(Press-News.org) For many hundreds of millions of years, the average temperature at the surface of the Earth has varied by not much more than 20° Celsius, facilitating life on our planet. To maintain such stable temperatures, Earth must have a ‘thermostat’ that regulates the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide over geological timescales, influencing global temperatures. The erosion and weathering of rocks are important parts of this ‘thermostat.’ A team led by LMU geologist Aaron Bufe and Niels Hovius from the German Research Centre for Geosciences has now modeled the influence of these processes on carbon in the atmosphere. Their surprising result: CO2 capture through weathering reactions is highest in low-relief mountain ranges with moderate erosion rates and not where erosion rates are fastest.
Weathering occurs where rock is exposed to water and wind. “When silicates weather, carbon is removed from the atmosphere and later precipitated as calcium carbonate. By contrast, weathering of other phases – such as carbonates and sulfides or organic carbon contained in rocks – releases CO2. These reactions are typically much faster than silicate weathering”, says Hovius. “As a consequence, the impact of mountain building on the carbon cycle is complex.”
Weathering model shows common mechanisms
To address this complexity, the researchers used a weathering model to analyze fluxes of sulfide, carbonate, and silicate weathering in a number of targeted study regions – such as Taiwan and New Zealand – with large ranges in erosion rates. “We discovered similar behaviors in all locations, pointing to common mechanisms,” says Bufe.
Further modelling showed that the relationship between erosion and CO2-fluxes is not linear, but that CO2 capture from weathering peaks at an erosion rate of approximately 0.1 millimeters per year. When rates are lower or higher, less CO2 is sequestered and CO2 may even be released into the atmosphere. “High erosion rates like in Taiwan or the Himalayas push weathering into being a CO2 source, because silicate weathering stops increasing with erosion rates at some point, whereas the weathering of carbonates and sulfides increases further,” explains Bufe.
In landscapes with moderate erosion rates of around 0.1 millimeters per year, the rapidly weathering carbonates and sulfides are largely depleted, whereas silicate minerals are abundant and weather efficiently. Where erosion is even slower than 0.1 millimeters per year, only few minerals are left to weather. The biggest CO2 sinks are therefore low-relief mountain ranges such as the Black Forest or the Oregon Coast Range, where erosion rates approach the optimum. “Over geological timescales, the temperature to which Earth’s ‘thermostat’ is set therefore depends strongly on the global distribution of erosion rates,” says Bufe. To understand the effects of erosion on Earth’s climate system in greater detail, Bufe thinks that future studies should additionally consider organic carbon sinks and weathering in floodplains.
END
Rock weathering and climate: Low-relief mountain ranges are largest carbon sinks
A team led by LMU geologist Aaron Bufe has investigated how erosion and weathering affect the CO2 budget over millions of years
2024-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Often seen, never studied: First characterization of a key postsynaptic protein
2024-03-07
A protein that appears in postsynaptic protein agglomerations has been found to be crucial to their formation. The Kobe University discovery identifies a new key player for synaptic function and sheds first light on its hitherto uncharacterized cellular role and evolution.
What happens at the synapse, the connection between two neurons, is a key factor in brain function. The transmission of the signal from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic neuron is mediated by proteins and their imbalance can lead to neuropsychiatric ...
How does a virus hijack insect sperm to control disease vectors and pests?
2024-03-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A widespread bacteria called Wolbachia and a virus that it carries can cause sterility in male insects by hijacking their sperm, preventing them from fertilizing eggs of females that do not have the same combination of bacteria and virus. A new study led by microbiome researchers at Penn State has uncovered how this microbial combination manipulates sperm, which could lead to refined techniques to control populations of agricultural pests and insects that carry diseases like Zika and dengue to humans.
The study is published in the March 8 issue of the journal Science.
“Wolbachia is the most widespread bacteria in ...
How the brain coordinates speaking and breathing
2024-03-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT researchers have discovered a brain circuit that drives vocalization and ensures that you talk only when you breathe out, and stop talking when you breathe in.
The newly discovered circuit controls two actions that are required for vocalization: narrowing of the larynx and exhaling air from the lungs. The researchers also found that this vocalization circuit is under the command of a brainstem region that regulates the breathing rhythm, which ensures that breathing remains dominant over speech.
“When you need to breathe in, you have to stop vocalization. We found that the neurons that control vocalization ...
Shape-shifting ultrasound stickers detect post-surgical complications
2024-03-07
EVANSTON, Ill. — Researchers led by Northwestern University and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a new, first-of-its-kind sticker that enables clinicians to monitor the health of patients’ organs and deep tissues with a simple ultrasound device.
When attached to an organ, the soft, tiny sticker changes in shape in response to the body’s changing pH levels, which can serve as an early warning sign for post-surgery complications such as anastomotic leaks. Clinicians then ...
The Malaria parasite generates genetic diversity using an evolutionary ‘copy-paste’ tactic
2024-03-07
By dissecting the genetic diversity of the most deadly human malaria parasite – Plasmodium falciparum – researchers at EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have identified a mechanism of ‘copy-paste’ genetics that increases the genetic diversity of the parasite at accelerated time scales. This helps solve a long-standing mystery regarding why the parasite displays hotspots of genetic diversity in an otherwise unremarkable genetic landscape.
Malaria is most commonly transmitted through the bites of female Anopheles mosquitoes infected with P. falciparum. The latest world malaria report ...
Loss of nature costs more than previously estimated
2024-03-07
Researchers propose that governments apply a new method for calculating the benefits that arise from conserving biodiversity and nature for future generations.
The method can be used by governments in cost-benefit analyses for public infrastructure projects, in which the loss of animal and plant species and ‘ecosystem services’ – such as filtering air or water, pollinating crops or the recreational value of a space – are converted into a current monetary value.
This process is designed to make biodiversity loss and the benefits of nature conservation more visible in political decision-making.
However, the international research team ...
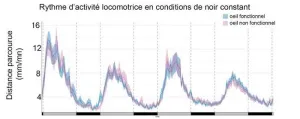
Lack of functional eyes does not affect biological clock in zebrafish
2024-03-07
Functional eyes are not required for a working circadian clock in zebrafish, as a research team1 including CNRS scientists has now shown.
Though it is understood that the eye plays a key role in mammalian adaptation to day-night cycles, the circadian clock is most often studied in nocturnal vertebrates such as mice. The zebrafish, in contrast, is a diurnal vertebrate. Through observation of various zebrafish larvae lacking functional eyes,2 the team of scientists has demonstrated that the latter are not needed to establish circadian rhythms that remain synchronized with light-dark ...
The who's who of bacteria: A reliable way to define species and strains
2024-03-07
What’s in a name? A lot, actually.
For the scientific community, names and labels help organize the world’s organisms so they can be identified, studied, and regulated. But for bacteria, there has never been a reliable method to cohesively organize them into species and strains. It’s a problem, because bacteria are one of the most prevalent life forms, making up roughly 75% of all living species on Earth.
An international research team sought to overcome this challenge, which has long plagued scientists who study bacteria. Kostas Konstantinidis, Richard ...
Forbes ranks the University of Colorado Denver | Anschutz Medical campus among America’s best employers
2024-03-07
The University of Colorado Denver | Anschutz Medical Campus is listed as one of Forbes America’s Best Large Employers for 2024.
The 2024 list of “America’s Best Employers” was conducted by Forbes and market research firm Statista, the world-leading statistics portal and industry ranking provider.
“This ranking is meaningful to our organization because the people who work at CU Anschutz drive our success as a leading academic medical campus by providing unparalleled patient care services, being a premier national leader in research and innovation, and fostering a supportive learning ...
NJIT professor trains college counselors to help fight antisemitism
2024-03-07
As data from the Anti-Defamation League shows antisemitism growing on college campuses in recent years and spiking after the Hamas-Israel conflict, a New Jersey Institute of Technology researcher is doing her part to combat the trend by developing a training model that will help prepare mental health professionals who work with Jewish students.
Modern students are hearing people chant slogans without understanding the intentions behind the words, or finding swastikas and other anti-Jewish graffiti on their campuses, but they are not encountering suitably trained counselors and psychologists who understand their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Rock weathering and climate: Low-relief mountain ranges are largest carbon sinksA team led by LMU geologist Aaron Bufe has investigated how erosion and weathering affect the CO2 budget over millions of years