Researchers model blood-brain barrier using “Tissue-in-a-CUBE" system
2024-02-28
(Press-News.org)
A research team at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) in Japan has succeeded in establishing a model of the blood-brain barrier using modularized tissue derived from human cells. The “Tissue-in-a-CUBE” is a small cubic structure that could provide a boost in the drug discovery field and be used as an alternative to animal models in pre-clinical studies. The study was published in Communications Biology on February 28.
The blood-brain barrier is a strict gatekeeper around the brain that prevents foreign substances in blood from entering the brain. Although protective, the barrier poses challenges when treatments need to affect the brain in order to work. When developing drugs for treating brain diseases, it is thus crucial not only to test the drug’s effectiveness inside the brain, but also to confirm that the drug can pass through the barrier.
Developing new drugs is time-consuming and costly. At the early, pre-clinical stages, conventional methods rely on animal testing. However, differences between animals and humans sometimes makes it difficult to predict a drug’s effectiveness in humans as well as any harmful side effects. Along with increases in the number of regulations governing animal experiments, these problems have encouraged researchers to develop research methods that do not rely on animal testing, such as using organoids—structures that mimic human organs—as well as organs-on-a-chip, with the ultimate aim to create artificial human organs for external use.
With this in mind, the research team led by Masaya Hagiwara at RIKEN BDR has developed a new model of the blood-brain barrier using the CUBE-type system that they recently established for modularizing different human tissues. Reconstructing multiple tissues simultaneously and analyzing their interactions is extremely challenging because drugs have to traverse different types of tissues before reaching the target area, but also crucially important. In the case of the blood-brain barrier, drugs must pass through vascular endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes before they can enter the brain.
To construct the blood-brain barrier model, the researchers created 5-mm CUBE frames, filled them with hydrogel embedded with astrocytes and pericytes derived from the human brain, and seeded vascular endothelial cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells onto the surface to form cell sheets. They then tested the device. According to Hagiwara, “We were happy to find that it accurately mimicked the real blood-brain barrier in terms of structure and function: with astrocytes and pericytes extending three-dimensionally beneath the sheet of endothelial cells, and that like the real barrier, it only allowed limited substances to pass through.”
One important feature of the CUBE frame is that it can be easily manipulated with forceps, allowing convenient handling of the blood-brain barrier model, with cell culturing being performed in a regular cell-culture plate. After maturation, the tissue was integrated with other prepared tissues in a fluidic chip to analyze inter-tissue interactions, thus fitting into the previously established modular Tissue-in-a-CUBE platform.
To demonstrate the usefulness of the system for drug development, the group conducted drug screening experiments. Brain tumor cells were cultured in the CUBE container to prepare a brain tumor module. The blood-brain barrier and brain tumor modules were then transferred into a fluidic chip and connected. This setup allowed researchers to verify how much of an anticancer drug could pass through the barrier, reach the brain tumor, and exert its effect.
“This innovative approach offers a promising alternative to animal testing for essential drug development tests, involving the understanding of drug behavior, effectiveness, and safety,” says Hagiwara. “Our modularized platform could be adapted for various diseases, including age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. In the future we plan to modularize and replicate connections between different organoids.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-28
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, but it can be challenging to predict which individuals are at highest risk.
Mass General Brigham experts in rheumatology and cardiovascular disease worked together to identify six biomarkers found in blood samples that can predict future risk of arterial inflammation among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The team is now working to test these biomarkers in a larger and more long-term cohort of patients with rheumatoid ...
2024-02-28
New York, NY [February 28, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and others have harnessed the power of machine learning to identify key predictors of mortality in dementia patients.
The study, published in the February 28 online issue of Communications Medicine [10.1038/s43856-024-00437-7], addresses critical challenges in dementia care by pinpointing patients at high risk of near-term death and uncovers the factors that drive this risk. Unlike previous studies that focused on diagnosing dementia, this research delves into predicting patient prognosis, shedding light on mortality ...
2024-02-28
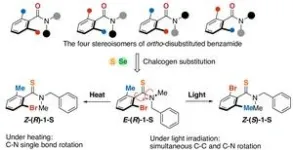
Molecules that are induced by light to rotate bulky groups around central bonds could be developed into photo-activated bioactive systems, molecular switches, and more.
Researchers at Hokkaido University, led by Assistant Professor Akira Katsuyama and Professor Satoshi Ichikawa at the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, have extended the toolkit of synthetic chemistry by making a new category of molecules that can be induced to undergo an internal rotation on interaction with light. Similar processes are believed to be important in some natural biological systems. Synthetic versions might ...
2024-02-28
LA JOLLA (February 28, 2024)—The brain is typically depicted as a complex web of neurons sending and receiving messages. But neurons only make up half of the human brain. The other half—roughly 85 billion cells—are non-neuronal cells called glia. The most common type of glial cells are astrocytes, which are important for supporting neuronal health and activity. Despite this, most existing laboratory models of the human brain fail to include astrocytes at sufficient levels or at all, which limits the models’ utility for studying ...
2024-02-28
Statement Highlights:
The American Heart Association encourages research and development of artificial intelligence (AI) and other related tools and services that may support and enable more precise approaches to cardiovascular and stroke research, prevention and care.
Academia, industry and governments worldwide are pouring resources into developing AI-based tools to transform how and when health care is delivered.
While promising research is beginning to emerge in many areas of cardiovascular medicine, AI-based tools, algorithms and systems of care have not yet been proven to improve care enough to justify widespread use.
AI and machine learning digital tools currently exist that ...
2024-02-28
Smoking cannabis associated with increased risk of heart attack, stroke
NIH-funded observational study shows risk grows sharply with more frequent use
Frequent cannabis smoking may significantly increase a person’s risk for heart attack and stroke, according to an observational study supported by the National Institutes of Health. The study, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, uses data from nearly 435,000 American adults, and is among the largest ever to explore the relationship ...
2024-02-28
● Simple modifications to ventilation systems improve airflow, making operations safer for both patients and surgical teams
● This research was conducted in close collaboration with a team of surgeons from Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi (CCAD)
Abu Dhabi, UAE, February 28, 2024: NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) engineers studying ventilation systems in surgical operating theaters have found that traditional ventilation systems may inadvertently facilitate the circulation of aerosolized pathogen-carrying particles. This, as a result, puts surgical teams at a higher risk of infection by COVID-19 and other airborne diseases.
Using basic engineering tools, including ...
2024-02-28
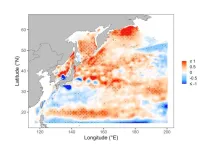
Fish weight in the western North Pacific Ocean dipped in the 2010s due to warmer water limiting food supplies, according to a new study at the University of Tokyo. Researchers analyzed the individual weight and overall biomass of 13 species of fish. In the 1980s and 2010s, the fish were lighter. They attributed the first period of weight loss to greater numbers of Japanese sardine, which increased competition with other species for food. During the 2010s, while the number of Japanese sardine and chub mackerel moderately increased, the effect of climate change warming the ocean appears to have resulted ...
2024-02-28
Kelp flies and marine yeast cultivated on by-products from the seafood industry can be used in feed for farmed salmon. Replacing fishmeal and soybeans can create more sustainable and circular food production, according to a thesis from the University of Gothenburg.
Food from aquaculture, such as farmed fish, is the food industry’s fastest growing sector. One key reason is that this is a nutritious and protein-rich food that is generally more sustainably produced than protein from land animals.
However, fish farming also has challenges. One is obtaining sufficient amounts of sustainable high-quality feed. Currently, fish feed accounts for about ...
2024-02-28
Scientists from the National Oceanography Centre (NOC) have discovered that increased meltwater in the North Atlantic can trigger a chain of events leading to hotter and drier European summers.
The paper, which will be published in the European Geosciences Union’s open access journal Weather and Climate Dynamics, suggests that European summer weather is predictable months to years in advance, due to higher levels of freshwater in the North Atlantic.
Discussing the implications, lead author Marilena Oltmanns, Research Scientist at the National Oceanography Centre, said: “While the UK and northern Europe experienced unusually cool and wet weather in Summer 2023, Greenland experienced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers model blood-brain barrier using “Tissue-in-a-CUBE" system