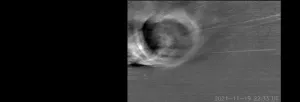
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON — The Wide-field Imager for Parker Solar Probe (WISPR) Science Team, led by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), captured the development of turbulence as a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) interacted with the ambient solar wind in the circumsolar space. This discovery is reported in the Astrophysical Journal.
Taking advantage of its unique location inside the Sun’s atmosphere, the NRL-built WISPR telescope on NASA’s Parker Solar Probe (PSP) mission, operated by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHUAPL), captured in unparalleled detail the interaction between a CME and the background ambient solar wind. To the surprise of the WISPR team, images from one of the telescopes showed what seemed like turbulent eddies, so-called Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities (KHI). Such structures have been imaged in the terrestrial atmosphere as trains of crescent wave-like clouds and are the results of strong wind shear between the upper and lower levels of the cloud. This phenomenon, while rarely imaged, is thought to occur regularly at the interface of fluid flows when the right conditions arise.
“We never anticipated that KHI structures could develop to large enough scales to be imaged in visible light CME images in the heliosphere when we designed the instrument,” said Angelos Vourlidas, Ph.D., JHUAPL and WISPR Project Scientist. “These fine detail observations show the power of the WISPR high sensitivity detector combined with the close-up vantage point afforded by Parker Solar Probe’s unique sun-encounter orbit,” said Mark Linton, Ph.D., head, NRL Heliophysics Theory and Modeling Section and Principal Investigator for the WISPR instrument.
The KHI structures were detected by the keen eye of an early career member of the WISPR team, Evangelos Paouris, Ph.D., George Mason University. Paouris, and his WISPR colleagues, undertook a thorough investigation to verify that the structures were indeed KHI waves. The results not only report an extremely rare phenomenon, even at Earth, but also open a new window of investigation with important consequences for the civilian and Department of Defense (DOD) communities.
“The turbulence that gives rise to KHI plays a fundamental role in regulating the dynamics of CMEs flowing through the ambient solar wind. Hence, understanding turbulence is key in achieving a deeper understanding of CME evolution and kinematics,” said Paouris. By extension, this knowledge will lead to more accurate forecasting of the arrival of CMEs in Earth’s vicinity and their effects on civilian and DOD space assets, thus safeguarding society and the warfighter.
“The direct imaging of extraordinary ephemeral phenomena like KHI with WISPR/PSP is a discovery that opens a new window to better understand CME propagation and their interaction with the ambient solar wind,” Paouris said.
WISPR is the only imaging instrument aboard the NASA Parker Solar Probe mission. The instrument, designed, developed and led by NRL, records visible-light images of the solar corona and solar outflow in two overlapping cameras that together observe more than 100-degrees angular width from the Sun. This NASA mission travels closer to the Sun than any other mission. PSP uses a series of Venus flyby’s to gradually reduce its perihelion from 36 solar radii in 2018 to 9.5 in 2025. The mission is approaching its 19th perihelion on March 30, 2024 at a distance of 11.5 solar radii from Sun center.
By observing the data the team found the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability is excited at the boundary between the CME and the ambient wind, as the two are flowing at distinctly different velocities. The resulting vortex-like structures are analyzed with respect to what the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability predicts, and inferences are presented about what the local magnetic field strength and density must be to allow such an instability in this environment.
About the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
NRL is a scientific and engineering command dedicated to research that drives innovative advances for the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps from the seafloor to space and in the information domain. NRL is located in Washington, D.C. with major field sites in Stennis Space Center, Mississippi; Key West, Florida; Monterey, California, and employs approximately 3,000 civilian scientists, engineers and support personnel.
For more information, contact NRL Corporate Communications at (202) 480-3746 or nrlpao@us.navy.mil.
END
WISPR team images turbulence within solar transients for the first time
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Undocumented immigrants faced unique mental health challenges during COVID-19 pandemic
2024-03-27
Four years after the U.S. shut down in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, research from Rice University suggests undocumented immigrants’ mental health challenges were compounded due to stresses stemming from their unauthorized status.
“Implications of Undocumented Status for Latinx Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Call to Action” appears in the Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology and examines how undocumented immigrants navigated the COVID-19 pandemic.
During a series of in-depth interviews with undocumented individuals or those from ...
Old immune systems revitalized in Stanford Medicine mouse study, improving vaccine response
2024-03-27
Planes, trains, boats, automobiles and even feet. During the past decades and centuries, global travel and human migration have made all of us more worldly — from our broadening awareness of the world beyond our birthplaces, to our more sophisticated palates, to our immune systems that are increasingly challenged by unfamiliar bacteria and viruses.
In the elderly, these newly imported pathogens can gain the upper hand frighteningly quickly. Unfortunately, however, vaccination in this age group isn’t as effective as it is in younger people.
Now a study conducted in mice by Stanford ...
Discovery has potential to solve the billion-dollar global cost of poorly managed wound healing
2024-03-27
Scientists have uncovered a key step in the wound healing process that becomes disabled in diseases like diabetes and ageing, contributing to a global healthcare cost of managing poorly healing wounds exceeding $250 billion a year. Importantly, the research published in Nature reveals a molecule involved in the healing of tissues that – when injected into animal models – leads to a drastic acceleration of wound closure, up to 2.5 times faster, and 1.6 times more muscle regeneration.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Mikaël Martino, from Monash University’s Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI) in Melbourne, Australia, said the discovery ...
Newly uncovered history of a key ocean current carries a warning on climate
2024-03-27
It carries more than 100 times as much water as all the world's rivers combined. It reaches from the ocean's surface to its bottom, and measures as much as 2,000 kilometers across. It connects the Indian, Atlantic and Pacific oceans, and plays a key role in regulating global climate. Continuously swirling around the southernmost continent, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current is by far the world's most powerful and consequential mover of water. In recent decades it has been speeding up, but scientists have been unsure whether ...
Evolution of the most powerful ocean current on Earth
2024-03-27
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current plays an important part in global overturning circulation, the exchange of heat and CO2 between the ocean and atmosphere, and the stability of Antarctica’s ice sheets. An international research team led by the Alfred Wegener Institute and the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory have now used sediments taken from the South Pacific to reconstruct the flow speed in the last 5.3 million years. Their data show that during glacial periods, the current slowed; during interglacials, it accelerated. Consequently, if ...
New topological metamaterial amplifies sound waves exponentially
2024-03-27
Researchers at AMOLF, in collaboration with partners from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, have realized a new type of metamaterial through which sound waves flow in an unprecedented fashion. It provides a novel form of amplification of mechanical vibrations, which has the potential to improve sensor technology and information processing devices. This metamaterial is the first instance of a so-called ‘bosonic Kitaev chain’, which gets its special properties from its nature as a topological material. It was realized by making nanomechanical resonators interact with laser light through radiation pressure forces. The discovery, which is published on March ...
Making long-term memories requires nerve-cell damage
2024-03-27
March 27, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Just as you can’t make an omelet without breaking eggs, scientists at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found that you can’t make long-term memories without DNA damage and brain inflammation. Their surprising findings were published online today in the journal Nature.
“Inflammation of brain neurons is usually considered to be a bad thing, since it can lead to neurological problems such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease,” said study leader Jelena Radulovic, M.D., Ph.D., professor in the Dominick P. Purpura Department of Neuroscience, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and the Sylvia ...
Anastasopoulos studying machine translation for Austronesian languages
2024-03-27
Anastasopoulos Studying Machine Translation For Austronesian Languages
Antonios Anastasopoulos, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding for: "Machine Translation for Austronesian Languages."
He is helping to develop a solution that can automatically translate languages of the southeast Asia and Pacific regions, with a particular focus on languages of lndonesia and the Philippines.
Anastasopoulos received $63,680 from Barron Associates, Inc., on a subaward from the U.S. Department of the Army for this project. Funding began ...
Complete sugarcane genome sequence opens up new era in breeding
2024-03-27
The first comprehensive reference genome for ‘R570’, a widely cultivated modern sugarcane hybrid, has been completed in a landmark advancement for agricultural biotechnology.
Sugarcane contributes $2.2 billion to the Australian economy and accounts for 80 per cent of global sugar supply. The mapping of its genetic blueprint opens opportunities for new tools to enhance breeding programs around the world for this valuable bioenergy and food crop.
It is one of the last major crops to be fully sequenced, due to the fact its genome is almost three times the size of humans’ and far more ...
Super permeable wearable electronics developed for stable, long-term biosignal monitoring by scientists at City University of Hong Kong
2024-03-27
Super wearable electronics that are lightweight, stretchable and increase sweat permeability by 400-fold have been developed by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK), enabling reliable long-term monitoring of biosignals for biomedical devices.
Led by Professor Yu Xinge in CityUHK’s Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME), the research team has recently developed a universal method to creating these super wearable electronics that allow gas and sweat permeability, solving the most critical issue facing wearable biomedical devices.
Wearable ...