(Press-News.org) In preparation for the 2024 Olympic surfing competition, a new judging tower is being constructed in the reef lagoon at Teahupo’o, Tahiti. Researchers from the University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa, UH Hilo, and Arizona State University and community partners in Tahiti recently published a study in Remote Sensing that assessed the potential impacts of the tower and emphasized the importance of protecting the valuable reef—both as an integral part of the ecosystem and a resource for the local community.
“We hope the International Olympic Committee, appropriate government officials and the greater international community can see how devastating this impact will be to not only the valuable coral reef habitat, but also the local community who depend on this reef for their livelihood and well-being,” John Burns, lead author of the study, associate professor in marine science and data science at UH Hilo, and MEGA Lab member.
Although there is an existing judging tower used by the World Surf League, the Paris 2024 Olympic organizers intend to invest approximately $5 million USD to construct a substantially larger tower to provide amenities for judges including toilets, air conditioning, and capacity for 40 people.
The researchers teamed up with community members from Vai Ara O Teahupo’o and used 3D photogrammetry techniques to create high-resolution habitat maps of three sites that will be impacted by dredging and tower construction. The resulting mosaics were analyzed to quantify species diversity, coral colony count, coral colony size, and percent of the ocean floor covered by live coral and other living organisms.
The resulting data show these sites support healthy and diverse coral communities that contribute to the ecological function of the larger reef system at Teahupo’o. In the 322 square meters (about the size of a tennis court) where the tower would be located, they identified the presence of 1,003 corals from 20 different species, indicating this site is a thriving coral habitat.
“Although these organisms' value will never be fully represented through a capitalistic lens, based on U.S. valuations used by the Hawai‘i Division of Aquatic Resources, our data show the value of just the corals and algae at this small portion of the reef is estimated to be worth at least $170,000,” said Haunani Kane, co-author, assistant professor of Earth Sciences in the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology at UH Mānoa, and MEGA Lab member.
In addition to an assessment of the reef where the structure will be built, the team mapped the lagoon area where the reef is being dredged to accommodate barge transport of tower materials. This dredging could directly impact 2,500 square meters of the reef (about half the size of a football field). If this were to occur, the authors report, it could cause a financial impact of at least $1.3 million by damaging the live reef habitat.
The team’s impact estimates are conservative—only accounting for direct impacts and not including the potential financial impacts for communities who depend on these resources or the impact on the much greater lagoon area if water quality is affected.
“With information in hand about the ecological impact and community concern, we hope construction of the tower will be reassessed and also that these maps will help to hold any future disruptors accountable,” said Cliff Kapono, co-author, assistant professor at Arizona State University and MEGA Lab member. “There are alternatives to constructing a new tower, such as using the existing tower, which the World Surf League uses for competitions.”
END
Olympic tower construction at Teahupo’o, Tahiti could damage reef ecosystem
2024-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UNH ingenuity offers unique way to track carbon emissions in bodies of water
2024-03-14
DURHAM, N.H. — Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are not typically associated with water ways, like streams and rivers, but emerging research shows that water bodies play an important role in storing and releasing carbon dioxide. As many states look for cost-effective ways to mitigate climate change, scientists at the New Hampshire Agricultural Experiment Station at the University of New Hampshire looked at a way to optimize CO2 sensors to better measure carbon dioxide emissions in lotic, or moving, bodies of water offering a new tool that can help provide valuable information for everything from land use to climate action plans.
“These sensors, adapted for highly ...
Blast-related concussions linked to higher Alzheimer’s risk
2024-03-14
U.S. veterans of the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq who suffered mild traumatic brain injury from exposure to explosive blasts were found to have changes in cerebrospinal fluid proteins that are typically seen in people who develop Alzheimer’s disease, according to researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine and VA Puget Sound Health Care System.
“While our research does not prove that veterans who experienced these injuries will develop Alzheimer’s disease, it raises the possibility that ...
Modest rise in UK cancer cases but substantial decline in deaths over last 25 years
2024-03-14
Cases of cancer among UK men and women aged 35-69 years have seen a modest rise over the last quarter of a century, but there has also been a substantial decline in death rates, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The results show a fall in death rates for all cancers combined and for 17 out of 22 cancer types examined, which the researchers say is likely due to fewer people smoking, screening programmes, and improved treatment, while a rise in some less common cancers may be due to higher levels of overweight and obesity, ...
Cancer deaths plummet in middle-aged people
2024-03-14
A first of its kind study by Cancer Research UK reveals premature cancer death rates in 35–69-year-olds fell by more than a third over 25 years
Improvements in the UK are a result of smokefree policies, prevention measures, early detection programmes like cancer screening, and more effective treatment options
But the study paints a mixed picture with cancer cases on the rise and cancer mortality rates still too high
The charity’s manifesto, ‘Longer, ...
How to upcycle low-energy light
2024-03-14
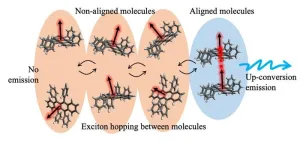
To combine two low-energy photons into one high-energy photon efficiently, the energy must be able to hop freely, but not too quickly, between randomly oriented molecules of a solid. This Kobe University discovery provides a much-needed design guideline for developing materials for more efficient PV cells, displays, or even anti-cancer therapies.
Light of different colors has different energies and is therefore useful for very different things. For the development of more efficient PV cells, OLED displays, or anti-cancer therapies it is desirable to be able to upcycle two low-energy photons into a high-energy photon, ...
Lives could be saved from tropical disease with new rapid test
2024-03-14
Globally, more than half of patients die after infection with the neglected tropical disease, melioidosis, often before they are diagnosed1. A new rapid test could save lives by diagnosing patients in hours, rather than several days taken by current bacterial culture methods, meaning they receive the correct antibiotics faster.
The test uses CRISPR to detect a genetic target that is specific to Burkholderia pseudomallei, the bacterium that causes melioidosis, with 93 per cent sensitivity. It was ...
Revolutionary chronic wound treatment could help millions
2024-03-14
Revolutionary chronic wound treatment could help millions
A team of international scientists has developed an effective treatment for preventing infection in chronic wounds that does not involve antibiotics
The treatment involves the plasma (electrical gas) activation of hydrogel dressings to produce a unique mix of different chemical oxidants that applied to the wound are effective in decontaminating and aiding healing in chronic wounds
The new method is a significant advance that could revolutionise the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and internal wounds
More than 540 million people ...
First-of-its-kind super minigene to boost spinal muscular atrophy research
2024-03-13
AMES, Iowa – Ravindra Singh has spent years studying a gene that when missing or mutated causes spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a deadly disease that’s among the most common genetic disorders in children. His team’s latest work will make the search for treatments even more effective in the years to come.
Singh, a professor of biomedical science at Iowa State University, led an eight-year project to create a truncated version of the Survival Motor Neuron 2 (SMN2) gene to facilitate quicker, cheaper and less fragmented research. Nucleic Acids Research, a peer-reviewed ...
NYU Tandon study exposes failings of measures to prevent illegal content generation by text-to-image AI models
2024-03-13
Researchers at NYU Tandon School of Engineering have revealed critical shortcomings in recently proposed methods aimed at making powerful text-to-image generative AI systems safer for public use.
In a paper that will be presented at the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), taking place in Vienna on May 7 - 11, 2024, the research team demonstrates how techniques that claim to "erase" the ability of models like Stable Diffusion to generate explicit, copyrighted, or otherwise unsafe ...
New analysis shows tirzepatide consistently reduces bodyweight regardless of body mass index (BMI) before treatment
2024-03-13
*Note – this is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity in Venice, Italy 12-15 May. Please credit the congress when using this research*
Tirzepatide, a medication authorised to treat obesity and/or type 2 diabetes, consistently reduces bodyweight regardless of the patient’s body mass index (BMI before treatment), from the range of overweight to class III obesity. The study, to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (Venice, Italy, 12-15 May) is by Prof Carel Le Roux, University ...