(Press-News.org) Alzheimer’s disease (AD) currently afflicts nearly seven million people in the U.S. With this number expected to grow to nearly 13 million by 2050, the lack of meaningful therapies represents a major unmet medical need. Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys have now identified promising real-world links between common HIV drugs and a reduced incidence of AD. The study, led by Jerold Chun, M.D., Ph.D., was published in Pharmaceuticals.
Chun’s new research builds on his lab’s landmark publication in Nature in 2018 that described how somatic gene recombination in neurons can produce thousands of new gene variants within Alzheimer’s disease brains. Importantly, it also revealed for the first time how the Alzheimer’s-linked gene, APP, is recombined by using the same type of enzyme found in HIV.
The enzyme, called reverse transcriptase (RT), copies RNA molecules and changes them into complementary DNA duplicates that can then be inserted back into DNA, producing permanent sequence changes within the cell’s DNA blueprint.
HIV and many other viruses rely on RT to hijack a host’s cells to establish a chronic infection, so drugs that block the RT enzyme’s activity have become a common part of treatment cocktails for keeping HIV at bay.
The brain appears to have its own RTs that are different from those in viruses, and the research team wondered if inhibiting brain RTs with HIV drugs actually helps AD patients.
To assess the link between real-world RT inhibitor exposure and AD in humans, the team analyzed anonymized medical records with prescription claims from more than 225,000 control and HIV-positive patients, and found that RT inhibitor exposure was associated with a statistically significant reduced incidence and prevalence of AD.
“Thus, we looked at HIV-positive individuals taking RT inhibitors and other combined antiretroviral therapies as they aged, and asked the question: How many of them got Alzheimer’s disease?” says Chun. “And the answer is that there were many fewer than might have been expected compared to the general population.”
Of the more than 225,000 individuals with claims data in the study, just shy of 80,000 were HIV-positive individuals over the age of 60. More than 46,000 had taken RT inhibitors during a nearly three-year observation period from 2016 to 2019. The data was obtained through a collaboration with health information technology and clinical research firm IQVIA, led by Tiffany Chow, M.D.
In living persons with HIV, there were 2.46 Alzheimer’s disease diagnoses per 1,000 persons among HIV-positive individuals taking these inhibitors, versus 6.15 for the general population. This control group was represented by more than 150,000 HIV-negative patients over the age of 60 with medical insurance claims related to treatment for the common cold.
“You cannot feasibly run a prospective clinical trial with this number of patients,” Chun adds. “This approach is a way to look at how a drug can act on a large patient population.”
Chun underscores that the drugs patients took in this retrospective study were designed to counter RT activity in HIV and likely only had a limited effect on many different possible forms of the enzyme active in the brain.
“What we’re looking at now is very crude,” says Chun. “The clear next step for our lab is to identify which versions of RTs are at work in the AD brain so that more targeted treatments can be discovered, while prospective clinical trials of currently available RT inhibitors on persons with early AD should be pursued.”
Jerold Chun, M.D. Ph.D., is a professor in the Center for Genetic Disorders and Aging Research at Sanford Burnham Prebys.
Additional authors on the study include Tiffany W. Chow, Mark Raupp, Matthew W. Reynolds, Siying Li and Gwendolyn E. Kaeser.
The work was supported by the National Institute on Aging – NIH (R01AG071465, R01AG065541 and R56AG073965), the Shaffer Family Foundation and the Bruce Ford & Anne Smith Bundy Foundation.
The study’s DOI is 10.3390/ph17040408.
END
Common HIV treatments may aid Alzheimer’s disease patients
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys uncover beneficial links between certain HIV drugs and Alzheimer’s disease.
2024-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Turner to receive funding for Israel Institute Postdoctoral Fellowship
2024-04-16
John Turner, Professor, Religious Studies, is set to receive funding for: “Israel Institute Postdoctoral Fellowship.”
This funding will support a postdoctoral teaching fellow for three (3) academic years starting in fall 2024.
Regarding the importance of this funding, Turner said, “Curricula across academic units at George Mason contain very little material about the modern State of Israel, a significant gap given the importance of the nation and region to contemporary politics and conflict. This grant will enable RELI to address this gap and add content on this important subject.”
Turner will receive $248,460 from Israel ...
How AI improves physician and nurse collaboration
2024-04-16
With large language models that take notes during patient visits and algorithms that identify disease, artificial intelligence has begun to prove its worth as an assistant for physicians. But a new study from Stanford Medicine shows the potential of AI as a facilitator — one that helps doctors and nurses connect to achieve more efficient, effective patient care.
The study, which published in JAMA Internal Medicine last month, describes an AI-based model in use at Stanford Hospital that ...
Diverse native wildflower plantings for pollinators in farmlands
2024-04-16
Pollinators are declining rapidly, largely due to land conversion and intensification of agriculture. To mitigate their crisis, low-disturbance habitats, such as sown wildflower plantings (commonly known forms are wildflower strips at the edges of arable fields), could promote pollinators by restoration of their resources (food, sheltering and nesting habitats). However, comprehensive knowledge is lacking on how landscape context, spatial configuration and age of wildflower plantings, seasonality and flower composition affect pollinator communities, especially from East-Central Europe.
To understand these effects, researchers from the HUN-REN Centre for Ecological Research, established ...
Study suggests adolescent stress may raise risk of postpartum depression in adults
2024-04-16
In a new study, a Johns Hopkins Medicine-led research team reports that social stress during adolescence in female mice later results in prolonged elevation of the hormone cortisol after they give birth. The researchers say this corresponds to the equivalent hormonal changes in postpartum women who were exposed to adverse early life experiences — suggesting that early life stress may underlie a pathophysiological exacerbation of postpartum depression (PPD).
The team’s findings, first published online Apr. 11, 2024, in Nature Mental Health, also suggest that current drug ...
New book gathers insights, methods from rising generation of Indigenous archaeologists
2024-04-16
LAWRENCE — A book co-edited by a University of Kansas scholar that collects the experiences and know-how of younger Indigenous archaeologists, titled “Indigenizing Archaeology: Putting Theory into Practice,” is newly published by the University Press of Florida.
Carlton Shield Chief Gover, acting assistant professor of anthropology and acting assistant curator of archaeology at KU, conceived and co-edited the new volume. Its chapters include lessons and case studies from the discipline.
“This is the first book to our knowledge completely comprised of Indigenous scholars in ...
Scientists identify cell vulnerability ‘fingerprint’ related to Parkinson’s, Lewy body dementia
2024-04-16
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (April 16, 2024) — A new study from Van Andel Institute scientists offers a first look into the complex molecular changes that occur in brain cells with Lewy bodies, which are key pathological hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease and some dementias.
The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, reveal that brain cells with Lewy bodies exhibit a specific gene expression pattern akin to a disease-related fingerprint.
“We’ve long known that Lewy bodies play a role in Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases but there are still many ...
Cooler transformers could help electric grid
2024-04-16
Most people do not give the U.S. electric grid a second thought — we flip a switch and the lights come on. Behind the scenes are thousands of power plants and utilities linked by millions of miles of transmission lines. And to make raw electricity useful, grid transformers convert high voltage to lower voltage that millions of households can plug into.
Transformers are aging and approaching an average of being 30 to 40 years old. Plus, they face more stress than ever before brought on by factors such as renewable energy and by extreme weather events such as hurricanes, heat waves, and winter storms. Case in point — the 2021 event in Texas that ...
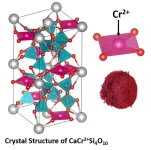
Oregon State researchers advance pigment chemistry with moon-inspired reddish magentas
2024-04-16
CORVALLIS, Oregon – An Oregon State University researcher who made color history in 2009 with a vivid blue pigment has developed durable, reddish magentas inspired by lunar mineralogy and ancient Egyptian chemistry.
Mas Subramanian, distinguished professor of chemistry, and collaborators at OSU report the findings of the study, funded by the National Science Foundation, in the journal Chemistry of Materials.
The new pigments, which could be used as energy-efficient coatings for vehicles and buildings, are based on divalent chromium, Cr2+, and are ...
Conformity to masculine gender norms is linked to muscle dysmorphia among young people
2024-04-16
Toronto, ON - A new research study out of the University of Toronto sheds light on the intricate relationship between conformity to masculine gender norms and muscle dysmorphia symptomatology among a diverse sample of Canadian adolescents and young adults. The study entitled "Exploring the Association Between Conformity to Masculine Gender Norms and Muscle Dysmorphia Symptomatology in a Gender-Diverse Canadian Population" was recently published in the journal Sex Roles.
Muscle dysmorphia, characterized ...
EuBiologics’ simplified OCV achieves WHO PQ
2024-04-16
- Euvichol-S, developed jointly by EuBiologics and IVI, improves productivity by approximately 40% over Euvichol-Plus®
- Production and supply of Euvichol-S expected to help address cholera vaccine shortages
April 15, 2024, SEOUL, Republic of Korea – EuBiologics and the International Vaccine Institute (IVI) announced that Euvichol-S, an improved oral cholera vaccine (OCV) developed jointly by EuBiologics and IVI, has achieved World Health Organization prequalification (PQ). Euvichol-S ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Common HIV treatments may aid Alzheimer’s disease patientsScientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys uncover beneficial links between certain HIV drugs and Alzheimer’s disease.