(Press-News.org) New DNA sequencing technologies have identified the historical remains of George Washington’s grandnephews, Samuel Walter Washington and George Steptoe Washington Jr., and their mother, Lucy Payne Washington, from unmarked, fragmentary bones left at the Harewood family cemetery in Charles Town, West Virginia, in the mid-1800s.
In addition to enabling the remains in question to be reunited and reburied if desired, the researchers plan to apply the validated DNA analysis techniques to their ongoing efforts to identify the remains of service members lost around the world in past conflicts going back to World War II. The findings appear March 28 in the journal iScience.
“The ability to test historical samples such as the Harewood Cemetery remains allows us to evaluate and improve the methodologies applied to our casework samples that are of similar quality to historical remains, and often times even more degraded,” says first author Courtney Cavagnino of the Armed Forces Medical Examiner System’s Armed Forces DNA Identification Laboratory (AFMES-AFDIL) at the Dover Air Force Base.
“This particular case gave us an opportunity to test methods for extended kinship prediction that we developed using a set of known, degraded DNA samples needing identity confirmation,” says senior author Charla Marshall, Deputy Director of DoD DNA Operations. “Our laboratory is currently validating these novel methods to be used in routine casework.”
AFMES-AFDIL is the Department of Defense’s only human remains DNA laboratory, supporting current-day operations as well as the Defense POW/MIA Accounting Agency’s (DPAA) mission to identify service members from past conflicts extending back to World War II. In the new study, the AFMES-AFDIL team set out to identify remains from unmarked grave sites at Harewood Cemetery.
To confirm the suspected identities of the recovered remains, they performed a range of DNA tests of the remains together with analyses of the DNA from a living descendant, S.W. Washington. The methods included Y chromosome DNA analysis to assess paternal relationships, mitochondrial DNA sequencing to assess maternal relationships, and a newly developed method to analyze next generation sequencing (NGS) data including about 95,000 nuclear single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (places in the genome where there is a single-letter typo) to predict more distant ancestry.
Their pairwise kinship comparisons between the living descendant, S.W. Washington, and the three buried individuals predicted relationships one degree closer than anticipated, they note. While that was a surprise, they were able to figure out that was due to cross-cousin marriages in the Washington family tree.
“Our data confirmed the identities of the three sets of remains, and we furthermore resolved which male was the direct ancestor of S.W. Washington, the living descendant,” Marshall said.
The most common method used for DNA profiling in forensics is known as short tandem repeat (STR) analysis. But STR typing is often impossible to use with degraded remains, especially those preserved with post-war embalming techniques involving formaldehyde, Marshall says. Their newly developed methods now open the door to new ways of making a positive ID in these more difficult cases, including those involving service members lost in past conflicts whose remains contain only heavily degraded DNA.
“These SNP methods will provide us with a method of positive identification from nuclear DNA,” Marshall says. “Very importantly, these methods will allow us to expand our pool of viable family reference sample donors to 3rd and 4th degree relatives in an effort to increase the number of DNA-assisted identifications, particularly those of past conflicts such as World War II, Korea, Cold War, and Southeast Asia/Vietnam.”
###
This research received no external funding. Declarations of interest can be found in the published paper.
iScience, Cavagnino et al.: “Unearthing who and Y at Harewood Cemetery and inference of George Washington’s Y-chromosomal haplotype.” https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(24)00574-1
iScience (@iScience_CP) is an open-access journal from Cell Press that provides a platform for original research and interdisciplinary thinking in the life, physical, and earth sciences. The primary criterion for publication in iScience is a significant contribution to a relevant field combined with robust results and underlying methodology. Visit http://www.cell.com/iscience. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
Familial Alzheimer’s disease can be transferred via bone marrow transplant, researchers show March 28 in the journal Stem Cell Reports. When the team transplanted bone marrow stem cells from mice carrying a hereditary version of Alzheimer’s disease into normal lab mice, the recipients developed Alzheimer’s disease—and at an accelerated rate.
The study highlights the role of amyloid that originates outside of the brain in the development of Alzheimer’s disease, which changes the paradigm of Alzheimer’s from being a disease ...
About The Study: In this survey study of 204 oncologists, few reported that patients needed to understand artificial intelligence (AI) models, but most agreed that patients should consent to their use, and many tasked patients with choosing between physician- and AI-recommended treatment regimens. These findings suggest that the implementation of AI in oncology must include rigorous assessments of its effect on care decisions as well as decisional responsibility when problems related to AI use arise.
Authors: Gregory A. Abel, M.D., M.P.H., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To ...
About The Study: From 2013 to 2022, U.S. physicians received $12.1 billion from industry. More than half of physicians received at least one payment. Payments varied widely between specialties and between physicians within the same specialty. A small number of physicians received the largest amounts, often exceeding $1 million, while the median physician received much less, typically less than a hundred dollars.
Authors: Andrew J. Foy, M.D., of the Penn State Milton S. Hershey ...
BOSTON -- Andrew E. Place, MD, PhD, has been named as Vice President, Pediatric Chief Medical Officer (CMO) at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (within the Department of Pediatric Oncology) and Boston Children’s Hospital (within the Division of Hematology/Oncology) for the Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center.
In this role, Place will work closely with institutional and departmental leaders at Boston Children’s Hospital (BCH) and Dana-Farber to help define and implement clinical strategies and operational approaches that enhance smooth and efficient running of clinical care ...
UVA Health researchers have discovered a potential explanation for some of the most perplexing mysteries of COVID-19 and long COVID. The surprising findings could lead to new treatments for the difficult acute effects of COVID-19, long COVID and possibly other viruses.
Researchers led by UVA’s Steven L. Zeichner, MD, PhD, found that COVID-19 may prompt some people’s bodies to make antibodies that act like enzymes that the body naturally uses to regulate important functions – blood pressure, for example. Related enzymes also regulate ...
Just as many people battle seasonal colds and flu, native plants face their own viral threats. People have long known that plants can succumb to viruses just like humans. Now, a new study led by Michigan State University and the University of California, Riverside reveals a previously unknown threat: non-native crop viruses are infecting and jeopardizing the health of wild desert plants.
“For years, the ecological field assumed wild plants were immune to invasive viruses that damage crops,” said Carolyn ...
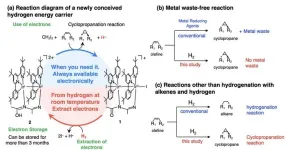
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University have developed a hydrogen energy carrier to address some of the biggest hurdles in the path towards a sustainable hydrogen economy. As explained in a paper published in JACS Au, this novel compound can efficiently “store electrons” from hydrogen in a solid state to use in chemical reactions later.
Hydrogen is a promising source of clean energy with a lot of untapped potential applications in industry and everyday life. Unlike conventional fuels, hydrogen can be used to generate electricity without producing greenhouse ...
Scientists at The Florey have developed an mRNA technology approach to target the toxic protein tau, which builds up in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
To date, mRNA has been predominantly used for vaccines, including those used to fight COVID-19.
New research published today in Brain Communications establishes The Florey as a key player in the mRNA field, with Dr Rebecca Nisbet taking the technology in a new direction.
“This is the first time mRNA has been explored for use in Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr Nisbet said. “Our work in cell models demonstrates that this technology ...
East Hanover, NJ – March 28, 2024 – Kessler Foundation received two grants from The New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research that will fuel innovative research in the field of spinal cord injury (SCI). These grants will fund efforts aimed at improving the cognitive assessment of individuals with traumatic SCI and pilot-testing the first-of-its-kind Spinal Cord Injury Personal Assistance Services Survey (SCI-PASS).
Traumatic spinal cord injury (tSCI) often leads to cognitive impairment, affecting up to 60 percent of individuals living with this condition. “The challenge lies in assessing cognitive functions in people with tSCI, as many existing tests rely on upper limb ...
Rising temperatures and disease outbreaks are decimating coral reefs throughout the tropics. Evidence suggests that higher latitude marine environments may provide crucial refuges for many at-risk, temperature-sensitive coral species. However, how coral populations expand into new areas and sustain themselves over time is constrained by the limited scope of modern observations.
What can thousands of years of history tell us about what lies ahead for coral reef communities? A lot. In a new study, Florida Atlantic University researchers and collaborators provide geological insights into coral range expansions by reconstructing the composition of a Late Holocene-aged subfossil coral ...