(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this observational study of 20,000 adults suggest that a measure of follow-up colonoscopy within defined periods after an abnormal result of a stool-based screening test for colorectal cancer is warranted based on low current performance rates and would be feasible to collect by health systems and produce valid, reliable results.
Authors: Elizabeth L. Ciemins, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.A., of the American Medical Group Association in Alexandria, Virginia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=032524
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Development of a follow-up measure to ensure complete screening for colorectal cancer
JAMA Network Open
2024-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breakthrough in modeling
2024-03-25
Coastal seas form a complex transition zone between the two largest CO2 sinks in the global carbon cycle: land and ocean. Ocean researchers have now succeeded for the first time in investigating the role of the coastal ocean in a seamless model representation. The team led by Dr. Moritz Mathis from the Cluster of Excellence for Climate Research CLICCS at Universität Hamburg and the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon was able to show: The intensity of CO2 uptake is higher in coastal seas than in the open ocean. This is evidenced by a study published in the journal Nature Climate Change.
To ...
Citizen scientists contribute vital information about 35 seahorse species: their geographic ranges, habitats, and pregnancy seasonality
2024-03-25
Thanks to diligent observers, seahorses, those enigmatic and charismatic fish, are not only being discovered in new habitats and expanded geographic ranges, they are also being found at new ocean depths. While their capacity for male pregnancy has long fascinated people, new information on sex ratio and pregnancy seasonality has been discovered by, well, you.
Researchers from Project Seahorse – a marine conservation team based at the University of British Columbia (UBC) and the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) – identified and reviewed new findings related to 35 of the 46 seahorse species found around the globe, ...
An effective method for improving energy storage performance in (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-based lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics
2024-03-25
Next-generation advanced high/pulsed power capacitors urgently require dielectric materials with outstanding energy storage performance. (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-based material, a typical lead-free ferroelectrics, has the characteristics of high polarization strength and excellent component compatibility, making it emerge as a potential candidate for energy storage applications.
Researchers have made an interesting breakthrough in the modification of the BNT-based ferroelectrics, an effective method for various properties such ...
Online dashboard to help fight to save children from deadly diarrheal diseases
2024-03-25
University of Virginia researchers are developing a flexible online tool for navigating information used in the fight to save children from deadly diarrheal diseases by identifying transmission hotspots and accelerating the deployment of treatments and new vaccines.
Diarrhea not only kills hundreds of thousands of children around the world every year, it contributes to malnutrition that can prevent kids from growing and developing to their full potential both physically and mentally, trapping them in poverty. While significant progress has been made against the disease in recent years, the UVA researchers say that ...
Caller ID of the sea
2024-03-25
For researchers studying the acoustic behavior of whales, distinguishing which animal is vocalizing is like a teacher trying to figure out which student responded first when the entire class is calling out the answer. This is because many of the techniques used to capture audio record a large sample size of sounds. A major example of this is passive acoustic monitoring (PAM), which records audio via a microphone in one location, usually a stationary or moving platform in the ocean. While this method allows researchers to gather acoustic data over a long time period, it ...
SwRI develops more effective particle conversion surfaces for space instruments
2024-03-25
SAN ANTONIO — March 25, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute is investing internal funding to develop more effective conversion surfaces to allow future spacecraft instruments to collect and analyze low-energy particles. Conversion surfaces are ultra-smooth, ultra-thin surfaces covering a silicon wafer that convert neutral atoms into ions to more effectively detect particles from outer space.
Changing the charge of particles simplifies and enhances detection and analysis capabilities. Dr. Jianliang Lin of the Institute’s Mechanical Engineering Division and Dr. Justyna Sokół of SwRI’s Space Science Division lead the multidisciplinary project. The project builds ...
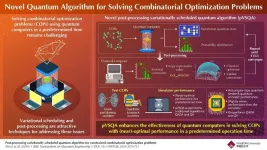
Novel quantum algorithm for high-quality solutions to combinatorial optimization problems
2024-03-25
Combinatorial optimization problems (COPs) have applications in many different fields such as logistics, supply chain management, machine learning, material design and drug discovery, among others, for finding the optimal solution to complex problems. These problems are usually very computationally intensive using classical computers and thus solving COPs using quantum computers has attracted significant attention from both academia and industry.
Quantum computers take advantage of the quantum property of superposition, using specialized qubits, that can exist in an infinite yet contained number of states of 0 or 1 or any combination of the two, to quickly ...
Persian plateau unveiled as crucial hub for early human migration out of Africa
2024-03-25
A new study combining genetic, palaeoecological, and archaeological evidence has unveiled the Persian Plateau as a pivotal geographic location serving as a hub for Homo sapiens during the early stages of their migration out of Africa.
This revelation sheds new light on the complex journey of human populations, challenging previous understandings of our species' expansion into Eurasia.
The study, published in Nature Communications, highlights a crucial period between approximately 70,000 to 45,000 years ago when human populations did not uniformly spread across Eurasia, ...
Honey bees at risk for colony collapse from longer, warmer fall seasons
2024-03-25
PULLMAN, Wash. – The famous work ethic of honey bees might spell disaster for these busy crop pollinators as the climate warms, new research indicates.
Flying shortens the lives of bees, and worker honey bees will fly to find flowers whenever the weather is right, regardless of how much honey is already in the hive. Using climate and bee population models, researchers found that increasingly long autumns with good flying weather for bees raises the likelihood of colony collapse in the spring.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, focused on the Pacific Northwest but holds implications for hives across the U.S. The researchers ...
20,000 years of shared history on the Persian plateau
2024-03-25
All present day non African human populations are the result of subdivisions that took place after their ancestors left Africa at least 60.000 years ago. How long did it take for these separations to take place? Almost 20.000 years, during which they were all part of a single population. Where did they live for all this time? We don’t know, yet.
This is a conversation that could have taken place one year ago, now it is possible to give clearer answers to these questions thanks to the study recently published in Nature Communications (1) led by the researchers from the University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Development of a follow-up measure to ensure complete screening for colorectal cancerJAMA Network Open