(Press-News.org) One of the grand challenges for materials science is the design and discovery of new materials that address global priorities such as Net Zero.
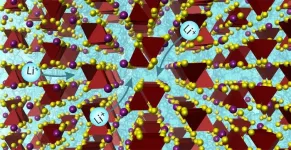
In a paper published in the journal Science, researchers at the University of Liverpool have discovered a solid material that rapidly conducts lithium ions. Such lithium electrolytes are essential components in the rechargeable batteries that power electric vehicles and many electronic devices.
Consisting of non-toxic earth-abundant elements, the new material has high enough Li ion conductivity to replace the liquid electrolytes in current Li ion battery technology, improving safety and energy capacity.
Using a transformative scientific approach to design the material, the interdisciplinary research team from the University synthesised the material in the laboratory, determined its structure (the arrangement of the atoms in space) and demonstrated it in a battery cell.
The new material is one of a very small number of solid materials that achieve Li ion conductivity high enough to replace liquid electrolytes, and operates in a new way because of its structure.
Its discovery was achieved through a collaborative computational and experimental workflow that used AI and physics-based calculations to support decisions made by chemistry experts at the University.
The new material provides a platform for the optimisation of chemistry to further enhance the properties of the material itself, and to identify other materials based on the new understanding provided by the study.
Professor Matt Rosseinsky, from the University of Liverpool’s Department of Chemistry, said: “This research demonstrates the design and discovery of a material that is both new and functional. The structure of this material changes previous understanding of what a high-performance solid-state electrolyte looks like.
“Specifically, solids with many different environments for the mobile ions can perform very well, not just the small number of solids where there is a very narrow range of ionic environments. This dramatically opens up the chemical space available for further discoveries.
Recent reports and media coverage herald the use of AI tools to find potentially new materials. In these cases, the AI tools are working independently and thus are likely to recreate what they were trained on in various ways, generating materials that may be very similar to known ones.
“This discovery research paper shows that AI and computers marshalled by experts can tackle the complex problem of real-world materials discovery, where we seek meaningful differences in composition and structure whose impact on properties is assessed based on understanding.”
“Our disruptive design approach offers a new route to discovery of these and other high-performance materials that rely on the fast motion of ions in solids.”
The study undertaken was a combined effort between researchers in University of Liverpool’s Department of Chemistry, Materials Innovation Factory, Leverhulme Research Centre for Functional Materials Design, Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy, Albert Crewe Centre, and School of Engineering.
The work was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), the Leverhulme Trust, and the Faraday Institution.
The paper `Superionic lithium transport via multiple coordination environments defined by two anion packing’ is published in Science.
END
Discovery of new Li ion conductor unlocks new direction for sustainable batteries
University of Liverpool researchers have discovered a new solid material that rapidly conducts lithium ions
2024-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unearthed: Why zebra go first in body-size-dependent grazing succession in the Serengeti
2024-02-15
Why do Serengeti zebra, wildebeest, and gazelle – all sharing limited food resources – follow the same migratory routes, one after another, in a body-size dependent way? This longstanding question has now been evaluated by researchers who used novel data to show how a balance of species interactions and ecological factors regulate this process. They say competition pushes zebra ahead of the wildebeest, and wildebeest then eat plants in a way that facilitates development of newer growth the trailing gazelle like. “Our results highlight a balance between facilitative and competitive forces,” the authors say. Large seasonal migrations are a ...
Oxygen increased in the tropical ocean during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum
2024-02-15
Oxygenation in the tropical North Pacific Ocean increased during a warm climatic interval that occurred roughly 56 million years ago, despite high global temperatures, according to a new study. Its findings offer insights into how modern tropical oceans may respond to ongoing anthropogenic climate warming. The availability and distribution of dissolved oxygen in Earth’s oceans play a fundamental role in supporting marine ecosystems and marine life. However, oxygen in the global oceans is declining in response to anthropogenic warming. Although these trends writ large are predicted to continue, the future of oxygen in the highly productive ...
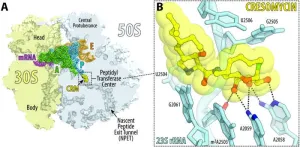
Introducing Cresomycin, a synthetic antimicrobial molecule highly effective against multidrug-resistant bacteria
2024-02-15
Cresomycin – a novel synthetic molecule – demonstrates remarkably robust efficacy against multiple, evolutionary divergent forms of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), researchers report. The emergence and widespread distribution of bacteria broadly resistant to approved antibiotics raises serious global public health concerns. Given the growing rate of deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) worldwide, it’s evident the pace of discovery and development of antibiotics effective against AMR has not kept up with the need. Many small ...
Prizewinner’s research unveils STING as a pivotal immune sensor channel
2024-02-15
For his work in furthering the understanding of how the human immune system senses dangerous invading pathogens, Bingxu Li has received the 2024 Michelson Philanthropies & Science Prize for Immunology. Li’s prize-winning essay investigates the role that Stimulator of Interferon Genes, or STING, plays in including multiple distinct defenses against viruses, bacteria, and tumors and in orchestrating myriad downstream responses upon activation – resolving a significant mystery in the field of innate immunity. The sensing and clearance of invading pathogens ...
Researchers observe highly excited ‘roaming’ energy pathway in chemical reactions
2024-02-15
Scientists have observed so-called 'roaming' chemical reactions, those that at certain points move away from the lowest minimum energy 'path of least resistance', in highly excited energy states for the first time.
Chemical reactions are supposed to occur along their minimum energy paths. In recent years, so-called roaming reactions that stray far from this path have begun to be observed, but only for chemical species in their ground state or, at most, their first excited state. However, researchers have now observed a roaming reaction even in highly excited energy states.
The researchers ...
MSU, Carnegie Science introduce a big new idea with the help of tiny plankton
2024-02-15
Researchers at Michigan State University and the Carnegie Institution for Science have developed a model that connects microscopic biology to macroscopic ecology, which could deepen our understanding of nature’s laws and create new opportunities in ecosystem management.
Reporting in the journal Science on Feb. 16, the team showed how microscopic relationships in plankton — such as between an organism’s size and nutrient consumption — scales up to predictably affect food webs.
“Using data that other researchers have measured at the microscale about these organisms, our model can predict what’s happening at the scale of whole ecosystems,” said Jonas ...
First-ever atomic freeze-frame of liquid water
2024-02-15
RICHLAND, Wash.—In an experiment akin to stop-motion photography, scientists have isolated the energetic movement of an electron while “freezing” the motion of the much larger atom it orbits in a sample of liquid water.
The findings, reported today in the journal Science, provide a new window into the electronic structure of molecules in the liquid phase on a timescale previously unattainable with X-rays. The new technique reveals the immediate electronic response when a target is hit with an X-ray, an important step in understanding the effects of radiation exposure on objects and people.
“The chemical reactions induced by radiation ...
Superbug killer: New synthetic molecule highly effective against drug-resistant bacteria
2024-02-15
A new antibiotic created by Harvard researchers overcomes antimicrobial resistance mechanisms that have rendered many modern drugs ineffective and are driving a global public health crisis.
A team led by Andrew Myers, Amory Houghton Professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, reports in Science that their synthetic compound, cresomycin, kills many strains of drug-resistant bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
“While we don’t yet know whether cresomycin and drugs like it are safe ...
With just a little electricity, MIT researchers boost common catalytic reactions
2024-02-15
CAMBRIDGE, MA — A simple technique that uses small amounts of energy could boost the efficiency of some key chemical processing reactions, by up to a factor of 100,000, MIT researchers report. These reactions are at the heart of petrochemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and many other industrial chemical processes.
The surprising findings are reported today in the journal Science, in a paper by MIT graduate student Karl Westendorff, professors Yogesh Surendranath and Yuriy Roman-Leshkov, and two others.
“The results are really striking,” says Surendranath, a professor of chemistry ...
Keeping telomerase in check
2024-02-15
The natural ends of chromosomes appear alarmingly like broken DNA, much as a snapped spaghetti strand is difficult to distinguish from its intact counterparts. Yet every cell in our bodies must have a way of differentiating between the two because the best way to protect the healthy end of a chromosome also happens to be the worst way to repair damaged DNA.
Consider the enzyme telomerase, which is responsible for maintaining protective telomeres at the natural ends of chromosomes. Were telomerase to seal off a broken strand of DNA with a telomere, it would prevent further repair of that break and delete essential genes. Now, a new study in Science describes how cells avoid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] Discovery of new Li ion conductor unlocks new direction for sustainable batteriesUniversity of Liverpool researchers have discovered a new solid material that rapidly conducts lithium ions