(Press-News.org) New research says the wide variety of skills displayed by people with conditions such as ADHD, dyslexia and autism should be celebrated to help reduce stigma and change society’s expectations.
Creativity, resilience and problem-solving are just some of the strengths exhibited and a study is now calling for a change in the way we think about people with neurodevelopmental conditions.
Dr Edwin Burns, senior lecturer from the School of Psychology at Swansea University, worked with academics from Edge Hill University on the study and their findings have just been published by online journal Neuropsychologia.
The researchers say people with these conditions are almost always discussed in terms of the problems that they face.
They are often characterised by a range of associated cognitive impairments in, for example, sensory processing, facial recognition, visual imagery, attention, and coordination.
However, Dr Burns said: “We would say that if only the wider public were aware that these groups exhibit many strengths and skills - some which are actually enhanced compared to the general population - then this should reduce stigma and improve their educational and employment outcomes.”
For the study, the team identified a wide variety of skills exhibited in different groups such as Williams syndrome, dyslexia, autism, ADHD, developmental coordination disorder, aphantasia.
These skills include improved social skills, creativity, problem-solving, resilience, and visual search.
The research also puts forward reasons why these skills occur such as genetics, experience adapting to the environment, repurposing the brain, and medication.
Dr Burns added: “In our research we present a table of potential strengths across conditions, and we hope that this may act as a stimulus for a major systematic review in the future. This should help reduce the stigma around neurodiversity, instead promoting greater social inclusion and significant societal benefits.”
END
Study says it’s time to highlight positive skills associated with neurodevelopmental conditions
People with conditions such as ADHD, dyslexia and autism have talents that deserve to be celebrated to help reduce stigma and change expectations
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Corporations use government grants to lighten debt load
2024-03-26
Local and state governments have a variety of tools at their disposal to attract businesses or entice them to stay. One is tax relief. Austin, for example, helped lure electric automaker Tesla in part with property tax rebates worth $14 million over 10 years.
In a study released today from Texas McCombs, Dean and Accounting Professor Lillian Mills finds that another kind of government aid — cash grants — has a different kind of impact. It helps companies lighten their balance sheets by borrowing less.
Corporations ...
C-Path launches consortium for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
2024-03-26
TUCSON, Ariz., March 26, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is excited to announce the launch of the Critical Path for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (CPA-1) Consortium. The CPA-1 consortium aims to accelerate drug development for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a rare disease that affects individuals and families worldwide. This will be achieved by integrating data through C-Path’s Rare Diseases Cures Accelerator–Data Analytics Platform (RDCA-DAP®) and leveraging those data for CPA-1 to collaboratively develop regulatory-grade solutions to continuously address unmet needs in drug development for this condition, including:
Generating evidence to ...
In paleontology, correct names are keys to accurate study
2024-03-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – When the skeletal remains of a giant ground sloth were first unearthed in 1796, the discovery marked one of the earliest paleontological finds in American history.
The animal, named Megalonyx by Thomas Jefferson in 1799, was the first genus of fossil named from the United States. Thought to have roamed North America during one of the last ice ages, the extinct giant ground sloth was an herbivorous mammal resembling a large bear — at full size, it likely reached nearly 10 feet tall (3 meters) and weighed about as much as a small elephant.
The report made by Jefferson, an avid fossil collector who was known to keep ...
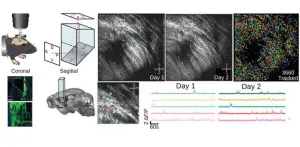
Imaging deep brain activity with microprisms
2024-03-26
Organisms constantly face the challenge of adapting their behavior to survive in a world full of uncertainties. This ability relies on complex neural circuits in the brain that help them find resources while avoiding danger. Scientists study how these neural circuits change over time to understand better how behaviors emerge.
One powerful way to study these changes is through optical imaging techniques that allow researchers to track the activity of individual brain cells. Traditional methods rely on observing the activity of cells directly, ...
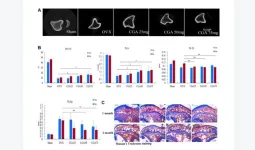
Chlorogenic acid prevents ovariectomized-induced bone loss by facilitating osteoblast functions and suppressing osteoclast formation
2024-03-26
“[...] chlorogenic acid appears to be a promising candidate for the management of osteoporosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 26, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 5, entitled, “Chlorogenic acid prevents ovariectomized-induced bone loss by facilitating osteoblast functions and suppressing osteoclast formation.”
Osteoporosis is a common bone disease in ...
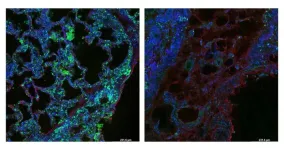
Researchers identify protein sensor that plays a role in lung fibrosis
2024-03-26
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have discovered a protein called SEL1L that plays a critical role in clearing collagen from tissue, and which may be a therapeutic target to help prevent fibrosis, scar tissue that interferes with organ function. The paper, published on Feb. 20 in Nature Communications, provides clues that could lead to drug development for diseases like lung fibrosis which have no therapeutic options currently.
Corresponding author, Dr. Michael J. Podolsky, assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, has led a team that searched the human genome for genes involved in the ...
Johns Hopkins Children’s Center study shows negative impact of COVID-19 pandemic on youth minority mental health
2024-03-26
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Recent historical, political and public health events, most notably the COVID-19 pandemic, have collectively contributed to increased stress and mental health challenges among many groups of people — including adolescents in racial and ethnic minorities.
In a study published Feb. 1 in Academic Pediatrics, Johns Hopkins Children’s Center researchers investigated the pandemic’s effect on preexisting mental health disparities among youth, and found rates of depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts and behaviors ...
Researchers a step closer to a cure for HIV
2024-03-26
By 2030, the World Health Organization (WHO), the Global Fund and UNAIDS are hoping to end the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS epidemic. An international team of researchers led by Eric Arts, professor at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and Jamie Mann, senior lecturer at the University of Bristol (U.K.), has brought us another step closer to meeting this goal, by finding an effective and affordable targeted treatment strategy for an HIV cure.
In a first, the study published ...
AI predicts the taste and quality of beer
2024-03-26
Leuven (Belgium) 26 March 2024 - Belgian scientists have developed AI models that can predict how a particular beer will be rated by consumers, and what aroma compounds brewers can add to improve it. The research was published today in the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications and may revolutionize how the food and beverage industry develops new products.
Tricky to compare
Comparing and ranking flavor profiles of different beers is a challenge. There are a multitude of guides on the market describing ...
A global map of how climate change is changing winegrowing regions
2024-03-26
Grapes grown to make wine are sensitive to climate conditions such as temperature and extreme drought. These effects are already visible worldwide on yields, the composition of grapes and the quality of wines, with already and soon-to-be-observed consequences on the geography of wine production. Understanding shifts in wine production potential due to climate change is a major scientific concern. Based on their expertise and a thorough analysis of the scientific literature — over 250 publications in the last 20 years – a research team has established a global map of evolving trends in the threats and potential benefits that climate change brings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Study says it’s time to highlight positive skills associated with neurodevelopmental conditionsPeople with conditions such as ADHD, dyslexia and autism have talents that deserve to be celebrated to help reduce stigma and change expectations