(Press-News.org)
A new study reveals that many people living in extreme poverty in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) have conditions that lead to heart disease, the world’s #1 cause of death — overturning ‘conventional wisdom’.
In the largest analysis of its kind exploring the relationship between poverty and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, experts discovered a high prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and dyslipidemia in LMICs regardless of income —yet most adults living in extreme poverty were not treated for these CVD-related conditions.
An international group of researchers note that their findings, published today (13 March) in Nature Human Behaviour, contradict the common assumption that the environment (eg. food scarcity) and lifestyles (eg. more physical labour) of those living in extreme poverty in LMICs protect against CVD risk factors.
Professor Justine Davies, from the University of Birmingham, commented: “Our study turns conventional wisdom about the relationship between poverty and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors on its head. As LMICs develop economically, overweight and obesity prevalence among the poorest segments of their societies will increase – creating a rise in unhealthy weight, along with growth of diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.”
Evidence on CVD risk factor prevalence among adults living below the World Bank’s international line for extreme poverty is sparse. To address this paucity of needed information, the researchers pooled data from 105 nationally representative household surveys across 78 countries.
Pascal Geldsetzer, Assistant Professor of Medicine at Stanford University, USA, commented: “Our detailed analyses of how CVD risk factor prevalence and treatment coverage vary around the world could help to effectively target interventions and policies to reduce CVD risk in vulnerable populations. Moreover, our study provides a crucial empirical foundation for future work in improving health outcomes for those living in the poorest sections of global society.”
The study demonstrates that CVD risk factors affect individuals across the full socio-economic spectrum, including those living in extreme poverty, within countries at all levels of economic development.
Prof. Dr. Till Baernighausen, from Heidelberg University, commented: “People living in extreme poverty experience a high prevalence of CVD risk factors and low levels of treatment for these conditions, suggesting that we need to reassess health policy in this space.
“Understanding how an assumption of low prevalence of CVD risk factors among those in extreme poverty holds true is important for setting priorities within health policy and care delivery, both for equity and effectiveness.”
Countries included in the researchers’ dataset are estimated to be home to 85% of individuals living in extreme poverty worldwide, 53% of the global population, and 64% of the global population living in LMICs.
Sebastian Vollmer, Professor of Development Economics at the University of Göttingen, commented: “Further research into mechanisms of CVD risk specifically affecting individuals living in extreme poverty is essential – uncovering the different pathways that may predispose various groups to CVD risk will be vital in reducing that risk.”
END
A study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, and the Barcelona Supercomputing Center - Centro Nacional de Supercomputación (BSC-CNS), has consistently estimated daily ambient concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, NO2 and O3 across a large ensemble of European regions between 2003 and 2019 based on machine learning techniques. The aim was to assess the occurrence of days exceeding the 2021 guidelines of the World Health Organization (WHO) for one or multiple pollutants, referred to as “unclean air days”.
The ...
SPOKANE, Wash. – Exposure to several combinations of toxic atmospheric pollutants may be triggering asthma symptoms among children, a recent analysis suggests.
The study, published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, showed that 25 different combinations of air pollutants were associated with asthma symptoms among 269 elementary school children diagnosed with asthma in Spokane, Washington. In line with previous research, the Washington State University-led study revealed a socioeconomic disparity—with one group of children from a lower-income neighborhood exposed to more toxic combinations, a total of 13 of the 25 ...
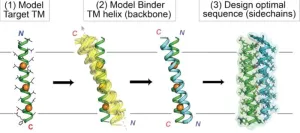
LA JOLLA, CA—Hitting targets embedded within the cell membrane has long been difficult for drug developers due to the membrane’s challenging biochemical properties. Now, Scripps Research chemists have demonstrated new custom-designed proteins that can efficiently reach these “intramembrane” targets.
In their study, published March 13, 2024, in Nature Chemical Biology, the researchers used a unique computer-based approach to design novel proteins targeting the membrane-spanning region of the erythropoietin (EPO) receptor, which controls red blood cell production and can go awry in cancers. In addition ...
A largescale new study has found that some people whose genetics are linked to the common iron overload condition haemochromatosis have substantially greater levels of liver, musculoskeletal and brain disease than previously reported, especially at older ages.
Haemochromatosis causes a build-up of iron in the body which can cause harm to joints and organs – although the extent of this harm is unclear, especially in older ages. The new research, led by a team at the University of Exeter and supported by the National Institute for Health and Care ...
One of the primary goals in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine is the development of artificial scaffolds that can serve as substitutes for damaged tissue. These materials must ideally resemble natural tissue and must have the ability to support cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. When considering scaffold materials, researchers account for the scaffold’s properties, such as its surface roughness, its water content (hydration state), and its flexibility or stiffness (elastic modulus), since these properties are known to affect cell ...
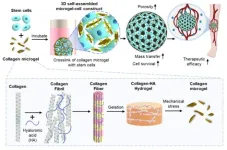
Critical limb ischemia is a condition in which the main blood vessels supplying blood to the legs are blocked, causing blood flow to gradually decrease as atherosclerosis progresses in the peripheral arteries. It is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that causes progressive closure of arteries in the lower extremity, leading to the necrosis of the leg tissue and eventual amputation. Current treatments include angioplasty procedures such as stent implantation and anti-thrombotic drugs, but there is a risk of blood vessel damage and recurrence of blood clots, which is why there is a strong interest ...
Philadelphia, March 13, 2024 – A new study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, published by Elsevier, challenges the prevailing view on the maternal death rate in the United States. The findings show that the rates of maternal death were stable between 1999-2002 and 2018-2021, instead of the dramatic upward trends previously reported by the National Vital Statistics System (NVSS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Additionally, the study indicates that direct obstetric causes of death declined over the last 20 years.
To determine whether the reported maternal death rates are accurate, a team of researchers took a deep dive into ...
Maternal death rates in the United States may be sharply overstated as a result of faulty surveillance techniques, according to an analysis by researchers at Rutgers Health and other universities.
The National Vital Statistics System (NVSS) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that maternal death rates have more than tripled over the last two decades to 32.9 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2021 – substantially more than in any other wealthy nation.
The new study that looked at all deaths in the United States from 1999 to 2021 published in The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology reports consistent death rates of slightly ...
What: Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered that symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are tied to atypical interactions between the brain’s frontal cortex and information processing centers deep in the brain. The researchers examined more than 10,000 functional brain images of youth with ADHD and published their results in the American Journal of Psychiatry. The study was led by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and National Human Genome Research Institute.
Luke Norman, Ph.D., a staff scientist in the NIMH Office of the Clinical Director, and colleagues ...
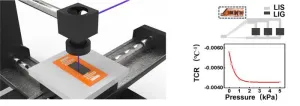
Laser direct writing (LDW) current researches mostly generate single type of materials for sensing layers or electrodes, while the sensor with different types of materials by LDW method is lacked. Researchers led by Prof. Gao Yang from East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST), China, are interested in expanded the application of LDW method, where can utilize the photo-thermal conversion, to synthesize materials and then engrave them with the desired morphologies and structures.
Focusing on the functionality of materials, the researchers use all-LDW method to generate laser induced silver (LIS) as electrodes and laser induced graphene ...