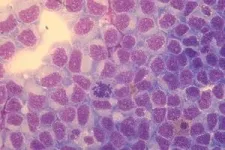
Seaports are hotspots of contagious cancer in mussels
2024-02-22
(Press-News.org)
Seaports act as hubs for the global spread of MtrBTN2,1 a rare contagious cancer affecting mussels. In this disease, cancer cells can be transmitted, like parasites, from one mussel to another nearby. While, in nature, such contagion mainly occurs between mussels in the same bed, ports and maritime transport facilitate the spread of MtrBTN2 to other locations, through biofouling, whereby diseased mussels attach themselves to ship hulls. This finding, the fruit of research by a team led by scientists from the CNRS and the University of Montpellier,2 will be published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B on February 21.
Higher incidence of the disease in ports was noted after studying 76 mussel populations along the coast of southern Brittany and the Vendée, within both natural and artificial habitats.
The research team asserts that their discovery argues in favour of biofouling mitigation policies, to stem the spread of the disease and preserve coastal ecosystems.
Notes
1 – MtrBTN2 = Mytilus trossulus Bivalve Transmissible Neoplasia 2.
2 – These scientists are affiliated with the Institut des Sciences de l'Évolution de Montpellier (CNRS / IRD / University of Montpellier) and the Interactions Hôtes-Pathogènes-Environnements research unit (CNRS / IFREMER / University of Perpignan Via Domitia). Their fellow team members are from the MIVEGEC research unit (CNRS / IRD / University of Montpellier) and the research support firms Eurêka Mer and Cochet Environnement.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-22
In their ‘letter to the world’ they say that cancer is a ‘defining health issue of our time’ that requires a united and collective worldwide response on a par with Covid-19. The scientists argue that we’re at a ‘tipping point’ that could transform how we understand and treat cancer – but more support for life-saving research is required to beat the disease.
The letter is published as Cancer Research UK launched its More Research, Less Cancer campaign ...
2024-02-22
Before orally administered drugs can make their way throughout the body, they must first bind to membrane proteins called drug transporters, which carry compounds across the intestinal tract and help them reach their intended targets. But because one drug can bind to several different drug transporters, they may struggle to get past this gut barrier, potentially leading to decreased drug absorption and efficacy. If another drug is added to the mix, interactions between the two compounds and their transporters can cause dangerous side effects.
Researchers ...
2024-02-22
University of Alaska Fairbanks researchers have devised a way to remotely detect large landslides within minutes of occurrence and to quickly determine whether they are close to open water and present a tsunami hazard.
They write in a new paper that their method of determining a landslide’s location, volume and potential impact is rapid enough to support the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s goal of issuing a tsunami warning within 5 minutes of a landslide.
“The warming climate is causing glaciers to retreat, leaving behind valleys whose mountainsides and hillsides have lost their ...
2024-02-22
Mars was once a wet world. The geological record of the Red Planet shows evidence for water flowing on the surface – from river deltas to valleys carved by massive flash floods.
But a new study shows that no matter how much rainfall fell on the surface of ancient Mars, very little of it seeped into an aquifer in the planet’s southern highlands.
A graduate student at The University of Texas at Austin made the discovery by modeling groundwater recharge dynamics for the aquifer using a range of methods ...
2024-02-21
Though artificial intelligence decreases human error in experimentation, human experts outperform AI when identifying causation or working with small data sets.
To capitalize on AI and researcher strengths, ORNL scientists, in collaboration with colleagues at National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan, and the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, developed a human-AI collaboration recommender system for improved experimentation performance.
During experiments, the system’s machine learning algorithms, described in npj Computational Materials, display preliminary ...
2024-02-21
Longstanding challenges in biomedical research such as monitoring brain chemistry and tracking the spread of drugs through the body require much smaller and more precise sensors. A new nanoscale sensor that can monitor areas 1,000 times smaller than current technology and can track subtle changes in the chemical content of biological tissue with sub-second resolution, greatly outperforming standard technologies.
The device, developed by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, is silicon-based and takes advantage of techniques developed for microelectronics manufacturing. ...
2024-02-21
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today was awarded 16 grants totaling over $25.5 million from the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) in support of cancer screening, early detection and prevention programs, faculty recruitment, and groundbreaking cancer research across all areas of the institution.
“We are grateful for CPRIT’s continued funding of impactful cancer research and prevention programs at MD Anderson, which propels our efforts to deliver new breakthroughs and to advance our mission to end cancer,” said Peter WT Pisters, M.D., president of MD Anderson. “These efforts are pivotal to our institutional strategy ...
2024-02-21
Systemic sclerosis causes the skin to tighten and harden resulting in a potentially fatal autoimmune condition that is associated with lung fibrosis and kidney disease.
University of Michigan Health researchers have studied the pathology of systemic sclerosis to understand better the disease and identify key pathways in the disease process that can be targeted therapeutically.
A research team led by University of Michigan Health’s Dinesh Khanna, M.B.B.S., M.Sc., professor of rheumatology and Johann Gudjonsson, M.D., Ph.D., professor of dermatology, ...
2024-02-21
It has been long assumed that Utah’s Bonneville Salt Flats was formed as its ancient namesake lake dried up 13,000 years ago. But new research from the University of Utah has gutted that narrative, determining these crusts did not form until several thousand years after Lake Bonneville disappeared, which could have important implications for managing this feature that has been shrinking for decades to the dismay of the racing community and others who revere the saline pan 100 miles west of Salt ...
2024-02-21
A $10.6 million training grant has been awarded to the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and University of Maryland, Baltimore (UMB) to administer Maryland’s Abortion Clinical Care Training Program. The grant will be used to expand the number of healthcare professionals with abortion care training, increase the racial and ethnic diversity among health care professionals with abortion care education, and support the identification of clinical sites needing training.
“Our training will target a major ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Seaports are hotspots of contagious cancer in mussels