(Press-News.org) Like other factors such as age, sex and genetics, smoking has a major impact on immune responses. This is the finding recently made by a team of scientists at the Institut Pasteur using the Milieu Intérieur cohort of 1,000 healthy volunteers, established to understand variability in immune responses. In addition to its short-term impact on immunity, smoking also has long-term consequences. For many years after they have quit the habit, smokers are left with effects on some of their bodies' defense mechanisms acquired while smoking. These findings, which for the first time reveal a long-term memory of the effects of smoking on immunity, will be published in the journal Nature on February 14, 2024.
Individuals' immune systems vary significantly in terms of how effectively they respond to microbial attacks. But how can this variability be explained? What factors cause these differences? "To answer this key question, we set up the Milieu Intérieur cohort comprising 1,000 healthy individuals aged 20 to 70 in 2011," comments Darragh Duffy, Head of the Translational Immunology Unit at the Institut Pasteur and last author of the study. While certain factors such as age, sex and genetics are known to have a significant impact on the immune system, the aim of this new study was to identify which other factors had the most influence."
The scientists exposed blood samples taken from individuals in the Milieu Intérieur cohort to a wide variety of microbes (viruses, bacteria, etc.) and observed their immune response by measuring levels of secreted cytokines(1). Using the large quantities of data gathered for individuals in the cohort, the team then determined which of the 136 investigated variables (body mass index, smoking, number of hours' sleep, exercise, childhood illnesses, vaccinations, living environment, etc.) had the most influence on the immune responses studied. Three variables stood out: smoking, latent cytomegalovirus infection(2) and body mass index. "The influence of these three factors on certain immune responses could be equal to that of age, sex or genetics," points out Darragh Duffy.
As regards smoking, an analysis of the data showed that the inflammatory response, which is immediately triggered by infection with a pathogen, was heightened in smokers, and moreover, the activity of certain cells involved in immune memory was impaired. In other words, this study shows that smoking disrupts not only innate immune mechanisms, but also some adaptive immune mechanisms. "A comparison of immune responses in smokers and ex-smokers revealed that the inflammatory response returned to normal levels quickly after smoking cessation, while the impact on adaptive immunity persisted for 10 to 15 years," observes Darragh Duffy. "This is the first time it has been possible to demonstrate the long-term influence of smoking on immune responses."
Basically, the immune system appears to have something resembling a long-term memory of the effects of smoking. But how? "When we realized that the profiles of smokers and ex-smokers were similar, we immediately suspected that epigenetic processes were at play(3)," says Violaine Saint-André, a bioinformatician in the Institut Pasteur's Translational Immunology Unit and first author of the study. "We demonstrated that the long-term effects of smoking on immune responses were linked to differences in DNA methylation(4) – with the potential to modify the expression of genes involved in immune cell metabolism – between smokers, ex-smokers and non-smokers." It therefore appears that smoking can induce persistent changes to the immune system through epigenetic mechanisms.
"This is a major discovery elucidating the impact of smoking on healthy individuals' immunity and also, by comparison, on the immunity of individuals suffering from various diseases," concludes Violaine Saint-André.
(1) proteins secreted by a large number of immune cells to communicate among themselves and participate in immune defense.
(2) a virus in the herpes family that is often asymptomatic though dangerous to fetuses.
(3) changes in DNA that affect how genes are expressed, i.e. how they are used by cells.
(4) methylation is a type of chemical modification. Methyl groups position themselves on DNA, changing the way in which the genome is read in the cell.
END
Smoking has long-term effects on the immune system
2024-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Male fertility gene discovery reveals path to success for sperm
2024-02-14
Discovery of a pair of genes that work in perfect harmony to protect male fertility, could provide new insights into some unexplained cases of the most severe form of infertility, research suggests.
Genetic analysis of cases of male infertility revealed that rare mutations in a gene, known as SPOCD1, disrupts the formation of healthy sperm during the earliest stages of their development.
The gene was also found to work in partnership with a previously unknown gene, C19orf84, to protect the early-stage precursors to sperm, known as germ cells, from damage.
The discovery of the essential role of these ...
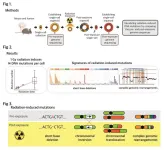
Genome sequencing unveils mutational impacts of radiation on mammalian cells
2024-02-14
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer ...
WashU awarded up to $20 million to create portable device to scan for eye diseases
2024-02-14
In the United States, more than one-fourth of adults over age 40 have an eye disease, including glaucoma, cataracts or age-related macular degeneration, or a chronic health condition that affects the eyes, such as diabetic retinopathy. These conditions are a strain on an individual’s health as well as on the health-care system, yet early diagnosis and management can help to prevent more than 90% of severe vision loss.
Chao Zhou, a professor of biomedical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has been working to improve optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems that can conduct high-resolution imaging of the ...
New understanding of avian eggshell attachment – implications for medical procedures and egg industry
2024-02-14
Athletes often suffer injuries to ligaments in their knees, particularly to the anterior cruciate ligament or ACL. While surgery to replace these torn ligaments is becoming increasingly common around the world it often needs to be repeated. That’s because it has proved challenging to anchor fibrous, soft and wet ligament grafting material into hard bone.
Now, McGill University researchers have new information from the eggshell membrane in chicken eggs that could help change this picture thanks to the potential it offers for improvements in tissue engineering ...
HHMI opens National Competition for Freeman Hrabowski Scholars Program
2024-02-14
Today, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) opened a national competition to select up to 30 early career faculty in science to join the 2025 cohort of the Freeman Hrabowski Scholars Program.
Freeman Hrabowski Scholars are outstanding basic researchers, including physician-scientists, who have strong potential to become leaders in their fields. Scholars are committed to advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion through their mentoring efforts and understanding of systemic exclusion and marginalization in science of trainees from different backgrounds. While pursuing excellence in their own research, Scholars work to create an inclusive lab climate ...
Study: New treatment method helps reduce suicide among military and veterans
2024-02-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is common among U.S. military veterans. It’s also linked with higher risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
A study led by researchers with The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine found that crisis response planning (CRP) can help. This brief intervention quickly reduced suicidal thoughts among patients receiving daily therapy for two weeks for PTSD. This type of therapy is called “cognitive processing therapy,” or CPT.
“This study shows that crisis response planning can rapidly reduce suicide risk. It is the first study to prove this technique works when ...
The CRISPR Journal announces the publication of its February 2024 issue
2024-02-14
The CRISPR Journal announces the publication of its February 2024 issue. The CRISPR Journal is devoted to publishing outstanding research in CRISPR biology, technology, and genome editing. Chief Editor is Professor Rodolphe Barrangou, PhD (North Carolina State University); Executive Editor is Dr. Kevin Davies. For full-text copies of articles or to arrange interviews with the editors, authors, or members of the editorial board, contact Kathryn Ryan at the Publisher.
1. Warrior spirit: An interview with sickle cell pioneer Victoria Gray,
The gene editing world and the sickle cell disease (SCD) ...
COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy protects infants for six months
2024-02-14
WHAT:
Women who receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination or booster during pregnancy can provide their infants with strong protection against symptomatic COVID-19 infection for at least six months after birth, according to a study from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. These findings, published in Pediatrics, reinforce the importance of receiving both a COVID-19 vaccine and booster during pregnancy to ensure that infants are born with robust protection that lasts until they are old enough to be vaccinated.
COVID-19 is especially dangerous for newborns and young infants, and even healthy infants are vulnerable ...
Love songs lead scientists to new populations of skywalker gibbons in Myanmar
2024-02-14
Skywalker gibbon couples wake up each morning and sing to each other, their voices echoing across the forest canopy of their home. The primate’s endearing love song helped scientists confirm what was formerly a strong hunch: Myanmar has the largest population of endangered Skywalker gibbons on Earth.
When Star Wars-loving scientists identified Skywalker gibbons as a distinct species in 2017, fewer than 200 individuals were known to exist, all in southwestern China. A study published today in the International Journal of Primatology is the first in the past century to confirm living Skywalker gibbons in ...
Case study: drug-resistant bacteria responds to phage-antibiotic combo therapy
2024-02-14
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 14, 2024 – It was a last-ditch effort. For years doctors had tried to keep a patient’s recurrent drug-resistant bacterial blood infection at bay, but it kept coming back and antibiotics were no longer working.
The family agreed to try an experimental treatment that uses viruses to kill bacteria. The patient’s Enterococcus faecium bacterial strain, which had become zombie-like and was almost impossible to treat with currently available antibiotics, was tested against wastewater collected from across the country to find a virus – called a bacteriophage – that scientists theorized would specifically target the drug-resistant bacteria.
It worked ...