Revolutionizing plant science: a groundbreaking method for expanding in situ root datasets using CycleGAN
2024-03-13
(Press-News.org)
The root system is crucial for plants to absorb water and nutrients, with in situ root research providing insights into root phenotypes and dynamics. While deep-learning-based root segmentation methods have advanced the analysis of root systems, they require extensive manually labeled datasets, which are labor-intensive and time-consuming to produce. Current methods of in situ root observation vary in their effectiveness. Moreover, traditional root image recognition methods face challenges such as subjectivity and low efficiency, whereas deep learning approaches offer improved accuracy but are hindered by the need for large, annotated datasets. Addressing the dataset limitation through innovative methods like CycleGAN for dataset generation presents a potential solution, yet challenges remain in ensuring the diversity and accuracy of the generated images for effective training and analysis in root segmentation studies.
In February 2024, Plant Phenomics published a research article entitled by “In Situ Root Dataset Expansion Strategy Based on an Improved CycleGAN Generator”.
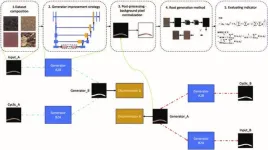
This research introduces a novel method for augmenting in situ root datasets through an improved CycleGAN generator, coupled with a spatial-coordinate-based method for target background separation, addressing the challenge of background pixel variation. By leveraging this approach, the study demonstrates significant enhancements in speed, accuracy, and stability over traditional threshold segmentation methods. The method also facilitates the inclusion of diverse culture mediums in root images, boosting dataset versatility. Experimental results, utilizing an RTX 3060 12 GB + 16 GB platform for training, show that the application of an Improved_UNet network to the augmented dataset yields a modest yet notable improvement in mean intersection over union (mIOU), F1 score, and accuracy, indicating the method's efficacy in improving dataset quality and generalization across different root system architectures. Specifically, the improved dataset contributed to a 0.63% increase in mIOU, 0.41% in F1 score, and 0.04% in accuracy, with generalization performance seeing even more significant increases. The research method involved detailed CycleGAN training with specific parameters and subsequent validation through comparative and subjective evaluations, including the input of various generator structures and postprocessing techniques.
In conclusion, the findings underscore the potential of the proposed dataset augmentation strategy to enhance the analysis of root systems, with future work aiming to achieve more realistic simulations through advanced shading and soil type variability. This expansion strategy, validated by the Improved_UNet network's performance on the augmented dataset, marks a promising advancement in root system analysis, offering a scalable solution to the limitations of existing root image datasets.
###
References
Authors
Qiushi Yu1†, Nan Wang1†, Hui Tang1, JiaXi Zhang1, Rui Xu2, and Liantao Liu3*
Affiliations
1College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hebei Agricultural University, 071000 Baoding, China.
2College of Foreign Languages, Hebei Agricultural University, 071000 Baoding, China.
3College of Agronomy, Hebei Agricultural University, 071000 Baoding, China.
About Liantao Liu
He is currently a Professor in the College of Agronomy at Hebei Agricultural University. His main research area is cotton cultivation physiology.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-13
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial of 345 patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, viral load rebound and symptom rebound were both common after a standard 5-day course of antiviral treatment with either VV116 or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir. Prolongation of treatment duration might be investigated to reduce COVID-19 rebound.
Authors: Yufang Bi, M.D., and Yiping Xu, M.Sc., of the Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
2024-03-13
About The Study: The findings of this study of 4,515 adolescents suggest that in-person schooling and several coping behaviors (caring for one’s body, exercising, and engaging in healthy behaviors) were associated with significantly higher positive affect and lower perceived stress during the COVID-19 pandemic among adolescents with high adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Adolescents with high ACEs demonstrated especially greater mental health scores when they reported in-person schooling. Future studies should build on these findings to identify clinical and school-based mental health protective ...
2024-03-13
Chlorophyll a fluorescence (ChlF) has been a pivotal tool in understanding plant photochemistry, offering insights into the energy transfer processes within chloroplasts and the efficiency of Photosystem II (PSII). Researchers have relied on quantifying ChlF through specific measures such as F0, Fm, and Fv under various lighting conditions to assess photosynthetic activities. Nonetheless, the technique encounters obstacles owing to the intrinsic uncertainties in gauging the absolute magnitude of ChlF and the fluctuation in baseline levels affected by environmental conditions. This complicates the interpretation of ...
2024-03-13
Allergic transfusion reactions (ATRs), a potentially life-threatening side effect of blood transfusions with unclear mechanisms, may be linked to food allergies in pediatric patients as per a recent study by scientists from Japan. They found that ATRs may be triggered by the presence of allergens in the donor’s blood, influenced by their pre-donation diet. These findings could pave the way for safer blood transfusions through the development of preventive measures and countermeasures for ATRs.
Blood transfusions are often life-saving procedures in various medical settings. They are required not only after severe blood loss ...
2024-03-13
Melissa A. Kelly, MS, CGC is the recipient of the 2024 ACMG Foundation Carolyn Mills Lovell Genetic Counselor Award. Ms. Kelly received the Lovell award for her platform presentation at the 2024 ACMG Annual Clinical Genetics Meeting, “Integrating genomic medicine into healthcare: Experience disclosing >5,000 clinically relevant results within the Geisinger MyCode Community Health Initiative.”
Ms. Kelly said, “Thank you to the ACMG Foundation. I am humbled and honored to receive the Carolyn Mills Lovell Genetic Counselor Award. Throughout my career, I have seen many ways in which patients and their families interact with and are impacted ...
2024-03-13
Rory James Tinker, MD is the recipient of the 2024 Richard King Trainee Award. This award was instituted by the ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine to encourage American Board of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ABMGG), international equivalents, or genetic counseling trainees in their careers and to foster the publication of the highest quality research in Genetics in Medicine (GIM), an official journal of the ACMG.
Each year the editorial board reviews all articles published in GIM by ...
2024-03-13
Meena Sethuraman, BS is the 2024 recipient of the ACMG Foundation/Revvity Travel Award. Ms. Sethuraman was selected to receive the award for her platform presentation, "Characterizing pathogenicity of ACADVL variants in very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.”
Meena Sethuraman is a third-year medical student in the Physician Scientist Training Program at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Her research, being conducted with Dr. Jerry Vockley, FACMG, involves studying genetic variants in fatty acid oxidation disorders. Meena previously received her BS in Neurobiology at the University of Washington. Her undergraduate and post-baccalaureate ...
2024-03-13
Each year, the ACMG Foundation for Genetic and Genomic Medicine grants its Next Generation fellowship awards to promising early career professionals in a range of medical genetics and genomics specialties including Clinical Biochemical Genetics Laboratory, Laboratory Genetics and Genomics, Medical Biochemical and Ophthalmic Genetics. Support for this year’s class of Fellows was generously provided by Pfizer, Sanofi, Spark Therapeutics, Bionano and Horizon Therapeutics. The ACMG Foundation depends on corporate ...
2024-03-13
Solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) and the photochemical reflectance index (PRI) have emerged as significant tools in assessing the photosynthetic and carbon sequestration capacities of terrestrial vegetation, particularly for estimating gross primary productivity (GPP). However, the relationship between SIF, PRI, and GPP encounters challenges due to large temporal and spatial variabilities as well as the influence of various observational factors such as canopy structure and physiological state. Despite the potential of multi-angle observations and the Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) model to mitigate these ...
2024-03-13
Corvallis, OR — The Alliance of World Scientists (AWS) is pleased to announce the six recipients of the 2024 Planet Earth Award: Dr. S Faizi, Dr. James Hansen, Dr. Denise Margaret S. Matias, Dr. Kimberly Nicholas, Dr. Jamie Pittock, and Dr. Fernando Valladares.
Planet Earth Award
The AWS Planet Earth Award acknowledges individuals who champion life on Earth. These individuals demonstrate exceptional creativity or contributions in their work in science-based advocacy with the public, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Revolutionizing plant science: a groundbreaking method for expanding in situ root datasets using CycleGAN