(Press-News.org) LAWRENCE — A book co-edited by a University of Kansas scholar that collects the experiences and know-how of younger Indigenous archaeologists, titled “Indigenizing Archaeology: Putting Theory into Practice,” is newly published by the University Press of Florida.
Carlton Shield Chief Gover, acting assistant professor of anthropology and acting assistant curator of archaeology at KU, conceived and co-edited the new volume. Its chapters include lessons and case studies from the discipline.
“This is the first book to our knowledge completely comprised of Indigenous scholars in archaeology, including our copy editors,” said Shield Chief Gover. “What makes this form of archaeology different within the field is its methods. This book is the ‘how-tos’ of Indigenous archaeology. It reflects how different people from different tribes do their version of archaeology. There’s not just some monolith of Native Americans. Rather, each nation has its own way of doing archaeology based on their own cultural practices.”
Shield Chief Gover said the book’s contributors were mostly scholars in early stages of their careers.
“My colleague and co-editor (Emily Van Alst, anthropologist at Washington State University) and I started this project when we were early in our Ph.D.s,” he said. “Everyone’s contributions in this volume are based either on their master's thesis or doctoral work. So, we’re all junior academics reflecting on how we were able to get through school and the methods that it took.”
According to Shield Chief Gover, the new tome is geared toward a general readership as a practical guide to Indigenous archaeology rather than a theoretical treatise. He said the rise of the field of Indigenous archaeology can be traced to passage of the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act in the 1990s.
“That’s what forced archaeologists and Indigenous people to sit down at the table with one another as equals to actually explore, ‘OK, well, how do we get these individuals and their grave goods back home to their communities — and which communities do they belong to?’” he said. “A lot at the base level of Indigenous archaeology is communication and collaboration. It's just engaging with the communities that you used to do research ‘on.’ Now you're doing research ‘with’ and having communities incorporated from beginning to end so they're part of the entire process, not just this little back-end piece, which was called ‘consulting.’ You did all the work; you did the research questions. Then, at the end you'd ask, ‘OK, hey, what do you guys think about this?’ You know, just to check a box.”
Shield Chief Gover said his fellow contributors’ insights and experiences especially benefit Indigenous cultural staff at institutions around the country and internationally.
“We’re hoping this book could be a tool for them to replicate our work through their own nationhood and to move their nations forward with archaeology,” he said. “It's really distinct from what’s been published before, which have been mostly theoretical ideas by well-established authors writing for scholars in this field. But our book is meant for the average NAGPRA officer or tribal historic preservation officer or early rising students in the field of archaeology, both Indigenous and non-Indigenous.”
Shield Chief Gover’s own contributed chapter reflects on his experiences as a graduate student on his way to becoming the first Pawnee academic archaeologist (as well as a member of a profession that often collided with Indigenous interests historically).
“It was difficult,” said the KU researcher. “My chapter reflects on how I did my master’s thesis. I struggled to communicate my thesis to my community and family, because it was so dense with statistics and the lexicon. So, I really looked at this chapter as an opportunity to say, ‘Well, this is how I went about it. This is why this is important. This is what it means. And this is how other cultural staff can utilize it to serve their own tribes’ purposes.’ At Wyoming, I was the only Indigenous graduate student there. I didn't even know there was a field of Indigenous archaeology.”
Shield Chief Gover said it wasn’t until he started working on his doctorate later at the University of Colorado at Boulder that he encountered a body of scholarly work by Indigenous archaeologists. In part, he hopes his new volume will make the field more accessible to young academics in a similar position.
“Until then, I had no idea of these resources — I was just on my own, or at least I thought I was,” he said. “Then I realized there was already literature about Indigenous archaeology and there were already people doing what I had ‘Forrest Gumped’ myself into on my own. I felt having a book dedicated less to the theory, but more to the methods would help other folks realize, ‘Oh, this is the actual nuts and bolts of how to do this’ — rather than, ‘Well, this is why you should do it and why it's important.’ Instead, we talk about where the rubber meets the road.”
To ensure the volume will be available to all with an interest in Indigenous archaeology, Shield Chief Gover and his colleagues made a point of providing a digital open-access copy.
“You can get an online copy of this book for free from the University Press of Florida,” he said. “We wanted to make our content freely accessible to disadvantaged communities that might not have $30 to spend, and we really wanted this accessible to cultural staff in Indian Country so they can readily have it to be employed by their offices.”
END
New book gathers insights, methods from rising generation of Indigenous archaeologists
2024-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists identify cell vulnerability ‘fingerprint’ related to Parkinson’s, Lewy body dementia
2024-04-16
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (April 16, 2024) — A new study from Van Andel Institute scientists offers a first look into the complex molecular changes that occur in brain cells with Lewy bodies, which are key pathological hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease and some dementias.
The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, reveal that brain cells with Lewy bodies exhibit a specific gene expression pattern akin to a disease-related fingerprint.
“We’ve long known that Lewy bodies play a role in Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases but there are still many ...
Cooler transformers could help electric grid
2024-04-16
Most people do not give the U.S. electric grid a second thought — we flip a switch and the lights come on. Behind the scenes are thousands of power plants and utilities linked by millions of miles of transmission lines. And to make raw electricity useful, grid transformers convert high voltage to lower voltage that millions of households can plug into.
Transformers are aging and approaching an average of being 30 to 40 years old. Plus, they face more stress than ever before brought on by factors such as renewable energy and by extreme weather events such as hurricanes, heat waves, and winter storms. Case in point — the 2021 event in Texas that ...
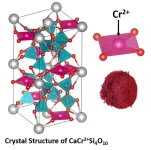
Oregon State researchers advance pigment chemistry with moon-inspired reddish magentas
2024-04-16
CORVALLIS, Oregon – An Oregon State University researcher who made color history in 2009 with a vivid blue pigment has developed durable, reddish magentas inspired by lunar mineralogy and ancient Egyptian chemistry.
Mas Subramanian, distinguished professor of chemistry, and collaborators at OSU report the findings of the study, funded by the National Science Foundation, in the journal Chemistry of Materials.
The new pigments, which could be used as energy-efficient coatings for vehicles and buildings, are based on divalent chromium, Cr2+, and are ...
Conformity to masculine gender norms is linked to muscle dysmorphia among young people
2024-04-16
Toronto, ON - A new research study out of the University of Toronto sheds light on the intricate relationship between conformity to masculine gender norms and muscle dysmorphia symptomatology among a diverse sample of Canadian adolescents and young adults. The study entitled "Exploring the Association Between Conformity to Masculine Gender Norms and Muscle Dysmorphia Symptomatology in a Gender-Diverse Canadian Population" was recently published in the journal Sex Roles.
Muscle dysmorphia, characterized ...
EuBiologics’ simplified OCV achieves WHO PQ
2024-04-16
- Euvichol-S, developed jointly by EuBiologics and IVI, improves productivity by approximately 40% over Euvichol-Plus®
- Production and supply of Euvichol-S expected to help address cholera vaccine shortages
April 15, 2024, SEOUL, Republic of Korea – EuBiologics and the International Vaccine Institute (IVI) announced that Euvichol-S, an improved oral cholera vaccine (OCV) developed jointly by EuBiologics and IVI, has achieved World Health Organization prequalification (PQ). Euvichol-S ...
GPT-4 matches radiologists in detecting errors in radiology reports
2024-04-16
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Large language model GPT-4 matched the performance of radiologists in detecting errors in radiology reports, according to research published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Errors in radiology reports may occur due to resident-to-attending discrepancies, speech recognition inaccuracies and high workload. Large language models, such as GPT-4, have the potential to enhance the report generation process.
“Our research offers a novel examination of the potential of OpenAI’s GPT-4,” said study lead author Roman J. Gertz, M.D., resident in the Department ...
SwRI to discuss automotive decarbonization, automation at SAE International’s WCX™ 2024
2024-04-16
SAN ANTONIO — August 16, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute helps the automotive industry transition to smart, sustainable mobility, developing hybrid, electric and hydrogen solutions and applying artificial intelligence for safe, eco-friendly driving. SwRI engineers will be in Detroit April 16-18 to share their expertise at the 2024 SAE International WCX™ World Congress Experience.
WCX invites mechanical, electrical and software engineers working in mobility from around the world to share new knowledge and advancements.
“The automotive and transportation sectors are going through tremendous change and challenges as they navigate ...
From a cryptic genetic element in the human gut to a sensitive biomarker
2024-04-16
A component of the human intestinal flora that has been little studied to date is the focus of a new study. Plasmids are small extrachromosomal genetic elements that frequently occur in bacterial cells and can influence microbial lifestyles – yet their diversity in natural habitats is poorly understood. An international team led by Prof. Dr. A. Murat Eren from the Helmholtz Institute for Functional Marine Biodiversity at the University of Oldenburg (HIFMB) reports in the science journal Cell, a mysterious plasmid, is one of the most numerous genetic elements in the human gut that could potentially serve as a powerful biomarker for identifying ...
Researchers can help shipowners achieve ambitious climate targets
2024-04-16
Shipowners around the world are in a very difficult position, because they are having to order new ships now that will run on fuel and technologies that are not yet fully developed.
A new study suggests that ammonia could be a smart and energy-efficient fuel in the race to achieve net zero in shipping. Researchers at the Department of Industrial Economics and Technology Management (IØT) and the Department of Marine Technology (IMT) at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) ...
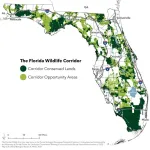
Florida Wildlife Corridor eases worst impacts of climate change
2024-04-16
From rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns to intense weather events such as hurricanes, Florida is experiencing significant climate-related challenges in tandem with skyrocketing insurance rates. As the state’s population continues to surge by 1,000 new residents a day, it is projected to lose 3.5 million acres of land to development by 2070, threatening Florida’s future ability to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem services.
A first-of-its-kind study highlights how Florida can buffer itself against both climate change ...