(Press-News.org) Expanding organic cropland can lead to increased pesticide use in surrounding conventional fields while reducing pesticide use on nearby organic fields, according to a study based in a leading U.S. crop-producing region. The findings provide insight into overlooked environmental impacts of organic agriculture and suggest that clustering organic fields could reduce pesticide use at the landscape scale. Organic agricultural practices are designed to have less negative local environmental impacts than other forms of intensive agriculture. However, the broader environmental and functional impacts of agricultural practices are only partially understood. By not using harmful chemical pesticides nor genetically modified seeds, organic cropland may function differently than conventionally managed fields, harboring more pest and beneficial species, or less. Some of these species may spill over into surrounding areas and affect pest control decisions for nearby fields. Using pesticide application data from nearly 100,000 observations from ~14,000 agricultural fields across Kern County, California – one of the leading crop-producing and pesticide-using counties in the U.S. – Ashley Larsen and colleagues evaluated how organic crop production influences pesticide use on surrounding organic and conventional fields. Larsen et al. found that organic fields can help reduce the use of pesticides in surrounding organic fields but increased their use in conventional fields. The level of pesticide use on conventional fields decreased the further away they were from nearby organic fields. By modeling the spatial configuration of different types of fields, the authors found that pests could be managed if organic and conventional fields were spatially segregated. When organic fields occupy a small share of acreage and are scattered across the landscape, expansion of organic farming increases overall pesticide use across the landscape. However, clustering organic fields close together lowers overall pesticide use on both organic and conventional farms by mitigating the spillover effects. Whether increasing pesticide use on conventional fields is due to spillover of pest species from organic fields or other farmer decision-making processes is unknown. “The analysis that Larsen et al. conducted documents how pesticide use can depend on the characteristics of neighboring farms, but it does not elucidate the mechanism that those patterns arise from,” writes Erik Lichtenberg in a related Perspective. “There is a continuing need for both ecological and economic fieldwork to elucidate the mechanisms at play.”
***A related embargoed news briefing was held at 11:00 a.m. U.S. ET on 19 March, as a Zoom Webinar. Video and audio recordings can be found here. The Science Advances paper mentioned during the Q&A is available here.***
END
Organic fields increase pesticide use in nearby conventional fields, but reduce it in organic neighbors
2024-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Revealed: A gene underlying visual mating behaviors in Heliconius butterflies
2024-03-21
A particular gene plays a critical role in visual preference for mate choice between closely related Heliconius butterflies, according to a new study. The findings provide insight into how visually guided behaviors can be encoded within the genome. Many species use color and other visual cues to attract and recognize suitable mates. As such, visual preferences are important drivers of mate choice and sexual selection. However, while the genetics and evolution of the traits that serve as these cues – such as butterfly wing color – are ...
Novel approach yields better single-copy artificial human chromosomes
2024-03-21
Constructing human artificial chromosomes (HACs) in budding yeast overcomes the long-standing problem of uncontrolled multimerization – the rampant joining of similar molecules – and results in HACs that are large, stable, and structurally well-defined, researchers report. The findings may help advance chromosome engineering for precise genome editing in mammals and many other organisms. Artificial chromosomes can carry large numbers of engineered genes. Their use in bacteria and yeast as vehicles for writing and rewriting genomes has hinted at their potential to provide an alternative approach to editing genetic material in human cell lines. Although the first HACs were ...
A path forward from the “equity versus excellence” conflict that has impeded mathematics education in U.S.
2024-03-21
In a Policy Forum, Alan Schoenfeld and Phil Daro argue that the “equity versus excellence” controversy over how mathematics is taught has long disrupted education in the United States, particularly for underrepresented ethnic and socioeconomic groups. According to Schoenfeld and Daro, K-12 mathematics education in the U.S. is structured in ways that are problematic and do not reflect international trends. For more than 50 years, the typical yet rigid sequence of hierarchical mathematics courses – algebra 1 to geometry to algebra II to precalculus to calculus – has disenfranchised ...
How butterflies choose mates: gene controls preferences
2024-03-21
Tropical Heliconius butterflies are well known for the bright colour patterns on their wings. These striking colour patterns not only scare off predators – the butterflies are poisonous and are distasteful to birds – but are also important signals during mate selection. A team led by evolutionary biologist Richard Merrill from LMU Munich, in cooperation with researchers from the Universidad del Rosario in Bogotá (Colombia) and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (Panama), has now exploited the diversity of warning patterns of various Heliconius species to investigate the genetic foundations of these preferences. ...
Mysterious exporter for brassinosteroid first identified
2024-03-21
When you are reading this article, there are multiple hormones working diligently inside your body to stabilize your health status. Same as human beings, it is impossible for plants to grow and reproduce without being regulated by phytohormones. One of the phytohormones is the Brassinosteroid (BR) hormones, also named as the sixth phytohormone.
According to a study published in Science on March 22, 2024, researchers led by Prof. SUN Linfeng from the Division of Life Sciences and Medicine of the University of Science and Technology ...
New reactor could save millions when making ingredients for plastics and rubber from natural gas
2024-03-21
Images
A new way to make an important ingredient for plastics, adhesives, carpet fibers, household cleaners and more from natural gas could reduce manufacturing costs in a post-petroleum economy by millions of dollars, thanks to a new chemical reactor designed by University of Michigan engineers.
The reactor creates propylene, a workhorse chemical that is also used to make a long list of industrial chemicals, including ingredients for nitrile rubber found in automotive hoses and seals as well as blue protective gloves. ...
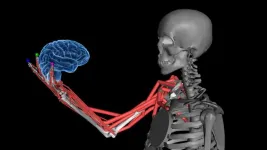
How the brain senses body position and movement
2024-03-21
How does your brain know the position and movement of your different body parts? The sense is known as proprioception, and it is something like a “sixth sense”, allowing us to move freely without constantly watching our limbs.
Proprioception involves a complex network of sensors embedded in our muscles that relay information about limb position and movement back to our brain. However, little is known about how the brain puts together the different signals it receives from muscles.
A new study led by Alexander Mathis at EPFL now sheds light on the question by exploring how our brains create a cohesive sense of body position and movement. Published in Cell, ...
Species diversity promotes ecosystem stability
2024-03-21
Species diversity promotes ecosystem stability
Biodiversity loss may accelerate ecosystem destabilization
What maintains stability within an ecosystem and prevents a single best competitor from displacing other species from a community? Does ecosystem stability depend upon the presence of a wide variety of species, as early ecologists believed, or does diversity do the exact opposite, and lead to instability, as modern theory predicts?
Resolving a long-standing debate among ecologists
A new study from McGill University and ...
University of Calgary research finds a direct communication path between the lungs and the brain
2024-03-21
University of Calgary researchers have discovered the lungs communicate directly with the brain when there is an infection. Findings show the brain plays a critical role in triggering the symptoms of sickness, which may change the way we treat respiratory infections and chronic conditions.
“The lungs are using the same sensors and neurons in the pain pathway to let the brain know there’s an infection,” says Dr. Bryan Yipp, MD '05, MSc'05, clinician researcher at the Cumming School of Medicine and ...
NSF awards grant for evolution-inspired design of therapeutic RNAs
2024-03-21
A team led by Dr. Samie Jaffrey, the Greenberg-Starr Professor of Pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been awarded a three-year, $1.65 million grant for RNA research under a biotechnology-development program run by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
The competitive Molecular Foundations for Biotechnology program funds cutting-edge research that lays the groundwork for future clinical and industrial biotechnologies. The new award is one of nine that have been given to research teams across the United States this year, with funding assistance from the National Institutes of Health, to advance the promise of RNA-based therapeutics and ...