(Press-News.org) Rory James Tinker, MD is the recipient of the 2024 Richard King Trainee Award. This award was instituted by the ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine to encourage American Board of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ABMGG), international equivalents, or genetic counseling trainees in their careers and to foster the publication of the highest quality research in Genetics in Medicine (GIM), an official journal of the ACMG.
Each year the editorial board reviews all articles published in GIM by eligible trainees who were either a first or corresponding author during that year. The manuscript considered to have the most merit is selected by the editors. Dr. Tinker received the award for his article, “Phenotypic Presentation of Mendelian Disease Across the Diagnostic Trajectory in Electronic Health Records,” which was published online in GIM in October 2023.
Dr. Tinker hails originally from London, United Kingdom. Currently, he is a combined pediatrics and genetics resident at the Vanderbilt University Medical Center, where his work with children with genetic disorders inspired him to pursue a career in Pediatric Genetics. His principal academic interest is how genetic technology can identify, diagnose, and ultimately, treat rare disorders.
“I am so happy to have received the King Trainee Award from the ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine. I would like to dedicate this award to my fantastic genetic mentors at Vanderbilt, including Drs. Phillips, Bastarache, Peterson, Hamid, Agrawal and Grochowsky. But above all I am incredibly grateful for the inspiration my patients with genetic disease provide every day,” said Dr. Tinker.
“One of my favorite activities as GIM Editor-in-Chief is helping to choose the winner of the King Award every year. I always look forward in December to reviewing papers we’ve published by trainees the previous year. 2023 was a great year for trainee publications at GIM. We had a truly impressive selection of outstanding publications authored by trainees this past year. I am thrilled to announce that Dr. Rory James Tinker has been selected for his authorship. It will be a real delight to officially honor the awardee at this year’s ACMG Annual Clinical Genetics Meeting,” said Robert D. Steiner, MD, FAAP, FACMG, editor-in-chief of GIM.
The award is given by the ACMG Foundation and is named for Dr. Richard King in recognition of his instrumental role in creating Genetics in Medicine and serving as the first and founding editor-in-chief of the journal.
About the ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine
The ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, is a community of supporters and contributors who understand the importance of medical genetics and genomics in healthcare. Established in 1992, the ACMG Foundation supports the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) mission to “translate genes into health.” Through its work, the ACMG Foundation fosters charitable giving, promotes training opportunities to attract future medical geneticists and genetic counselors to the field, shares information about medical genetics and genomics, and sponsors important research. To learn more and support the ACMG Foundation mission to create “Better Health through Genetics” visit www.acmgfoundation.org.
Note to editors: To arrange interviews with experts in medical genetics, contact ACMG Senior Director of Communications and Public Relations, Kathy Moran, MBA at kmoran@acmg.net.
END
Rory James Tinker, MD receives the 2024 Richard King Award for Best Publication by a Trainee in Genetics in Medicine
2024-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ACMG Foundation/Revvity 2024 Travel Award presented to Meena Sethuraman, BS
2024-03-13
Meena Sethuraman, BS is the 2024 recipient of the ACMG Foundation/Revvity Travel Award. Ms. Sethuraman was selected to receive the award for her platform presentation, "Characterizing pathogenicity of ACADVL variants in very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.”
Meena Sethuraman is a third-year medical student in the Physician Scientist Training Program at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Her research, being conducted with Dr. Jerry Vockley, FACMG, involves studying genetic variants in fatty acid oxidation disorders. Meena previously received her BS in Neurobiology at the University of Washington. Her undergraduate and post-baccalaureate ...
The ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine presents seven Next Generation fellowship awards at the 2024 ACMG Annual Clinical Genetics Meeting
2024-03-13
Each year, the ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine grants its Next Generation fellowship awards to promising early career professionals in a range of medical genetics and genomics specialties including Clinical Biochemical Genetics Laboratory, Laboratory Genetics and Genomics, Medical Biochemical and Ophthalmic Genetics. Support for this year’s class of Fellows was generously provided by Pfizer, Sanofi, Spark Therapeutics, Bionano and Horizon Therapeutics. The ACMG Foundation depends on corporate ...
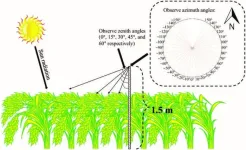
Enhancing crop productivity analysis: a novel approach using SIF and PRI for accurate GPP estimation in rice canopies
2024-03-13
Solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) and the photochemical reflectance index (PRI) have emerged as significant tools in assessing the photosynthetic and carbon sequestration capacities of terrestrial vegetation, particularly for estimating gross primary productivity (GPP). However, the relationship between SIF, PRI, and GPP encounters challenges due to large temporal and spatial variabilities as well as the influence of various observational factors such as canopy structure and physiological state. Despite the potential of multi-angle observations and the Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) model to mitigate these ...
The Alliance of World Scientists announces 2024 Planet Earth Award laureates
2024-03-13
Corvallis, OR — The Alliance of World Scientists (AWS) is pleased to announce the six recipients of the 2024 Planet Earth Award: Dr. S Faizi, Dr. James Hansen, Dr. Denise Margaret S. Matias, Dr. Kimberly Nicholas, Dr. Jamie Pittock, and Dr. Fernando Valladares.
Planet Earth Award
The AWS Planet Earth Award acknowledges individuals who champion life on Earth. These individuals demonstrate exceptional creativity or contributions in their work in science-based advocacy with the public, ...
Staying in the loop: how superconductors are helping computers “remember”
2024-03-13
Computers work in digits — 0s and 1s to be exact. Their calculations are digital; their processes are digital; even their memories are digital. All of which requires extraordinary power resources. As we look to the next evolution of computing and developing neuromorphic or “brain like” computing, those power requirements are unfeasible.
To advance neuromorphic computing, some researchers are looking at analog improvements. In other words, not just advancing software, but advancing hardware too. Research from the University of California San Diego and UC Riverside shows a promising new way to store and transmit information ...
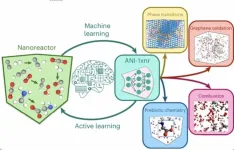
SMU chemist and colleagues develop machine learning model for atomic-level interactions
2024-03-13
DALLAS (SMU) – What exactly happens at the tiny scale at which individual atoms exist and interact? SMU chemist Elfi Kraka and her colleagues have been working on developing a computational tool aimed at providing answers to that mystery.
Mathematical functions used to calculate the potential energy of a system of atoms are called interatomic potentials. Machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIP)s have become an efficient and less expensive alternative to traditional quantum chemical simulations, which even on today’s high-performance computing often become out of reach for larger ...
Breastfeeding mothers who exercise pass on a beneficial hormone to their children
2024-03-13
Although women have breastfed since the beginning of time, there is very little scientific research on how exercise affects breast milk.
Online forums for pregnant women and new mothers are full of questions about this exact issue:
Can exercise cause breast milk to go sour? What happens to breast milk if you do high-intensity interval training? Will strenuous exercise affect your milk supply?
“There are so many myths about exercise and breast milk. We simply need more knowledge,” says researcher Trine Moholdt at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
She heads several international research projects ...
Christiana Wang, BS is the recipient of the 2024 ACMG Foundation/David L. Rimoin Inspiring Excellence Award
2024-03-13
The ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine is proud to present the ACMG Foundation/David L. Rimoin Inspiring Excellence Award to Christiana Wang, BS for her featured platform presentation at the 2024 ACMG Annual Clinical Genetics Meeting, “Antisense oligonucleotide targeting a linked-SNP provides allele-specific and effective knockdown to a dominant negative SPTAN1 pathogenic variant.”
Christiana Wang, BS, is a second-year PhD candidate in the Department of Molecular ...
New research at Georgia Aquarium helps conserve endangered beluga whales in Alaska
2024-03-13
ATLANTA – New data provided by studying the beluga whales at Georgia Aquarium helps close a key information gap about how much food these whales need to thrive. The information will inform important management decisions for their counterparts in Alaska’s Cook Inlet, which are protected under the U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA).
A new study released in the Journal of Experimental Biology, led by Terrie M. Williams, Director of the Integrative Carnivore EcoPhysiology Lab, with her graduate student Jason John at the University of California-Santa Cruz in partnership ...
Federal housing programs protect residents from lead exposure
2024-03-13
Americans already living in housing supported by federal housing assistance programs have significantly lower blood lead levels than counterparts who would later join these programs, according to new research led by environmental health scientists at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Tufts Medical Center. The findings appear in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
“Living in federally-supported housing—especially public housing—limited opportunities for residents’ exposure to lead,” says first author MyDzung Chu, Ph.D., assistant professor in the Institute for ...