(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 1, 2024 — Adding milk to an alcoholic drink and then curdling that milk is a 300-year-old preservation technique that was used by none other than Ben Franklin. Join George as he discovers the chemistry that makes this technique so useful, and learn how to make the best espresso martini you’ll ever taste. https://youtu.be/ef0heKtiuvQ?si=W5uDUccoh_bOWtZy
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | Instagram
END
Using chemistry and a 300-year-old technique to reinvent a drink (video)
2024-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reducing hospitalizations and multidrug-resistant organisms via regional decolonization in hospitals and nursing homes
2024-04-01
About The Study: In this quality improvement study of 35 health care facilities in Orange County, California, using quasi-experimental design, chlorhexidine bathing and nasal decolonization were associated with significantly lower multidrug-resistant organism prevalence and incident clinical cultures. Infection-related hospitalizations, associated costs, and deaths among nursing home residents also decreased.
Authors: Susan S. Huang, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California Irvine School of Medicine in Irvine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
Reliability and validity of smartphone cognitive testing for frontotemporal lobar degeneration
2024-04-01
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that smartphones could offer a feasible, reliable, valid, and scalable solution for remote evaluations of frontotemporal lobar degeneration, a neurodegenerative pathology causing early-onset dementia syndromes, and may improve early detection. Smartphone assessments should be considered as a complementary approach to traditional in-person trial designs. Future research should validate these results in diverse populations and evaluate the utility of these tests for longitudinal monitoring.
Authors: Adam ...
App may pave way to treatments for no. 1 dementia in under-60s
2024-04-01
UCSF-led research shows smartphone cognitive testing is comparable to gold-standard methods; may detect FTD in gene carriers before symptoms start.
A smartphone app could enable greater participation in clinical trials for people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a devastating neurological disorder that often manifests in midlife.
Research into the condition has been hampered by problems with early diagnosis and difficulty tracking how people are responding to treatments that are only likely to be effective at the early stages ...
Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality
2024-04-01
About The Study: In this nationally representative cohort study, polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) exposure was significantly associated with an increased risk of cancer mortality. Since the 1970s, PBDEs have been used as flame retardants in a wide array of consumer products, such as building materials, furnishings, and electronics. Further studies are needed to replicate the findings and determine the underlying mechanisms.
Authors: Wei Bao, M.D., Ph.D., and Buyun Liu, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, Anhui, China, ...
Binge drinking among sports gamblers
2024-04-01
About The Study: In this survey study, binge drinking in both men and women was reported at greater frequency among sports wagering individuals compared with nongamblers and non–sports gamblers.
Authors: Joshua B. Grubbs, Ph.D., of the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5473)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
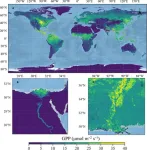
New satellite dataset sheds light on Earth's plant growth
2024-04-01
In the field of environmental and climate science, researchers have developed the Comprehensive Mechanistic Light Response (CMLR) gross primary production (GPP) dataset. Derived from the TROPOMI satellite's solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) observations, this global dataset offers unprecedented insights into Earth's GPP, the process through which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into essential resources.
Gross Primary Production (GPP), the process through which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into glucose and oxygen, is the Earth's largest carbon flux. Accurate quantification ...
Machine learning provides a new picture of the great gray owl
2024-04-01
The great gray owl has long been thought of as a sentinel of the Alaska wilderness, keeping watch over snow-laden forests as far north as the Brooks Range, well away from human populations.
In a study published last week with Nature Scientific Reports, a team of University of Alaska Fairbanks researchers upends the notion that the iconic bird — known as the phantom of the North — lives far from cities, towns and other markers of human density.
“We like to think of our wildlife, especially in Alaska, as existing in pristine wilderness untouched by humans,” said Falk Huettmann, professor ...
Pilot study shows ketogenic diet improves severe mental illness
2024-04-01
For people living with serious mental illness like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, standard treatment with antipsychotic medications can be a double-edged sword. While these drugs help regulate brain chemistry, they often cause metabolic side effects such as insulin resistance and obesity, which are distressing enough that many patients stop taking the medications.
Now, a pilot study led by Stanford Medicine researchers has found that a ketogenic diet not only restores metabolic health in these patients as they continue their medications, but it further improves their psychiatric conditions. The results, published March 27 in Psychiatry Research, suggest that a dietary intervention ...
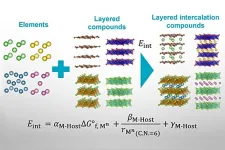
Physics-based predictive tool will speed up battery and superconductor research
2024-04-01
Tokyo, Japan – From lithium-ion batteries to next-generation superconductors, the functionality of many modern, advanced technologies depends on the physical property known as intercalation. Unfortunately, it's difficult to identify in advance which of the many possible intercalated materials are stable, which necessitates a lot of trial-and-error lab work in product development.
Now, in a study recently published in ACS Physical Chemistry Au, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, ...
New advance against a form of heart failure prevalent in men
2024-04-01
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a gene on the Y chromosome that contributes to the greater incidence of heart failure in men.
Y chromosome loss in men occurs progressively throughout life and can be detected in approximately 40% of 70-year-old men. UVA’s Kenneth Walsh, PhD, discovered in 2022 that this loss can contribute to heart muscle scarring and lead to deadly heart failure. (That finding was the first to directly link Y chromosome loss to a specific harm to men’s health; Y chromosome loss is increasingly thought ...