(Press-News.org) If you had to estimate the number of people in a room, without counting them one-by-one, by nature you would overcount them. That’s because, simply put from a Darwinian perspective of how we have evolved, it’s better to overcount potentially harmful agents and predators than to underestimate them. This overcounting social behaviour is shown to be true in humans as well as animals. It’s certainly better to detect too many tigers (even if absent) during a jungle excursion than to miss a hungry one!
Now, EPFL neuroscientists show that if you experience hallucinations, especially when related to an illness like Parkinson’s disease, then you will over-estimate the number of people in a room to a greater degree. They also show that if you have hallucinations but are asked to estimate the number of boxes in a room, which are inanimate control objects, then no extra over-estimation occurs, shedding light on the social nature of this overcounting. The results are published in Nature Communications.
“The fact that patients of Parkinson’s disease have a much higher over-estimation in counting people is mind-blowing because Parkinson’s disease is classically viewed as a movement disorder,” says Olaf Blanke who leads EPFL’s Laboratory of Cognitive Neuroscience which is part of Neuro-X. “We show that Parkinson’s may also be a perceptual disorder, especially of social stimuli, and that invisible presences in Parkinson’s Disease may impair even more the counting social brain!”
The category of hallucinations investigated by the neuroscientists is called presence hallucinations, for which people report an invisible presence next to them, even though no-one is there. Such hallucinations are considered to be minor compared to visual hallucinations for instance. They may be experienced early on in patients with Parkinson’s disease, sometimes even before diagnosis. Presence hallucinations are also a known early marker of cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease.
The results of the study support the idea that the invisible presence (and related brain mechanisms) are responsible for this overcounting of people. When presence hallucinations are experienced – either due to disease or induced artificially – this extra presence gets subconsciously translated into an over-estimation of the number of people we think we see. In essence, the invisible presence gets added in the counting process, but only in counting people!
The numerosity experiment and technodelics
To test the hypothesis that presence hallucinations lead to extra over-counting of people, the researchers merge virtual reality with robotics. The researchers refer to this unique combination of VR and robotics as “technodelics” for technology-induced altered states of consciousness, used in the present study for the special case of technology-induced hallucinations. Virtually reality is used for the “human numerosity experiment” which consists of showing virtual, 3D scenes of five, six, seven, or eight people in an empty room for a split-second (200 milliseconds), so too many people and too fast to count them accurately one by one. Robotics is used to induce presence hallucinations artificially, which consists of a robotic finger poking the user’s back out-of-sync with the user’s own poking movement. In evaluating one’s susceptibility to hallucinations, the scientists find that healthy individuals on technodelics indeed overcount.
“The advantage of our technodelics environment is that it gives us an objective way to measure hallucinations which are highly subjective states,” explains Louis Albert, lead author of the study. “We are essentially engineering hallucinations, inducing hallucinations and getting a clear, implicit read-out of hallucination susceptibility at a given time.”
The platform provides an almost automated way of determining if someone is susceptible to hallucinations, in contrast to current methods that range from simply asking someone if they experience hallucinations, to questionnaires or other methods that involve subjective analysis by medical specialist.
Monitor hallucinations at home
For the study, the researchers also developed a simplified version of the numerosity experiment, which can be done in the lab but also online, unobtrusively, from the comfort of one’s own home and without requiring extra training of medical staff.
“We now have an online test that can determine if someone is prone to hallucinations, a much-needed objective tool for measuring hallucination susceptibility in patients,” continues Albert. “The test can be carried out independently by patients, directly from home on their computer or tablet, thus has the potential to reach a large demographic at minimal cost. Without the need for specific equipment or specialized staff for hallucination testing and interviewing, and without the need for patients to travel to the clinic, this test is accessible and can reach people living far away from medical centers and in low-income countries.”
Some 170 patients with Parkinson’s disease were recruited for the online test, of which 69 of them had presence hallucinations. With this version of the test, the scientists also found that patients with presence hallucinations overcount more than patients without hallucinations. Some patients with reported seeing as many as 11 or more people when only 8 were shown.
“We have strategies for determining if a patient with Parkinson’s disease experiences presence hallucinations or not, which means that in the future we should be able to identify and monitor those who are more prone to cognitive decline for early treatment,” says Fosco Bernasconi, co-author of the study.
Founded in 2022, EPFL's Neuro X Institute specializes in translational research across neuroscience, neural engineering, and neurocomputation. With 14 laboratories comprising a team of 250 experts, the institute aims to accelerate the development of new therapies by integrating advanced research in brain functions, innovative neural interfaces, and AI-driven neurocomputational models.
From body ownership to technodelics
Almost a decade ago, EPFL scientists designed a robotic task to do something entirely different than to evaluate susceptibility to hallucinations, a reminder of the serendipity of science. The robotic task was initially designed to explore embodiment and how the mind uses sensory information to create a feeling of body ownership. But when participants of the task repeatedly reported spooky feelings of being accompanied by ghosts, the EPFL researchers realized – instead of brushing it off as a coincidence – that they had stumbled upon a mechanism to provoke presence hallucinations in healthy people with possible applications in people with disease. The researchers knew at this point that they had a subjective way to induce presence hallucinations, thanks to the robotic task that muddles up the user’s senses.
END
The surprising effect of presence hallucinations on social perception
How invisible presences hijack the social counting brain
2024-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Seismological study shows ancient lower mantle flow field under Philippine sea plate
2024-03-12
Researchers from China and Japan have discovered distinct characteristics of the lower mantle flow field. They investigated seismic anisotropy in the upper part of the lower mantle beneath the Philippine Sea Plate (PSP) and found that the ancient lower mantle flow field is still preserved there.
The study was published in Nature Geoscience.
The lower mantle is an important layer of the Earth and may play an important role in the evolution and material cycling of Earth's interior. It is generally believed to be not only the final destination of subducted slabs, ...
Age-related changes in skin may contribute to melanoma metastases
2024-03-12
*EMBARGOED UNTIL TUESDAY, MARCH 12, AT 6 A.M. ET
Age-related changes that cause the skin to stiffen and become less elastic may also contribute to higher rates of metastatic skin cancer in older people, according to research by investigators from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study, published March 12 in Nature Aging, shows that increased stiffness in aging skin increases the release of a protein called ICAM1. Increased ICAM1 levels stimulate blood vessel growth in the tumor, helping it grow. It also makes the blood vessels “leaky,” enabling tumor cells ...
A coral superhighway in the Indian Ocean
2024-03-12
Despite being scattered across more than a million square kilometres, new research has revealed that remote coral reefs across the Seychelles are closely related. Using genetic analyses and oceanographic modelling, researchers at Oxford University demonstrated for the first time that a network of ocean currents scatter significant numbers of larvae between these distant islands, acting as a ‘coral superhighway.’ These results are published today in Scientific Reports.
Dr April Burt (Department of Biology, University of Oxford, and Seychelles Islands Foundation), lead author of the study, said: ‘This discovery is very important because a key factor ...
Scientists develop a rapid gene-editing screen to find effects of cancer mutations
2024-03-12
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Tumors can carry mutations in hundreds of different genes, and each of those genes may be mutated in different ways — some mutations simply replace one DNA nucleotide with another, while others insert or delete larger sections of DNA.
Until now, there has been no way to quickly and easily screen each of those mutations in their natural setting to see what role they may play in the development, progression, and treatment response of a tumor. Using a variant of CRISPR genome-editing known as prime editing, MIT researchers have ...
Rainforest's next generation of trees threatened 30 years after logging
2024-03-12
Rainforest seedlings are more likely to survive in natural forests than in places where logging has happened – even if tree restoration projects have taken place, new research shows.
Scientists monitored over 5,000 seedlings for a year and a half in North Borneo.
They studied a landscape containing both natural forest and areas logged 30 years ago – some of which were recovering naturally, while some had been restored by methods including tree planting.
A drought had triggered “mast fruiting” across ...
Expertly engineered saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strain in the optimized production of carotenoids
2024-03-12
More than 90% of the commercially available carotenoids are synthetically produced using chemicals. To meet the increasing demand for cost-effective natural compounds in carotenoid synthesis, researchers at Xiamen University, China, have developed an engineered S. cerevisiae yeast strain capable of selectively overproducing carotenoids. They redesigned the genomic sequence and critical pathways to optimize carotenoid production. This novel and successful research approach can be extended to other model ...
Beer byproduct behind Marmite could help us recycle metal waste
2024-03-12
When we recycle electronic devices we can no longer use, we expect to make the most out of the precious natural resources that went into building them. But electronic waste is notoriously difficult to recycle, because it’s hard to separate the different metals in the waste from each other. Scientists have now found a way of selectively capturing metals from a waste stream using spent brewer’s yeast, the same beer byproduct that goes into Marmite. Not only that: the yeast can be reused, making the process even more eco-friendly.
“Electronic waste is difficult to recycle because it is very heterogeneous,” said Dr Klemens Kremser ...
Guessing game: Response may bias understanding of future scenarios
2024-03-12
Does previous experience bias a person in future estimations? Yes, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers in Japan report, but only if the person engages higher processing powers by responding, as opposed to simply observing.
They made their findings through experiments involving participants estimating the number of dots flashed on a screen. Participants either had to input their estimate before making another estimate on a new set of dots or were not prompted to do anything but observe. The researchers found ...
KKH-led study reveals low COVID-19 transmission rate from mothers to newborns
2024-03-12
11 March 2024, Singapore – A study[1] by KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital (KKH), Singapore General Hospital (SGH) and National University Hospital (NUH) has revealed that COVID-19 transmission from mothers to their newborns is low.
The study involving 371 women who had COVID-19 infection during pregnancy and their newborns found that only four infants or 1.1 per cent of the babies were diagnosed with COVID-19 after birth, of which three (1.1 per cent) were from mothers who were COVID-19 vaccinated and one infant (1.3 per cent) was from a mother who was not vaccinated.
Senior Author of the study, Dr Yeo Kee Thai, Senior Consultant, Department of Neonatology, KKH ...
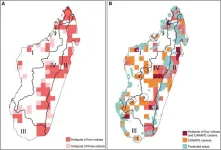
Scientists identify biodiversity conservation gaps in Madagascar
2024-03-12
Despite the importance of biodiversity and the urgency to conserve it, assessing what aspect of biodiversity requires the highest priority has proven complex, especially when conservation resources are limited. A new study published in Current Biology sheds light on this question.
Prof. CHEN Zhiduan's team from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBCAS) and international collaborators have identified the spatial heterogeneity of biodiversity hotspots and endemism centers. With ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] The surprising effect of presence hallucinations on social perceptionHow invisible presences hijack the social counting brain