(Press-News.org) UC San Francisco researchers examined COVID-19 patients across the United States who survived some of the longest and most harrowing battles with the virus and found that about two-thirds still had physical, psychiatric, and cognitive problems for up to a year later.
The study, which appears April 10, 2024, in the journal Critical Care Medicine, reveals the life-altering impact of SARS-CoV-2 on these individuals, the majority of whom had to be placed on mechanical ventilators for an average of one month.
Too sick to be discharged to a skilled nursing home or rehabilitation facility, these patients were transferred instead to special hospitals known as long-term acute care hospitals (LTACHs). These hospitals specialize in weaning patients off ventilators and providing rehabilitation care, and they were a crucial part of the pandemic response.
Among the 156 study participants, 64% reported having a persistent impairment after one year, including physical (57%), respiratory (49%), psychiatric (24%), and cognitive (15%). Nearly half, or 47%, had more than one type of problem. And 19% continued to need supplemental oxygen.
The long-term follow up helps to outline the extent of the medical problems experienced by those who became seriously ill with COVID early in the pandemic.
“We have millions of survivors of the most severe and prolonged COVID illness globally,” said the study’s first author, Anil N. Makam, MD, MAS, an associate professor of medicine at UCSF. “Our study is important to understand their recovery and long-term impairments, and to provide a nuanced understanding of their life-changing experience.”
Disabilities from long-term hospital stays
Researchers recruited 156 people who had been transferred for COVID to one of nine LTACHs in Nebraska, Texas, Georgia, Kentucky, and Connecticut between March 2020 and February 2021. They questioned them by telephone or online a year after their hospitalization. The average total length of stay in the hospital and the LTACH for the group was about two months. Their average age was 65, and most said they had been healthy before getting COVID.
In addition to their lingering ailments from COVID, the participants also had persistent problems from their long hospital stays, including painful bedsores and nerve damage that limited the use of their arms or legs.
“Many of the participants we interviewed were most bothered by these complications, so preventing these from happening in the first place is key to recovery,” Makam said.
Although 79% said they had not returned to their usual health, 99% had returned home, and 60% of those who had previously been employed said they had gone back to work.
They were overwhelmingly grateful to have survived, often describing their survival as a “miracle.” But their recovery took longer than expected.
The results underscore that it is normal to for someone who has survived such severe illness to have persistent health problems.
“The long-lasting impairments we observed are common to survivors of any prolonged critical illness, and not specific to COVID, and are best addressed through multidisciplinary rehabilitation,” Makam said.
Authors: Additional UCSF co-authors include Oanh Kieu Nguyen, MD, MAS, Eddie Espejo, MA, Cinthia Blat, MPH, W. John Boscardin, PhD and Kenneth E. Covinsky, MD, MPH.
Funding: The work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging (K23AG052603), the UCSF Research Evaluation and Allocation Committee (Carson and Hampton Research Funds) and the National Association of Long Term Hospitals. The authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at https://ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Survivors of severe COVID face persistent health problems
Most of those who were discharged to long-term acute care centers had ailments that lasted for more than a year
2024-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New report ‘braids’ Indigenous and Western knowledge for forest adaptation strategies against climate change
2024-04-10
Link to release:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2024/04/10/forest-report/
Link to related coverage:
https://today.oregonstate.edu/news/indigenous-knowledge-western-science-braided-recommendations-land-managers
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at end)
For Immediate Release
April 10, 2024
There are 154 national forests in the United States, covering nearly 300,000 square miles of forests, woodlands, shrublands, wetlands, meadows ...
Improving dementia care in nursing homes: Learning from the pandemic years
2024-04-10
INDIANAPOLIS – No one associated with nursing homes – as residents or their families, friends, staff or administrators – is unaware of the massive impact of the pandemic on these facilities which provide essential services to a growing number of older adults, many living with cognitive impairment.
In “Learning from the experience of dementia care for nursing home residents during the pandemic,” an editorial published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of ...
Respiratory allergies: newly discovered molecule plays a major role in triggering inflammation
2024-04-10
The inflammation process plays a crucial role in allergic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. Although the pulmonary epithelium, the carpet of cells that forms the inner surface of the lungs, is recognised as a major player in the respiratory inflammation that causes these diseases, the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood.
A research team has identified one of the molecules responsible for triggering these allergic reactions, in a study co-led by two CNRS and Inserm scientists working at l’Institut de pharmacologie et de biologie structural (CNRS/Université Toulouse ...
A BiCIKL ride to the Empowering Biodiversity Research conference for a report on a 3-year endeavor towards FAIR biodiversity data
2024-04-10
Leiden - also known as the ‘City of Keys’ and the 'City of Discoveries' - was aptly chosen to host the third Empowering Biodiversity Research (EBR III) conference. The two-day conference - this time focusing on the utilisation of biodiversity data as a vehicle for biodiversity research to reach to Policy - was held in a no less fitting locality: the Naturalis Biodiversity Center.
On 25th and 26th March 2024, the delegates got the chance to learn more about the latest discoveries, trends and innovations from scientists, as well as various stakeholders, including representatives of policy-making bodies, research institutions and infrastructures. ...
Visiting white parts of town make some Black kids feel less safe
2024-04-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Some Black youth feel less safe when they visit predominantly white areas of their city, a new study in Columbus has found.
And it was those Black kids who spent the most time in white-dominated areas who felt less safe, said Christopher Browning, lead author of the study and professor of sociology at The Ohio State University.
“Familiarity with white neighborhoods doesn’t make Black kids feel more comfortable and safer. In fact, familiarity seems to reveal ...
Deforestation harms biodiversity of the Amazon’s perfume-loving orchid bees
2024-04-10
LAWRENCE — A survey of orchid bees in the Brazilian Amazon state of Rondônia, carried out in the 1990s, is shedding new light the impact of deforestation on the scent-collecting pollinators, which some view as bellwethers of biodiversity in the neotropics.
The findings, from a researcher at the University of Kansas, are published today in the peer-reviewed journal Biological Conservation.
“This study on orchid bees was an add-on to previous research on stingless bees. Orchid bees are so easy to collect, so we added them to ...
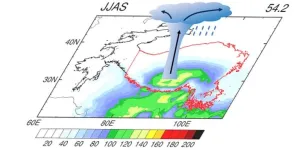
Long-term satellite observations show climatological characteristics of isolated deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau
2024-04-10
The Tibetan Plateau is a prevalent region for deep convection owing to its unique thermodynamic forcing. Deep convection can exist as isolated deep convection (IDC), which is small in size, or mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), which are convective storms organized into larger and longer-lived systems. Most previous research has focused on MCSs over the Tibetan Plateau, but less so on IDC systems (hereafter, IDCs).
Dr. Ying Na from Wuxi University, and Dr. Chaofan Li from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, examined the climatological features of IDCs by using high-resolution satellite observations in June to September ...
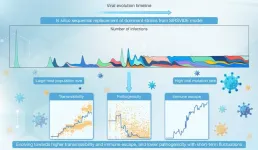
Modeling viral evolution: A novel SIRSVIDE framework with application to SARS-CoV-2 dynamics
2024-04-10
Understanding the mutation and evolution of viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2) is crucial for effective public health management and response. Traditional epidemiological models often assume that viral transmissibility and pathogenicity remain constant during disease transmission, ignoring the fact that viruses continuously evolve through natural selection and random mutations. This simplification limits the accuracy of these models in predicting epidemic trends, especially when facing rapidly mutating viruses.
To overcome these limitations, ...
New data: UTSA economic development institute added $2.6 billion to Texas’ economy
2024-04-10
SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS — The Valdez Institute for Economic Development (VIED) at UTSA generated an overall direct economic impact of $2.6 billion for the Texas economy in 2023, according to the organization’s 2023 annual report, which was released Tuesday.
The latest figure represents the work of the institute’s portfolio of time-tested economic development strategies and new innovations that enabled business owners and entrepreneurs to start and grow their small businesses.
During the 2023 fiscal year, the institute:
Served 41,231 business ...
Waterproof ‘e-glove’ could help scuba divers communicate
2024-04-10
When scuba divers need to say “I’m okay” or “Shark!” to their dive partners, they use hand signals to communicate visually. But sometimes these movements are difficult to see. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have constructed a waterproof “e-glove” that wirelessly transmits hand gestures made underwater to a computer that translates them into messages. The new technology could someday help divers communicate better with each other and with boat crews on the surface.
E-gloves — gloves fitted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Survivors of severe COVID face persistent health problemsMost of those who were discharged to long-term acute care centers had ailments that lasted for more than a year