(Press-News.org) New study infers our wellbeing by analyzing the language we use around ageing, using language markers to enable "a different type of access to individuals’ inner worlds"
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302103
Article Title: When I am sixty-four… evaluating language markers of well-being in healthy aging narratives
Author Countries: Switzerland, USA, Australia
Funding: Funding by the Jacobs Foundation (https://jacobsfoundation.org/en/; awarded to TM) and the Swiss National Science Foundation SNF ((https://www.snf.ch/en/; fellowship P2ZHP1_199409 awarded to TM), as well as by the “Gerontopsychology and Gerontology” unit, Department of Psychology, University of Zurich, Switzerland (https://www.psychology.uzh.ch/en/areas/dev/geronto.html) helped to conduct this research. The preparation of this manuscript was further supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (https://www.nih.gov; U19AG065169 awarded to MRM). The views, opinions, and findings contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be construed as position, policy, or decision of the aforementioned agencies, unless so designated by other documents. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
New study infers our wellbeing by analyzing the language we use around ageing, using language markers to enable "a different type of access to individuals’ inner worlds"
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research confirms plastic production is directly linked to plastic pollution
2024-04-24
APRIL 24, 2024 – A research paper published today in Science Advances reveals a direct correlation between plastic production and plastic pollution, such that every 1% increase in plastic production is associated with a 1% increase in plastic pollution in the environment. The study finds that fast-moving consumer goods companies disproportionately contribute to the problem more than household and retail companies. The study marks the first robust quantification of the global relationship between plastic production and pollution.
The research, led by scientists ...
MSU researchers uncover 'parallel universe' in tomato genetics
2024-04-24
In a new paper appearing in Science Advances, Michigan State University researchers have unraveled a surprising genetic mystery centered on sugars found in what gardeners know as “tomato tar.”
Anyone who has pruned tomato plants barehanded has likely found their fingers darkened with a sticky, gold-black substance that won’t quite wash off.
This tomato tar is sticky for good reason. It’s made of sugars — acylsugars, to be precise — and acts as a sort of natural flypaper for ...
Grey cuckoo, red cuckoo: unveiling the genomic secrets of color polymorphism in female cuckoo birds
2024-04-24
NEW YORK, April 24, 2024 — Sexual dimorphism—the visible difference between females and males—can be seen in diverse animals, including humans. One intriguing aspect of this phenomenon is sex-limited polymorphism, where one sex displays greater variations in a particular trait than the other. In a recent study published in Science Advances, a team of researchers delve into the genetic underpinnings behind the color polymorphism observed in adult females of the brood parasitic Cuculus, more widely known as cuckoo birds, shedding light on the evolution and functional significance of this phenomenon.
Several species of cuckoos, a genus of birds ...
CHOP researchers discover underlying biology behind Fontan-associated liver disease
2024-04-24
Philadelphia, April 24, 2024 – As patients with congenital heart diseases live longer, researchers are attempting to understand some of the other complications they may face as they age. In a new study, a team from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) used state-of-the-art technologies to understand the underlying biology of Fontan-associated liver disease (FALD).
The findings, published today in Science Translational Medicine, reveal unprecedented insights into how the disease develops and potential therapeutic targets for future treatment options.
The Fontan operation is ...
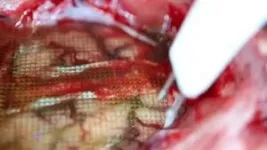
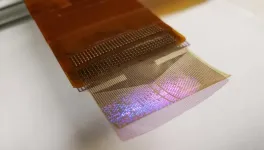
A flexible microdisplay can monitor brain activity in real-time during brain surgery
2024-04-24
A thin film that combines an electrode grid and LEDs can both track and produce a visual representation of the brain’s activity in real-time during surgery–a huge improvement over the current state of the art. The device is designed to provide neurosurgeons visual information about a patient’s brain to monitor brain states during surgical interventions to remove brain lesions including tumors and epileptic tissue.
Each LED in the device mirrors the activity of a few thousand neurons. In a series of proof-of-concept experiments in rodents and large non-primate mammals, researchers showed that ...
Diversity and productivity go branch-in-branch
2024-04-24
Kyoto, Japan -- Climate change can be characterized as the Grim Reaper or some other harbinger of dire times for humanity and natural environment, including forests. Previous studies reporting a decline in forest productivity due to climate warming and long-term drought may suggest that trees' survival hangs in the balance.
Now, a study by an international group, including Kyoto University, found that forests with higher trait diversity not only adapt better to climate change but may also thrive.
The study, conducted by researchers from Lakehead ...
Color variants in cuckoos: the advantages of rareness
2024-04-24
Every cuckoo is an adopted child – raised by foster parents, into whose nest the cuckoo mother smuggled her egg. The cuckoo mother is aided in this subterfuge by her resemblance to a bird of prey. There are two variants of female cuckoos: a gray morph that looks like a sparrowhawk, and a rufous morph. Male cuckoos are always gray.
“With this mimicry, the bird imitates dangerous predators of the host birds, so that they keep their distance instead of attacking,” says Professor Jochen Wolf from LMU Munich. Together with researchers at CIBIO (Centro de Investigação ...
Laser technology offers breakthrough in detecting illegal ivory
2024-04-24
A new way of quickly distinguishing between illegal elephant ivory and legal mammoth tusk ivory could prove critical to fighting the illegal ivory trade. A laser-based approach developed by scientists at the Universities of Bristol and Lancaster, could be used by customs worldwide to aid in the enforcement of illegal ivory from being traded under the guise of legal ivory. Results from the study are published in PLOS ONE today [24 April].
Despite the Convention on the International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) ban on ivory, poaching associated with its illegal trade has ...
Why can’t robots outrun animals?
2024-04-24
Robotics engineers have worked for decades and invested many millions of research dollars in attempts to create a robot that can walk or run as well as an animal. And yet, it remains the case that many animals are capable of feats that would be impossible for robots that exist today.
“A wildebeest can migrate for thousands of kilometres over rough terrain, a mountain goat can climb up a literal cliff, finding footholds that don't even seem to be there, and cockroaches can lose a leg and not slow down,” ...
After spinal cord injury, neurons wreak havoc on metabolism
2024-04-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Conditions such as diabetes, heart attack and vascular diseases commonly diagnosed in people with spinal cord injuries can be traced to abnormal post-injury neuronal activity that causes abdominal fat tissue compounds to leak and pool in the liver and other organs, a new animal study has found.
After discovering the connection between dysregulated neuron function and the breakdown of triglycerides in fat tissue in mice, researchers found that a short course of the drug gabapentin, commonly prescribed for nerve pain, prevented ...