(Press-News.org) FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Recent historical, political and public health events, most notably the COVID-19 pandemic, have collectively contributed to increased stress and mental health challenges among many groups of people — including adolescents in racial and ethnic minorities.
In a study published Feb. 1 in Academic Pediatrics, Johns Hopkins Children’s Center researchers investigated the pandemic’s effect on preexisting mental health disparities among youth, and found rates of depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts and behaviors significantly increased during the pandemic and in the post-pandemic period, especially among Black, Asian and Hispanic females.
“Our findings show this is a real problem that we need to urgently address on all fronts,” says Laura Prichett, Ph.D., M.H.S., the first author of the study, an assistant professor in general pediatrics at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and a Building Interdisciplinary Research Careers in Women’s Health Scholar at the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research.
Using electronic medical record data from Johns Hopkins Community Physicians, a health care system with 40 locations throughout Maryland, researchers evaluated changes in annual rates of depression, anxiety and suicide risk-related diagnoses among 29,117 adolescents ranging in age from 8 to 20. Researchers organized participants into subgroups based on gender, race and ethnicity — Asian, Black, Hispanic and white young males and females.
The researchers found that almost all racial and gender subgroups had significantly higher rates of depression and anxiety after the start of the pandemic, compared to the years prior. Data shows rates of anxiety significantly increased — especially among Asian females, who saw a 136% increase (25.4 to 59.9 out of 1,000). In addition, rates of depression rose substantially among all subgroups, with the highest rates among females across all racial groups. Hispanic males had a 190% increase in rates of depression (12.1 to 35.1 out of 1,000). Researchers also found suicidal thoughts and behaviors substantially increased among all subgroups — most notably female subgroups, with the largest increases among Asian females, who saw a 171% increase (2.8 to 7.5 out of 1,000), and Black females, who had a 90.2% increase (5.1 to 9.7 out of 1,000).
The study authors note there are specific stressors and sociocultural constructs unique to each of the subgroups that are contributing to these mental health trends seen among adolescents. In addition to the stress caused by isolation from peers, economic concerns and health worries directly related to the COVID-19 pandemic, many of these subgroups have also experienced racism-specific stress.
However, the study authors note these trends could also reflect better identification of mental health indicators, increased willingness to ask practitioners for help or more openness to discuss mental health concerns.
“These trends we are seeing, I think are a combination of good things — like doctors noticing more that kids need help, and then really bad things having to do with the COVID-19 pandemic, isolation from peers, racism and financial stress,” says Prichett. “No matter what, it is clear that these past few years have significantly impacted young peoples’ mental health. This is a serious problem, and we need to take urgent action.”
Prichett and the other investigators believe there are important next steps to address the concern, including universal screening of youth in school and in primary care, broadening understanding of effective treatment and support options for patients and practitioners, and more funding for mental health support services for young people and their families at school, work and home.
If you want to learn more about the study and this important issue, Laura Prichett is available for interviews.
END
Johns Hopkins Children’s Center study shows negative impact of COVID-19 pandemic on youth minority mental health
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers a step closer to a cure for HIV
2024-03-26
By 2030, the World Health Organization (WHO), the Global Fund and UNAIDS are hoping to end the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS epidemic. An international team of researchers led by Eric Arts, professor at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and Jamie Mann, senior lecturer at the University of Bristol (U.K.), has brought us another step closer to meeting this goal, by finding an effective and affordable targeted treatment strategy for an HIV cure.
In a first, the study published ...
AI predicts the taste and quality of beer
2024-03-26
Leuven (Belgium) 26 March 2024 - Belgian scientists have developed AI models that can predict how a particular beer will be rated by consumers, and what aroma compounds brewers can add to improve it. The research was published today in the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications and may revolutionize how the food and beverage industry develops new products.
Tricky to compare
Comparing and ranking flavor profiles of different beers is a challenge. There are a multitude of guides on the market describing ...
A global map of how climate change is changing winegrowing regions
2024-03-26
Grapes grown to make wine are sensitive to climate conditions such as temperature and extreme drought. These effects are already visible worldwide on yields, the composition of grapes and the quality of wines, with already and soon-to-be-observed consequences on the geography of wine production. Understanding shifts in wine production potential due to climate change is a major scientific concern. Based on their expertise and a thorough analysis of the scientific literature — over 250 publications in the last 20 years – a research team has established a global map of evolving trends in the threats and potential benefits that climate change brings ...
SwRI’s Dr. Rohini Giles receives NASA Early Career Achievement Medal
2024-03-26
SAN ANTONIO — March 26, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute Senior Research Scientist Dr. Rohini Giles has received the NASA Early Career Achievement Medal. The medal recognizes unusual and significant performance supporting NASA’s mission during the first 10 years of their career. Giles was cited for “significant early career achievements in the analysis of Juno data to study Jovian Transient Luminous Events and the distribution of constituents in Jupiter’s atmosphere.”
“It’s ...
Sodium intake and cause-specific mortality among predominantly low-income Black and white residents
2024-03-26
About The Study: In this cohort study of 64,000 low-income Americans, nearly 80% of study participants consumed sodium exceeding the current recommended daily amount, which was associated with 10% to 30% of cardiovascular disease mortality. Public health programs targeted to reduce sodium intake among this underserved population may be beneficial.
Authors: Xiao-Ou Shu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3802)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Exclusive breastfeeding duration and risk of childhood cancers
2024-03-26
About The Study: In this cohort study including 309,000 Danish children, longer duration of exclusive breastfeeding was associated with reduced risk of childhood B-cell precursor-acute lymphoblastic leukemia, corroborating results of previous case-control investigations in this field. To inform future preemptive interventions, continued research should focus on the potential biologic mechanisms underlying the observed association.
Authors: Signe Holst Søegaard, Ph.D., of the Danish Cancer Society in Copenhagen, is the corresponding ...
Ancient DNA reveals origin of racial/ethnic disparity in a childhood cancer
2024-03-26
There are 40% more Hispanic/Latino kids diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) than white non-Hispanic/Latino children; actually, Hispanic/Latino individuals have the highest risk of ALL in the United States. However, the basis for this difference is not well understood. Researchers recently identified a genetic variant that accounts for the increased risk of B-cell ALL in Hispanic/Latino children, and using ancient DNA, they traced the mutation all the way back to the first migrants who ...
USC researchers find genetic variant contributing to disparities in childhood leukemia risk
2024-03-26
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood cancer, disproportionately affects children of Hispanic/Latino origin in the United States. They are 30-40% more likely to get ALL than non-Hispanic white children, but the exact genetic basis and cause of that increased risk are unknown.
Now, a study from the Keck School of Medicine of USC has revealed a key genetic variant contributing towards the increased risk, as well as details about the biological basis of ALL. The team used genetic fine-mapping analysis, a statistical method that allows researchers ...
Structural basis for the regulatory mechanism of mammalian mitochondrial respiratory chain megacomplex-I2III2IV2
2024-03-26
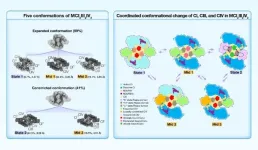
Mammalian mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes are the most important and complicated protein machinery in mitochondria. Although this system has been studied for more than a century, its composition and molecular mechanism are still largely unknown. Here, Yang’s group report the high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of porcine respiratory chain megacomplex-I2III2IV2 (MCI2III2IV2) in five different conformations, including State 1, State 2, Mid 1, Mid 2, and Mid 3. High-resolution cryo-EM imaging, combined with super-resolution gated stimulated emission depletion microscopy (gSTED), strongly supports ...
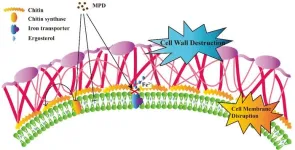
Antifungal activity of a maleimide derivative: Disruption of cell membranes and interference with iron ion homoeostasis
2024-03-26
This study is led by Prof. Ying Li (Xuzhou Medical University), Prof. Zuobin Zhu (Xuzhou Medical University), and Prof. Wenqiang Chang (Shandong University). A small molecule library consisting of 40 compounds, specifically N-substituted maleimide and its derivatives were initially screened in the study. Among them, twelve maleimides, each with a distinct N-protection group, were synthesized using ring-opening and ring-closing reactions involving various amines and maleic anhydride. Additionally, a set of twenty-eight ...