(Press-News.org)
Living beings can evolve to lose biological structures due to potential survival benefits from such losses. For example, certain groups of ray-finned fishes show such regressive evolution—medakas, minnows, puffera, and wrasses do not have a stomach in the gastrointestinal tract, making them agastric or stomachless fishes. However, the specific evolutionary mechanisms underlying the evolution of agastric fishes remains unclear.
Studies about Slc26a9—a molecular transporter highly expressed in the stomach of many species—in fishes provided the initial clue. Researchers in Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, and Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, The University of Tokyo found that the slc26a9 gene was absent in many agastric ray-finned fishes but present in many gastric ray-finned fishes. These findings led them to ponder if more genes required for gastric function were absent in agastric fishes. Could such convergent gene losses account for stomach loss in agastric fishes?
A team of scientists from Japan and the USA, led by Associate Professor Akira Kato from Tokyo Tech, sought to answer this question. Kato explains, "We compared gene losses between agastric and gastric ray-finned fishes and identified additional genes co-deleted in agastric fishes." Accordingly, the researchers identified several genes required for gastric functions that are co-deleted or pseudogenized (gene inactivation through mutations resulting in pseudogenes) in agastric fishes compared to gastric fishes, namely slc26a9, kcne2, cldn18a, and vsig1. Their findings are published in Communications Biology.
Specifically, they identified four gene deletions—slc26a9, kcne2, cldn18a, and vsig1—resulting in a reduction or loss of stomach structure in ray-finned fishes through comparative genomic analyses (a set of experiments for comparing similarities and differences among different genomes). Not surprisingly, each of these four genes codes for essential gastric functions. slc26a9 codes for the chlorine ion channel transporter. kcne2 codes for a regulatory subunit of the potassium ion channel. slc26a9 and kcne2 functions are, thus, essential for secretions of gastric acids, such as hydrochloric acid. cldn18a similarly codes for a barrier protecting the gastric cells from acid-induced damage from hydrogen ions, while vsig1 codes for controlling stomach development.
In addition, the researchers found that agastric egg-laying mammals, such as echidna and platypus, also have kcne2 and vsig1 either deleted or pseudogenized. Moreover, the researchers discovered that cldn18, if present in agastric bony fishes, is mutated compared to gastric fishes. All these findings indicate that the gene losses correlated with stomach loss represent a genotypic convergence.
Furthermore, they observed that the gastric fish, stickleback, expressed kcne2, pga, pgc, vsig1, and cldn18a in organs other than the stomach, indicating gene functions other than gastric functions. They deduced that agastric fishes could possess other genes to compensate for such gene functions, facilitating the observed gene losses.
Kato concludes, "We identified novel genes absent in agastric fishes among four major bony fish lineages, which suggests a convergent evolution scenario in the context of stomach loss. Our findings, thus, imply that a similar cassette of gene losses occurred independently during or after stomach loss in the several agastric fish groups." Indeed, this study is a milestone in understanding the novel genotypic convergence that fine-tuned the agastric fish body to suit its specific ecological niche.
END
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Even subtle differences in the wording of social media messages may be enough to sway young people’s beliefs about depression and anxiety and their treatment.
In a new study, researchers found that college students were more optimistic about the possibility of successfully treating mental health problems after they read social media messages conveying what is called a “growth mindset.”
But social media posts written with a “fixed mindset” led young people to feel that depression and anxiety were more stable and innate, and not so easy to treat.
Growth mindset is the belief that a feature, such ...
Electronic devices are getting more and more complex as they are built to carry out an ever-increasing number of functions. This can be seen in the increased functionality in our personal devices such as our phones, tablets and watches, let alone in industrial devices. However, their growing complexity can lead to performance and safety issues. These issues include device overheating or emitting microwaves that can result in health issues and that can reduce a device’s performance and interfere with other devices.
Chinese scientists from Beijing Normal University have been ...
(Boston)—Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB), is distinct from most germs in its capacity to silently infect individuals for months and even years before waking up and causing active disease that can lead to severe illness and death. The immune system plays an important role in controlling the germ and keeping it dormant.
Decades of epidemiological data have linked undernutrition to TB. While undernourished individuals have blunted immune systems, a phenomenon which has been dubbed nutritionally acquired ...
In the field of aerospace, a high-temperature piezoelectric vibration sensor is one of the few key devices that can be monitored in a high-temperature and harsh environment, so it is particularly urgent to develop high performance high-temperature piezoelectric ceramics as the core component of this kind of sensor. Bi4Ti3O12 (BIT), as one vital type of bismuth layered structure ferroelectrics (BLSFs), has great application prospects in high-temperature environments due to its excellent TC of 675 ℃. However, the volatilization of Bi during the sintering process in BIT-based ceramics leads to the generation of oxygen vacancy ...
Background and Aims
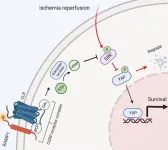
Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI) is a prevalent complication of liver transplantation, partial hepatectomy, and severe infection, necessitating the development of more effective clinical strategies. Receptor activity–modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), a member of the G protein–coupled receptor adapter family, has been implicated in numerous physiological and pathological processes. The study aimed to investigate the pathogenesis of RAMP1 in HIRI.
Methods
We established a 70% liver ischemia-reperfusion model in RAMP1 knockout (KO) and wild-type mice. Liver and ...
Thermophilic fungi are chief components of mycoflora in a variety of natural and manmade composting systems, including rotting hay, stored grains, wood mulch, nesting material of birds and animals, municipal refuse, and self-heating accumulated organic matter. Thermophilic fungi are also a potential source of natural products, which complement the metabolite libraries of mesophilic fungi and bacteria.
The research team led by Prof. Dr. Xuemei Niu (State Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Bio-Resources in Yunnan, Yunnan University) has been working on the discovery of secondary metabolites in thermophilic fungi and their biological ...
DALLAS, April 23, 2024 — Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, estimated to affect about 12.1 million U.S. adults by 2030.[1] The abnormal firing of electrical impulses causes part of the heart to quiver, or fibrillate, often leading to complications and up to a fivefold increased risk of stroke. To help ensure all patients with AFib receive the most appropriate care, the American Heart Association is launching a new effort to educate and engage pharmacists, an important but underrepresented voice in AFib care.
This ...
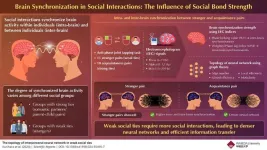
We experience the world and connect with others through social interactions. Engaging in activities, such as conversations, cooperative tasks, and intimate relationships, deeply affect brain activity leading to coordinated neural activity within an individual's brain (intra-brain synchronization) and between the brains of multiple individuals (inter-brain synchronization).
Researchers study brain synchronizations to understand the neural processes behind social behaviors. This knowledge can help diagnose and treat conditions like social anxiety and communication-related disorders. However, investigations on brain synchronization ...
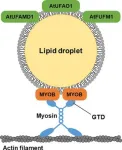
Lipids are biomolecules essential for the proper functioning of the living cell, ranging from comprising cell membranes to forming integral components of cell signaling pathways. Plant cells possess cell subcellular structures or organelles called lipid droplets (LDs) in the leaves and seeds, which store excess lipids (fats).
Recent studies have shown that LDs also localize unique plant proteins that perform essential molecular functions. For example, seed LDs localize plant proteins called oleosins, which help seeds weather freezing temperatures and germinate properly. With an expanding body of proof ...
NEW YORK, April 23, 2024 — Single-photon emitters (SPEs) are akin to microscopic lightbulbs that emit only one photon (a quantum of light) at a time. These tiny structures hold immense importance for the development of quantum technology, particularly in applications such as secure communications and high-resolution imaging. However, many materials that contain SPEs are impractical for use in mass manufacturing due to their high cost and the difficulty of integrating them into complex devices.
In 2015, scientists discovered SPEs within a material called hexagonal boron nitride (hBN). Since then, hBN has gained widespread attention and ...