Study: New treatment method helps reduce suicide among military and veterans
2024-02-14
(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is common among U.S. military veterans. It’s also linked with higher risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
A study led by researchers with The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine found that crisis response planning (CRP) can help. This brief intervention quickly reduced suicidal thoughts among patients receiving daily therapy for two weeks for PTSD. This type of therapy is called “cognitive processing therapy,” or CPT.
“This study shows that crisis response planning can rapidly reduce suicide risk. It is the first study to prove this technique works when used during massed therapy for PTSD,” said principal investigator Craig J. Bryan, PsyD. He is a clinical psychologist, professor and director of the Division of Recovery and Resilience at Ohio State’s Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health.
Findings are published online in the Journal of Anxiety Disorders.
Researchers randomly assigned 157 U.S. military members and veterans to receive CRP or self-guided safety planning (SP) before starting massed CPT.
Study participants had one-hour virtual or in-person therapy sessions for 10 days in a row in outpatient clinical settings as part of Ohio State’s Suicide and Trauma Reduction Initiative (STRIVE). This schedule is called “massed” therapy.
Key findings include:
CRP is a low-cost and effective way to reduce suicide risk among patients with PTSD.
The severity of suicidal thoughts after CRP was about half of that in SP.
Fewer participants in CRP reported attempting suicide.
“Next we want to learn if using CRP with other treatments can similarly reduce suicidal thoughts and suicide attempts across patient groups and clinic types,” said lead author Justin Baker. He is an assistant professor in Ohio State’s Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Health and clinical director of the STRIVE Program.
Based in part on these results, the STRIVE Program received a new research grant from the U.S. Department of Defense to further develop this intervention among high-risk military members.
This work was funded in part by the Bob Woodruff Foundation, the USAA Foundation, and the Boeing Company. Charitable contributions from Honor 365, Ride To Zero, 33 Forever and other private donors also helped fund this study.
Disclosures: Researchers Craig Bryan and AnnaBelle Bryan report ownership of Anduril, LLC, outside the submitted work. Researchers Lauren Khazem, Christina Rose Bauder and Justin Baker report personal fees from Anduril, LLC, outside the submitted work.
# # #
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-14
The CRISPR Journal announces the publication of its February 2024 issue. The CRISPR Journal is devoted to publishing outstanding research in CRISPR biology, technology, and genome editing. Chief Editor is Professor Rodolphe Barrangou, PhD (North Carolina State University); Executive Editor is Dr. Kevin Davies. For full-text copies of articles or to arrange interviews with the editors, authors, or members of the editorial board, contact Kathryn Ryan at the Publisher.
1. Warrior spirit: An interview with sickle cell pioneer Victoria Gray,
The gene editing world and the sickle cell disease (SCD) ...
2024-02-14
WHAT:
Women who receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination or booster during pregnancy can provide their infants with strong protection against symptomatic COVID-19 infection for at least six months after birth, according to a study from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. These findings, published in Pediatrics, reinforce the importance of receiving both a COVID-19 vaccine and booster during pregnancy to ensure that infants are born with robust protection that lasts until they are old enough to be vaccinated.
COVID-19 is especially dangerous for newborns and young infants, and even healthy infants are vulnerable ...
2024-02-14
Skywalker gibbon couples wake up each morning and sing to each other, their voices echoing across the forest canopy of their home. The primate’s endearing love song helped scientists confirm what was formerly a strong hunch: Myanmar has the largest population of endangered Skywalker gibbons on Earth.
When Star Wars-loving scientists identified Skywalker gibbons as a distinct species in 2017, fewer than 200 individuals were known to exist, all in southwestern China. A study published today in the International Journal of Primatology is the first in the past century to confirm living Skywalker gibbons in ...
2024-02-14
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 14, 2024 – It was a last-ditch effort. For years doctors had tried to keep a patient’s recurrent drug-resistant bacterial blood infection at bay, but it kept coming back and antibiotics were no longer working.
The family agreed to try an experimental treatment that uses viruses to kill bacteria. The patient’s Enterococcus faecium bacterial strain, which had become zombie-like and was almost impossible to treat with currently available antibiotics, was tested against wastewater collected from across the country to find a virus – called a bacteriophage – that scientists theorized would specifically target the drug-resistant bacteria.
It worked ...
2024-02-14
ETRI’s researchers have developed an AI-powered e-sports analysis platform that provides real-time win rate prediction services by analyzing gameplay screens. This platform was notably applied to the highly popular League of Legends (LoL) during a recent international e-sports tournament, garnering positive feedback.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) has developed a technology that recognizes real-time game situations by analyzing play elements extracted from game videos and automatically generates highlights by identifying key play events in the game.
Also, this e-sports service platform, based ...
2024-02-14
Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) and the University of California, Davis have reached a new breakthrough in pancreatic cancer research—eight years in the making. It could help slow the disease’s deadly spread.
In 2017, as a postdoc in CSHL’s Tuveson lab, Chang-il Hwang and collaborators from the Vakoc lab uncovered a protein essential for jumpstarting metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Now an assistant professor at UC Davis, Hwang recently reunited with CSHL Professors David Tuveson and Christopher Vakoc. The trio once again set their sights on PDAC. The disease is known for its aggressiveness. ...
2024-02-14
While pesticides protect crops from hungry animals, pesky insects, or even microbial infections, they also impact other vital organisms, including bees and earthworms. And today, research published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters reveals that worms are affected by the relatively small amounts of chemicals that can leach out of pesticide-treated seeds. Exposure to nonlethal amounts of these insecticides and fungicides resulted in poor weight gain and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage in the worms.
Pesticide treatment can be introduced at several different ...
2024-02-14
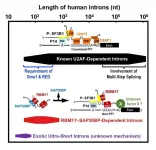
In humans, the length of pre-mRNA varies extensively (from 30 to 1,160,411 nucleotides by recent studies). The fundamental mechanism of splicing has been studied with model pre-mRNAs including 158- and 231-nt introns, for historical instance, that are spliced very efficiently in vitro and in vivo. Such an ideal pre-mRNA contains good splicing signal sequences, i.e., the 5′ splice site, the branch-site (BS) sequence, and the polypyrimidine tract (PPT) followed by the 3′ splice site that are recognized by U1 snRNP, U2 snRNP and U2AF2–U2AF1, respectively. Prof. Mayeda says, “Given the diverse lengths ...
2024-02-14
Corals searching for food in the cold and dark waters of the deep sea are building higher and higher mountains to get closer to the source of their food. But in doing so, they may find themselves trapped when the climate changes. That is shown in the thesis that theoretical ecologist Anna van der Kaaden of NIOZ in Yerseke and the Copernicus Institute for Sustainable Development in Utrecht will defend on Feb. 20 at the University of Groningen. “When the water gets warmer, these creatures prefer to be deeper, but a coral doesn’t just walk down the mountain,” Van der Kaaden said.
Deep and dark
Unlike the famous, colorful tropical corals, cold-water corals live ...
2024-02-14
Surgeons who routinely change surgical gloves and instruments are incurring similar costs to those using the same equipment, a new study has found.
The economic evaluation funded by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) follows a clinical trial conducted at 80 hospitals in Benin, Ghana, India, Mexico, Nigeria, Rwanda, and South Africa which established that routine change of gloves and instruments reduces surgical site infections (SSIs) by 13%.
The evaluation, published by the Lancet Global ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study: New treatment method helps reduce suicide among military and veterans