by a team of scientists at the Institut Pasteur using the Milieu Intérieur cohort of 1,000 healthy volunteers, established to understand variability in immune responses. In addition to its short-term impact on immunity, smoking also has long-term consequences. For many years after they have quit the habit, smokers are left with effects on some of their bodies' defense mechanisms acquired while smoking. These findings, which for the first time reveal a long-term memory of the effects of smoking ...
Male fertility gene discovery reveals path to success for sperm
2024-02-14
Discovery of a pair of genes that work in perfect harmony to protect male fertility, could provide new insights into some unexplained cases of the most severe form of infertility, research suggests.
Genetic analysis of cases of male infertility revealed that rare mutations in a gene, known as SPOCD1, disrupts the formation of healthy sperm during the earliest stages of their development.
The gene was also found to work in partnership with a previously unknown gene, C19orf84, to protect the early-stage precursors to sperm, known as germ cells, from damage.
The discovery of the essential role of these ...
Genome sequencing unveils mutational impacts of radiation on mammalian cells
2024-02-14
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer ...
WashU awarded up to $20 million to create portable device to scan for eye diseases
2024-02-14
In the United States, more than one-fourth of adults over age 40 have an eye disease, including glaucoma, cataracts or age-related macular degeneration, or a chronic health condition that affects the eyes, such as diabetic retinopathy. These conditions are a strain on an individual’s health as well as on the health-care system, yet early diagnosis and management can help to prevent more than 90% of severe vision loss.
Chao Zhou, a professor of biomedical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has been working to improve optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems that can conduct high-resolution imaging of the ...
New understanding of avian eggshell attachment – implications for medical procedures and egg industry
2024-02-14
Athletes often suffer injuries to ligaments in their knees, particularly to the anterior cruciate ligament or ACL. While surgery to replace these torn ligaments is becoming increasingly common around the world it often needs to be repeated. That’s because it has proved challenging to anchor fibrous, soft and wet ligament grafting material into hard bone.
Now, McGill University researchers have new information from the eggshell membrane in chicken eggs that could help change this picture thanks to the potential it offers for improvements in tissue engineering ...
HHMI opens National Competition for Freeman Hrabowski Scholars Program
2024-02-14
Today, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) opened a national competition to select up to 30 early career faculty in science to join the 2025 cohort of the Freeman Hrabowski Scholars Program.
Freeman Hrabowski Scholars are outstanding basic researchers, including physician-scientists, who have strong potential to become leaders in their fields. Scholars are committed to advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion through their mentoring efforts and understanding of systemic exclusion and marginalization in science of trainees from different backgrounds. While pursuing excellence in their own research, Scholars work to create an inclusive lab climate ...
Study: New treatment method helps reduce suicide among military and veterans
2024-02-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is common among U.S. military veterans. It’s also linked with higher risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
A study led by researchers with The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine found that crisis response planning (CRP) can help. This brief intervention quickly reduced suicidal thoughts among patients receiving daily therapy for two weeks for PTSD. This type of therapy is called “cognitive processing therapy,” or CPT.
“This study shows that crisis response planning can rapidly reduce suicide risk. It is the first study to prove this technique works when ...
The CRISPR Journal announces the publication of its February 2024 issue
2024-02-14
The CRISPR Journal announces the publication of its February 2024 issue. The CRISPR Journal is devoted to publishing outstanding research in CRISPR biology, technology, and genome editing. Chief Editor is Professor Rodolphe Barrangou, PhD (North Carolina State University); Executive Editor is Dr. Kevin Davies. For full-text copies of articles or to arrange interviews with the editors, authors, or members of the editorial board, contact Kathryn Ryan at the Publisher.
1. Warrior spirit: An interview with sickle cell pioneer Victoria Gray,
The gene editing world and the sickle cell disease (SCD) ...
COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy protects infants for six months
2024-02-14
WHAT:
Women who receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination or booster during pregnancy can provide their infants with strong protection against symptomatic COVID-19 infection for at least six months after birth, according to a study from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. These findings, published in Pediatrics, reinforce the importance of receiving both a COVID-19 vaccine and booster during pregnancy to ensure that infants are born with robust protection that lasts until they are old enough to be vaccinated.
COVID-19 is especially dangerous for newborns and young infants, and even healthy infants are vulnerable ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Researchers uncover mechanisms behind enigmatic shapes of nucleiScientists may be able to direct immune cells toward diseased areas